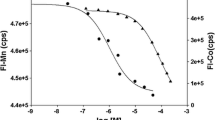
Abstract
The three dimensional structure of Ferric uptake regulation protein dimer from E. coli, determined by molecular modeling, was docked on a DNA fragment (iron box) and Zn2+ ions were added in two steps. The first step involved the binding of one Zn2+ ion to what is known as the zinc site which consists of the residues Cys 92, Cys 95, Asp 137, Asp141, Arg139, Glu 140, His 145 and His 143 with an average metal-Nitrogen distance of 2.5 Å and metal-oxygen distance of 3.1–3.2 Å. The second Zn2+ ion is bound to the iron activating site formed from the residues Ile 50, His 71, Asn 72, Gly 97, Asp 105 and Ala 109. The binding of the second Zn2+ ion strengthened the binding of the first ion as indicated by the shortening of the zinc-residue distances. Fe2+, when added to the complex consisting of 2Zn2+/Fur dimer/DNA, replaced the Zn2+ ion in the zinc site and when a second Fe2+ was added, it replaced the second zinc ion in the iron activating site. The binding of both zinc and iron ions induced a similar change in Fur conformations, but shifted residues closer to DNA in a different manner. This is discussed along with a possible role for the Zn2+ ion in the Fur dimer binding of DNA in its repressor activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Escolar L, Perez-Martin J, de Lorenzo V (1999) Opening the iron box: transcriptional metalloregulation by Fur protein. J Bacteriol 181:6223–6229
Bagg A, Neilands JB (1987) Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing Iron(II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an Iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 26:5471–5477. doi:10.1021/bi00391a039
Escolar L, Perez-Martin J, de Lorenzo V (1997) Metalloregulation in vitro of the aerobactin promoter of Escherichia coli by the fur (ferric uptake regulation) protein. J Mol Microbiol 26:799–808. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.6211987.x
Bsat N, Helmann JD (1999) Interaction of Bacillus subtilis Fur (Ferric Uptake Repressor) with the dhb operator in vitro and in vivo. J Bacteriol 181:4299–4307
Lee JW, Helmann JD (2007) Functional specialization within the fur family of metalloregulators. Biometals 20:485–499. doi:10.1007/s10534-006-9070-7
Baichoo N, Helmann JD (2002) Recognition of DNA by Fur: a rainterpretation of the Fur box consensus sequence. J Bacteriol 184:5826–5832. doi:10.1128/JB.184.21.5826-5832.2002
Lavrrar JL, McInosh MA (2003) Architecture of a Fur binding site: a comparative analysis. J Bacteriol 185:2194–2202. doi:10.1128/JB.185.7.2194-2202.2003
Lavrrar JL, Christoffersen CA, McIontosh MA (2002) Fur–DNA interactions at bidirectional fep DGC-entS promoter region in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 322:983–995. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00849-5
Frechon D, Le Cam E (1994) Fur (Ferric uptake Regulation) protein interaction with target DNA: comparison of gel retardation, footprinting and electron microscopy analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 201:346–355
Jacquamet L, Aberdam D, Adrait A, Hazemann JL, Latour JM, Michaud-Soret I (1998) X-ray absorption spectroscopy of a new zinc site in the fur protein from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 37:2564–2571. doi:10.1021/bi9721344
D’Autreaux B, Pecqueur L, de Peredo AG, Diederix REM, Caux-Thang C, Tabet L, Bersch B, Forest E, Michaud-Soret I (2007) Reversible redox- and Zinc-dependant dimerization of the Escherichia coli Fur protein. Biochemistry 46:1329–1342. doi:10.1021/bi061636r
Barondeau DP, Getzoff ED (2007) Structural insights into protein-metal ion partnerships. Curr Opin Struct Biol 14:765–774
Gabella A, Helmann JD (1998) Identification of a Zinc-specific metalloregulatory protein, Zur, controlling Zinc transport operons in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 180:5815–5821
Lewin AC, Doughty PA, Flegg L, Moore GR, Spiro S (2002) The ferric uptake regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa has no essential cystine residues and does not contain a structural zinc ion. J Microbiol 148:2449–2456
Althaus EW, Outten CE, Olson KE, Cao H, O’Halloran TV (1999) The ferric uptake regulation is a zinc metalloprotein. Biochemistry 38:6559–6569. doi:10.1021/bi982788s
