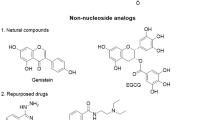
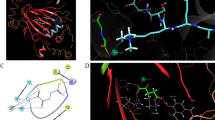
Abstract
DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) is an emerging epigenetic target for the treatment of cancer and other diseases. To date, several inhibitors from different structural classes have been published. In this work, we report a comprehensive molecular modeling study of 14 established DNTM1 inhibitors with a herein developed homology model of the catalytic domain of human DNTM1. The geometry of the homology model was in agreement with the proposed mechanism of DNA methylation. Docking results revealed that all inhibitors studied in this work have hydrogen bond interactions with a glutamic acid and arginine residues that play a central role in the mechanism of cytosine DNA methylation. The binding models of compounds such as curcumin and parthenolide suggest that these natural products are covalent blockers of the catalytic site. A pharmacophore model was also developed for all DNMT1 inhibitors considered in this work using the most favorable binding conformations and energetic terms of the docked poses. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first pharmacophore model proposed for compounds with inhibitory activity of DNMT1. The results presented in this work represent a conceptual advance for understanding the protein–ligand interactions and mechanism of action of DNMT1 inhibitors. The insights obtained in this work can be used for the structure-based design and virtual screening for novel inhibitors targeting DNMT1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones PA, Baylin SB (2002) The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 3:415–428
Robertson KD (2005) DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 6:597–610
Miller CA, Gavin CF, White JA, Parrish RR, Honasoge A, Yancey CR, Rivera IM, Rubio MD, Rumbaugh G, Sweatt JD (2010) Cortical DNA methylation maintains remote memory. Nat Neurosci 13:664–666
Zawia NH, Lahiri DK, Cardozo-Pelaez F (2009) Epigenetics, oxidative stress, and Alzheimer disease. Free Radical Biol Med 46:1241–1249
Bestor T, Laudano A, Mattaliano R, Ingram V (1988) Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding DNA methyltransferase of mouse cells: the carboxyl-terminal domain of the mammalian enzymes is related to bacterial restriction methyltransferases. J Mol Biol 203:971–983
Okano M, Xie S, Li E (1998) Cloning and characterization of a family of novel mammalian DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nat Genet 19:219–220
Bacolla A, Pradhan S, Roberts RJ, Wells RD (1999) Recombinant human DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferase. II. Steady-state kinetics reveal allosteric activation by methylated DNA. J Biol Chem 274:33011–33019
Cheng X, Blumenthal RM (2008) Mammalian DNA methyltransferases: a structural perspective. Structure 16:341–350
Schaefer M, Lyko F (2009) Solving the Dnmt2 enigma. Chromosoma 119:35–40
Goll MG, Kirpekar F, Maggert KA, Yoder JA, Hsieh CL, Zhang X, Golic KG, Jacobsen SE, Bestor TH (2006) Methylation of tRNAAsp by the DNA methyltransferase homolog Dnmt2. Science 311:395–398
Kumar S, Horton JR, Jones GD, Walker RT, Roberts RJ, Cheng X (1997) DNA containing 4′-thio-2′-deoxycytidine inhibits methylation by HhaI methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res 25:2773–2783
Jurkowski TP, Meusburger M, Phalke S, Helm M, Nellen W, Reuter G, Jeltsch A (2008) Human DNMT2 methylates tRNAAsp molecules using a DNA methyltransferase-like catalytic mechanism. RNA 14:1663–1670
Hermann A, Gowher H, Jeltsch A (2004) Biochemistry and biology of mammalian DNA methyltransferases. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2571–2587
Sorm F, Pískala A, Cihák A, Veselý J (1964) 5-Azacytidine, a new, highly effective cancerostatic. Experientia 20:202–203
Jones PA, Taylor SM (1980) Cellular differentiation, cytidine analogs and DNA methylation. Cell 20:85–93
Kaminskas E, Farrell AT, Wang YC, Sridhara R, Pazdur R (2005) FDA drug approval summary: azacitidine (5-azacytidine, vidaza™) for injectable suspension. Oncologist 10:176–182
Yu N, Wang M (2008) Anticancer drug discovery targeting DNA hypermethylation. Curr Med Chem 15:1350–1375
Amatori S, Bagaloni I, Donati B, Fanelli M (2010) DNA demethylating antineoplastic strategies: a comparative point of view. Genes Cancer 1:197–209
