Abstract
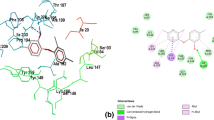
Drugs have been discovered in the past mainly either by identification of active components from traditional remedies or by unpredicted discovery. A key motivation for the study of structure based virtual screening is the exploitation of such information to design targeted drugs. In this study, structure based virtual screening was used in search for putative quorum sensing inhibitors (QSI) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The virtual screening programme Glide version 5.5 was applied to screen 1,920 natural compounds/drugs against LasR and RhlR receptor proteins of P. aeruginosa. Based on the results of in silico docking analysis, five top ranking compounds namely rosmarinic acid, naringin, chlorogenic acid, morin and mangiferin were subjected to in vitro bioassays against laboratory strain PAO1 and two more antibiotic resistant clinical isolates, P. aeruginosa AS1 (GU447237) and P. aeruginosa AS2 (GU447238). Among the five compounds studied, except mangiferin other four compounds showed significant inhibition in the production of protease, elastase and hemolysin. Further, all the five compounds potentially inhibited the biofilm related behaviours. This interaction study provided promising ligands to inhibit the quorum sensing (QS) mediated virulence factors production in P. aeruginosa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adonizio A, Kong KF, Mathee K (2008) Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by south florida plant extracts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:198–203
Annapoorani A, Jabbar AKKA, Musthafa SKS, Pandian SK, Ravi AV (2012) Inhibition of quorum sensing mediated virulence factors production in urinary pathogen Serratia marcescens PS1 by marine sponges. Indian J Microbiol 52:160–166
Annapoorani A, Parameswari R, Pandian SK, Ravi AV (2012) Methods to determine antipathogenic potential of phenolic and flavonoid compounds against urinary pathogen Serratia marcescens. J Microbiol Methods. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2012.06.007
Anwar H, Dasgupta MK, Costerton JW (1990) Testing the susceptibility of bacteria in biofilms to antibacterials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34:2043–2046
Bjarnsholt T, Jensen PO, Burmolle M, Hentzer M, Haagensen JAJ, Hougen HP, Calum H, Madsen KG, Moser C, Molin S, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2005) Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolerance to tobramycin, hydrogen peroxide and polymorphonuclear leukocytes is quorum-sensing dependent. Microbiology 151:373–383
Bosgelmez GT, Ulusoy S (2008) Characterization of N- butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL) deficient clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb Pathog 44:13–19
Bottomley MJ, Muraglia E, Bazzo R, Carfi A (2007) Molecular insights into quorum sensing in the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the structure of the virulence regulator LasR bound to its autoinducer. J Biol Chem 282:13592–13600
Carmeli Y, Troillet N, Karchmer AW, Samore MH (1999) Health and economic outcomes of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Intern Med 159:1127–1132
Ciofu O, Giwercman B, Pedersen SS, Hoiby N (1994) Development of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa during two decades of anti pseudomonal treatment at the Danish CF Center. APMIS 102:674–680
Costerton JW (2001) Cystic fibrosis pathogenesis and the role of biofilms in persistent infection. Trends Microbiol 9:50–52
Diggle SP, Gardner A, Stuart AW, Griffin AS (2007) Evolutionary theory of bacterial quorum sensing: when is a signal not a signal? Phil Trans R Soc B 362:1241–1249
Harjai K, Kumar R, Sukhvinder S (2010) Garlic blocks quorum sensing and attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 58:161–168
Hentzer M, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Heydorn A, Andersen JB, Parsek MR, Rice SA, Eberl L, Molin S, Hoiby N, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M (2002) Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 148:87–102
Hentzer M, Wu H, Andersen JB, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Bagge N, Kumar N, Schembri MA, Song Z, Kristoffersen P, Manefield M, Costerton JW, Molin S, Eberl L, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2003) Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J 22:3803–3815
Kessler E, Israel M, Landshman N, Chechick A, Blumberg S (1982) In vitro inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase by metal-chelating peptide derivatives. Infect Immun 38:716–723