Lucarelli D, Russo S, German E, Milano A, Meyer-Klaucke W, Pohl E (2007) Crystal structure and function of the zinc uptake regulator FurB from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem 282:9914–9922. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609974200
Pecqueur L, D’Autreaux B, Dupuy J, Nicolet Y, Jacquamet L, Brutcher B, Michaud-Soret I, Bersch B (2007) Structural changes of Escherichia coli ferric uptake regulator during metal-dependant dimerization and activation explored by NMR and X-ray crystallography. J Biol Chem 281:21286–21295. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601278200
Zheleznova EE, Crosa JH, Brennan RG (2000) Characterization of the DNA- and metal-binding properties of Vibro anguillarum Fur reveals conservation of a structural Zn2+ ion. J Bacteriol 182:6264–6267. doi:10.1128/JB.182.21.6264-6267.2000
De Peredo AG, Saint-Pierre C, Adrait A, Jacquamet L, Latour JM, Michaud-Soret I, Forest E (1999) Identification of the two zinc-bound cysteine in the ferric uptake regulation protein from Esherichia coli: chemical modification and mass spectroscopy analysis. Biochemistry 38:8582–8589. doi:10.1021/bi9902283
Pohl E, Haller JC, Mijovilovich A, Meyer-Klancke W, German E, Vasil ML (2003) Architecture of a protein central to iron homeostasis: crystal structure and spectroscopic analysis of the ferric uptake regulator. Mol Microbiol 47:903–915. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03337.x
Freidman YE, O’Brian MR (2004) The ferric uptake regulator (Fur) protein from Bradyrhizobium japonicun is an iron-responsive transcriptional repressor in vitro. J Biol Chem 279:32100–32105. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404924200
Bai E, Rossel FI, Lige B, Mauk MR, LelJ-Garolla B, Moore MR, Mauk AG (2006) Functional characterization of dimerization domain of the ferric uptake regulator (Fur) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J 400:385–392. doi:10.1042/BJ20061168
Adrait A, Jacquamet L, Le Pape L, de Peredo AG, Aberdam D, Hazeman J, Matour J, Michaud-Soret I (1999) Spectroscopic and saturation magnetization of the manganese and cobalt-substituted Fur protein from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 38:6248–6260. doi:10.1021/bi9823232
Hamed M, Al-Jabour S (2006) Iron triggered conformational changes in Escherichia coli fur upon DNA binding: a study using molecular modeling. J Mol Graph Model 25:234–246. doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2005.12.010
Case DA, Pearlman DA, Caldwell JW, Cheatham TEIII, Wang J, Ross WS, Simmerling CL, Darden TA, Merz KM, Stanton RV, Cheng AL, Vencent JJ, Crawley M, Tsui V, Gohlke H, Radmer RJ, Duan Y, Pietera J, Massova I, Seibel GL, Singh UC, Weiner PK, Kollman PA (2006) Amber9. University of California, San Francisco
Pearlman DA, Case DA, Caldwell JW, Ross WR, Chealtham TE, DeBolt S, Ferguson IIID, Seibel G, Kollman P (1995) AMBER, a package of computer programs for applying molecular mechanics, normal mode analysis, molecular dynamics and free energy calculation to simulate the structural and energetic properties of molecules. Comput Phys Commun 91:1–41. doi:10.1016/0010-4655(95)00041-D
Coy M, Neilands JB (1991) Structural dynamics and functional domains of the fur protein. Biochemistry 30:8201–8210. doi:10.1021/bi00247a016
Coy M (1995) The interaction of the ferric uptake regulation protein with DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 212:784–792. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.2037
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 62 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOC 55 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOC 47 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
(DOC 42 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabour, S., Hamed, M.Y. Binding of the Zn2+ ion to ferric uptake regulation protein from E. coli and the competition with Fe2+ binding: a molecular modeling study of the effect on DNA binding and conformational changes of Fur. J Comput Aided Mol Des 23, 199–208 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-008-9251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-008-9251-2