Dacogen (2006) Decitabine: FDA approves new treatment for myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/NEWS/2006/NEW01366.html. Accessed 10 May 2011
Kantarjian H, Issa JP, Rosenfeld CS, Bennett JM, Albitar M, DiPersio J, Klimek V, Slack J, de Castro C, Ravandi F, Helmer R III, Shen L, Nimer SD, Leavitt R, Raza A, Saba H (2006) Decitabine improves patient outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 106:1794–1803
Palii SS, Van Emburgh BO, Sankpal UT, Brown KD, Robertson KD (2007) DNA methylation inhibitor 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine induces reversible genome-wide DNA damage that is distinctly influenced by DNA Methyltransferases 1 and 3B. Mol Cell Biol 28:752–771
Ferguson AT, Vertino PM, Spitzner JR, Baylin SB, Muller MT, Davidson NE (1997) Role of estrogen receptor gene demethylation and DNA methyltransferase DNA adduct formation in 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine-induce cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 272:32260–32266
Appleton K, Mackay HJ, Judson I, Plumb JA, McCormick C, Strathdee G, Lee C, Barrett S, Reade S, Jadayel D, Tang A, Bellenger K, Mackay L, Setanoians A, Schätzlein A, Twelves C, Kaye SB, Brown R (2007) Phase I and pharmacodynamic trial of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor decitabine and carboplatin in solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:4603–4609
Beumer JH, Parise RA, Newman EM, Doroshow JH, Synold TW, Lenz HJ, Egorin MJ (2008) Concentrations of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine (FdCyd) and its cytotoxic metabolites in plasma of patients treated with FdCyd and tetrahydrouridine (THU). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:363–368
Beumer JH, Eiseman JL, Parise RA, Joseph E, Holleran JL, Covey JM, Egorin MJ (2006) Pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and oral bioavailability of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-fluoro-2′-deoxycytidine in mice. Clin Cancer Res 12:7483–7491
Ben-Kasus T, Ben-Zvi Z, Marquez V, Kelley J, Agbaria R (2005) Metabolic activation of zebularine, a novel DNA methylation inhibitor, in human bladder carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 70:121–133
Bradbury J (2004) Zebularine: a candidate for epigenetic cancer therapy. Drug Discovery Today 9:906–907
Cheng JC, Yoo CB, Weisenberger DJ, Chuang J, Wozniak C, Liang G, Marquez VE, Greer S, Orntoft TF, Thykjaer T, Jones PA (2004) Preferential response of cancer cells to zebularine. Cancer Cell 6:151–158
Holleran JL, Parise RA, Joseph E, Eiseman JL, Covey JM, Glaze ER, Lyubimov AV, Chen YF, D’Argenio DZ, Egorin MJ (2005) Plasma pharmacokinetics, oral bioavailability, and interspecies scaling of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, zebularine. Clin Cancer Res 11:3862–3868
Scott SA, Lakshimikuttysamma A, Sheridan DP, Sanche SE, Geyer CR, DeCoteau JF (2007) Zebularine inhibits human acute myeloid leukemia cell growth in vitro in association with p15INK4B demethylation and reexpression. Exp Hematol 35:263–273
Bayet-Robert M, Kwiatkowski F, Leheurteur M, Gachon F, Planchat E, Abrial C, Mouret-Reynier MA, Durando X, Barthomeuf C, Chollet P (2010) Phase I dose escalation trial of docetaxel plus curcumin in patients with advanced and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 9:8–14
Dhillon N, Aggarwal BB, Newman RA, Wolff RA, Kunnumakkara AB, Abbruzzese JL, Ng CS, Badmaev V, Kurzrock R (2008) Phase II trial of curcumin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:4491–4499
Liu Z, Xie Z, Jones W, Pavlovicz R, Liu S, Yu J, Li P, Lin J, Fuchs J, Marcucci G (2009) Curcumin is a potent DNA hypomethylation agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:706–709
Garciapineres A, Lindenmeyer M, Merfort I (2004) Role of cysteine residues of p65/NF-κB on the inhibition by the sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide and N-ethyl maleimide, and on its transactivating potential. Life Sci 75:841–856
Kwok B, Koh B, Ndubuisi M, Elofsson M, Crews C (2001) The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits IκB kinase. Chem Biol 8:759–766
Steele AJ, Jones DT, Ganeshaguru K, Duke VM, Yogashangary BC, North JM, Lowdell MW, Kottaridis PD, Mehta AB, Prentice AG, Hoffbrand AV, Wickremasinghe RG (2006) The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide induces selective apoptosis of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro. Leukemia 20:1073–1079