Kolb P, Rafaela SF, John JI, Brian KS (2009) Docking and chemoinformatic screens for new ligands and targets. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:429–436
Lyne PD (2002) Structure-based virtual screening: an overview. Drug Discov Today 7:1047–1055
Musthafa SK, Ravi AV, Annapoorani A, Packiavathy ISV, Pandian SK (2010) Evaluation of antiquorum sensing activity of edible plants and fruits through inhibition of AHL system in Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemotherapy 56:333–339
Musthafa SK, Saroja V, Pandian SK, Ravi AV (2011) Antipathogenic potential of marine Bacillus sp. SS4 on N-acyl-homoserine-lactone-mediated virulence factors production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1). J Biosci 36:55–67
Ohman DE, Cryz SJ, Iglewski BH (1980) Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J Bacteriol 142:836–842
Persson T, Givskov M, Nielsen J (2005) Quorum sensing inhibition: targeting chemical communication in gram-negative bacteria. J Curr Med Chem 12:3103–3115
Pesci E, Milbank JBJ, Pearson JP, Mcknight S, Kende AS, Greenberg EP, Iglewski BH (1999) Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:11229–11234
Protein Model Portal, Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, Biozentrum. http://www.proteinmodelportal.org/query/uniprot/P54292
Rasmussen TB, Givskov M (2006) Quorum sensing inhibitors: a bargin of effects. Microbiology 152:895–904
Rasmussen TB, Givskov M (2006) Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int J Med Microbiol 296:149–161
Roger SS, Barbara HI (2003) Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing as a potential antimicrobial target. J Clin Invest 112:1460–1465
Schneider G, Bohm HJ (2002) Virtual screening and fast automated docking methods. Drug Discov Today 7:64–70
Selan L, Berlutti F, Passariello C, Comodi-Ballanti MR, Thaller MC (1993) Proteolytic enzymes: a new treatment strategy for prosthetic infections? Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37:2618–2621
Selvaraj C, Singh SK, Tripathi SK, Reddy KK, Rama M (2011) In silico screening of indinavir-based compounds targeting proteolytic activity in HIV PR: binding pocket fit approach. Med Chem Res. doi:10.1007/s00044-011-9941-5
Smith KM, Bu Y, Suga H (2003) Library screening for synthetic agonists and antagonists of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer. Chem Biol 10:563–571
Stephen PD, Winzer K, Siri Ram C, Kathryn EW, Cámara M, Williams P (2003) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol Microbiol 50(1):29–43
Suga H, Smith KM (2003) Molecular mechanisms of bacterial quorum sensing as a new drug target. Curr Opin Chem Biol 7(5):586–591
Van Delden C, Iglewski BH (1998) Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg Infect Dis 4:551–560
Vattem DA, Mihalik K, Crixell SH, McLean RJ (2007) Dietary phytochemicals as quorum sensing inhibitors. Fitoterapia 78:302–310
Whitehead NA, Barnard AM, Slater H, Simpson NJ, Salmond GP (2001) Quorum-sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:365–404
Yang L, Rybtke MT, Jakobsen TH, Hentzer M, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M, Nielsen T (2009) Computer-aided identification of recognized drugs as Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:2432–2443
Zeng Z, Li Q, Lixiang C, Hongming T, Yali H, Xiaoli X, Yong S, Shining Z (2008) Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:119–126
Acknowledgments
We extend our sincere thanks to computational and bioinformatics facility provided by the Alagappa University Bioinformatics Infrastructure Facility (funded by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India; Grant No. BT/BI/25/001/2006). We thank Schrodinger, LLC, New York, USA for providing free access of their bioinformatics tools. We also extend our sincere thanks to Dr. K. Syed Ibrahim, Research Associate, Department of Biotechnology, Mizoram University, Aizawl and Mr. C. Selvaraj, Research Scholar, Department of Bioinformatics, Alagappa University, Karaikudi for their assistance in the bioinformatics part of this manuscript. A. Annapoorani gratefully acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for the financial assistance rendered [CSIR SRF No. 9/688 (0014)/2011].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Annapoorani, A., Umamageswaran, V., Parameswari, R. et al. Computational discovery of putative quorum sensing inhibitors against LasR and RhlR receptor proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa . J Comput Aided Mol Des 26, 1067–1077 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-012-9599-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-012-9599-1