Curry EA III, Murry DJ, Yoder C, Fife K, Armstrong V, Nakshatri H, O’Connell M, Sweeney CJ (2004) Phase I dose escalation trial of feverfew with standardized doses of parthenolide in patients with cancer. Invest New Drugs 22:299–305
Liu Z, Liu S, Xie Z, Pavlovicz RE, Wu J, Chen P, Aimiuwu J, Pang J, Bhasin D, Neviani P, Fuchs JR, Plass C, Li PK, Li C, Huang TH, Wu LC, Rush L, Wang H, Perrotti D, Marcucci G, Chan KK (2009) Modulation of DNA methylation by a sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:505–514
Suzuki T, Tanaka R, Hamada S, Nakagawa H, Miyata N (2010) Design, synthesis, inhibitory activity, and binding mode study of novel DNA methyltransferase 1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:1124–1127
Daiber A, Oelze M, Coldewey M, Kaiser K, Huth C, Schildknecht S, Bachschmid M, Nazirisadeh Y, Ullrich V, Mülsch A, Münzel T, Tsilimingas N (2005) Hydralazine is a powerful inhibitor of peroxynitrite formation as a possible explanation for its beneficial effects on prognosis in patients with congestive heart failure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1865–1874
Segura-Pacheco B, Trejo-Becerril C, Perez-Cardenas E, Taja-Chayeb L, Mariscal I, Chavez A, Acuña C, Salazar AM, Lizano M, Dueñas-Gonzalez A (2003) Reactivation of tumor suppressor genes by the cardiovascular drugs hydralazine and procainamide and their potential use in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 9:1596–1603
Zambrano P, Segura-Pacheco B, Perez-Cardenas E, Cetina L, Revilla-Vazquez A, Taja-Chayeb L, Chavez-Blanco A, Angeles E, Cabrera G, Sandoval K, Trejo-Becerril C, Chanona-Vilchis J, Duenas-González A (2005) A phase I study of hydralazine to demethylate and reactivate the expression of tumor suppressor genes. BMC Cancer 5:44
Candelaria M, Gallardo-Rincón D, Arce C, Cetina L, Aguilar-Ponce JL, Arrieta O, González-Fierro A, Chávez-Blanco A, de la Cruz-Hernández E, Camargo MF, Trejo-Becerril C, Pérez-Cárdenas E, Pérez-Plasencia C, Taja-Chayeb L, Wegman-Ostrosky T, Revilla-Vazquez A, Dueñas-González A (2007) A phase II study of epigenetic therapy with hydralazine and magnesium valproate to overcome chemotherapy resistance in refractory solid tumors. Ann Oncol 18:1529–1538
Singh N, Dueñas-González A, Lyko F, Medina-Franco JL (2009) Molecular modeling and molecular dynamics studies of hydralazine with human DNA methyltransferase 1. ChemMedChem 4:792–799
Villar-Garea A, Fraga MF, Espada J, Esteller M (2003) Procaine is a DNA-demethylating agent with growth-inhibitory effects in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 63:4984–4989
Zhang J, Dong B, Zheng L, Li G (2006) Effect of procaine hydrochloride on the micellization of double tailed surfactants in the aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A 290:157–163
Brueckner B, Lyko F (2004) DNA methyltransferase inhibitors: old and new drugs for an epigenetic cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:551–554
Lee BH, Yegnasubramanian S, Lin X, Nelson WG (2005) Procainamide Is a specific inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase 1. J Biol Chem 280:40749–40756
Fang MZ, Wang Y, Ai N, Hou Z, Sun Y, Lu H, Welsh W, Yang CS (2003) Tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 63:7563–7570
Gao Z, Xu Z, Hung MS, Lin YC, Wang T, Gong M, Zhi X, Jablon DM, You L (2009) Promoter demethylation of WIF-1 by epigallocatechin-3-gallate in lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res 29:2025–2030
Gu B, Ding Q, Xia G, Fang Z (2009) EGCG inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma through TFPI-2 overexpression. Oncol Rep 21:635–640
Zaveri NT (2006) Green tea and its polyphenolic catechins: medicinal uses in cancer and noncancer applications. Life Sci 78:2073–2080
Medina-Franco JL, López-Vallejo F, Kuck D, Lyko F (2011) Natural products as DNA methyltransferase inhibitors: a computer-aided discovery approach. Mol Diversity 15:293–304
Jagadeesh S, Sinha S, Pal BC, Bhattacharya S, Banerjee PP (2007) Mahanine reverses an epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor gene RASSF1A in human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:212–217
Sinha S, Pal BC, Jagadeesh S, Banerjee PP, Bandyopadhaya A, Bhattacharya S (2006) Mahanine inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through the deactivation of Akt and activation of caspases. Prostate 66:1257–1265
Brueckner B, Garcia Boy R, Siedlecki P, Musch T, Kliem HC, Zielenkiewicz P, Suhai S, Wiessler M, Lyko F (2005) Epigenetic reactivation of tumor suppressor genes by a novel small-molecule inhibitor of human DNA methyltransferases. Cancer Res 65:6305–6311
Schirrmacher E, Beck C, Brueckner B, Schmitges F, Siedlecki P, Bartenstein P, Lyko F, Schirrmacher R (2006) Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of biotinylated RG108: a high affinity compound for studying binding interactions with human DNA methyltransferases. Bioconjugate Chem 17:261–266
Siedlecki P, Garcia Boy R, Musch T, Brueckner B, Suhai S, Lyko F, Zielenkiewicz P (2006) Discovery of two novel, small-molecule inhibitors of DNA methylation. J Med Chem 49:678–683
Kuck D, Singh N, Lyko F, Medina-Franco JL (2010) Novel and selective DNA methyltransferase inhibitors: docking-based virtual screening and experimental evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem 18:822–829
Podvinec M, Lim SP, Schmidt T, Scarsi M, Wen D, Sonntag LS, Sanschagrin P, Shenkin PS, Schwede T (2010) Novel inhibitors of dengue virus methyltransferase: discovery by in vitro-driven virtual screening on a desktop computer grid. J Med Chem 53:1483–1495
Schrump DS, Fischette MR, Nguyen DM, Zhao M, Li X, Kunst TF, Hancox A, Hong JA, Chen GA, Pishchik V, Figg WD, Murgo AJ, Steinberg SM (2006) Phase I study of decitabine-mediated gene expression in patients with cancers involving the lungs, esophagus, or pleura. Clin Cancer Res 12:5777–5785
Issa JP, Kantarjian HM, Kirkpatrick P (2005) Azacitidine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:275–276
Medina-Franco JL, Caulfield T (2011) Advances in the computational development of DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 16:418–425
Consortium UniProt (2010) The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) in 2010. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D142–D148
Siedlecki P, Garcia Boy R, Comagic S, Schirrmacher R, Wiessler M, Zielenkiewicz P, Suhai S, Lyko F (2003) Establishment and functional validation of a structural homology model for human DNA methyltransferase 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306:558–563
Dolan MA, Keil M, Baker DS (2008) Comparison of composer and ORCHESTRAR. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 72:1243–1258
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26:283–291
Macromodel, version 9.8, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2010
Loving K, Salam NK, Sherman W (2009) Energetic analysis of fragment docking and application to structure-based pharmacophore hypothesis generation. J Comput-Aided Mol Des 23:541–554
Salam NK, Nuti R, Sherman W (2009) Novel method for generating structure-based pharmacophores using energetic analysis. J Chem Inf Model 49:2356–2368
Zhou L, Cheng X, Connolly BA, Dickman MJ, Hurd PJ, Hornby DP (2002) Zebularine: a novel DNA methylation inhibitor that forms a covalent complex with DNA methyltransferases. J Mol Biol 321:591–599
Kuttan G, Kumar KB, Guruvayoorappan C, Kuttan R (2007) Antitumor, anti-invasion, and antimetastatic effects of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:173–184
Dueñas-González A, García-López P, Herrera LA, Medina-Franco JL, González-Fierro A, Candelaria M (2008) The prince and the pauper. A tale of anticancer targeted agents. Mol Cancer 7:82
Arce C, Segura-Pacheco B, Perez-Cardenas E, Taja-Chayeb L, Candelaria M, Dueñnas-Gonzalez A (2006) Hydralazine target: from blood vessels to the epigenome. J Transl Med 4:10
Lee WJ, Shim JY, Zhu BT (2005) Mechanisms for the inhibition of DNA methyltransferases by tea catechins and bioflavonoids. Mol Pharmacol 68:1018–1030
Evans DA, Bronowska AK (2009) Implications of fast-time scale dynamics of human DNA/RNA cytosine methyltransferases (DNMTs) for protein function. Theor Chem Acc 125:407–418
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Dr. Fabian López-Vallejo and Dr. Thomas Caulfield for helpful discussions. We also thank Karen Gottwald for proofreading the manuscript. This work was supported by the Menopause & Women’s Health Research Center and the State of Florida, Executive Office of the Governor’s Office of Tourism, Trade, and Economic Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, J., Medina-Franco, J.L. Homology modeling, docking and structure-based pharmacophore of inhibitors of DNA methyltransferase. J Comput Aided Mol Des 25, 555–567 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-011-9441-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-011-9441-1