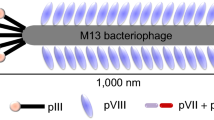
Abstract
Using phage display technique, we identified tissue-targeting peptide sets that recognize specific tissues (bone-marrow dendritic cell, kidney, liver, lung, spleen and visceral adipose tissue). In order to rapidly evaluate tissue-specific targeting peptides, we performed machine learning studies for predicting the tissue-specific targeting activity of peptides on the basis of peptide sequence information using four machine learning models and isolated the groups of peptides capable of mediating selective targeting to specific tissues. As a representative liver-specific targeting sequence, the peptide “DKNLQLH” was selected by the sequence similarity analysis. This peptide has a high degree of homology with protein ligands which can interact with corresponding membrane counterparts. We anticipate that our models will be applicable to the prediction of tissue-specific targeting peptides which can recognize the endothelial markers of target tissues.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alley SC, Okeley NM, Senter PD (2010) Antibody-drug conjugates: targeted drug delivery for cancer. Curr Opin Chem Biol 14:529–537
Vives E, Schmidt J, Pelegrin A (2008) Cell-penetrating and cell-targeting peptides in drug delivery. BBA Rev Cancer 1786:126–138
Ray P, White RR (2010) Aptamers for targeted drug delivery. Pharmaceuticals 3:1761–1778
Singha R, Lillard JWM (2009) Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp Mol Pathol 86:215–223
Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (1996) Organ targeting in vivo using phage display peptide libraries. Nature 380:364–366
Rajotte D, Arap W, Hagedorn M, Koivunen E, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (1998) Molecular heterogeneity of the vascular endothelium revealed by in vivo phage display. J Clin Invest 102:430–437
Trepel M, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2000) Exploring vascular heterogeneity for gene therapy targeting. Gene Ther 7:2059–2060
William CA (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium : I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100:158–173
William CA (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium. Circ Res 100:174–190
Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (1998) Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 279:377–380
Kolonin MG, Pasqualini R, Arap W (2001) Molecular addresses in blood vessels as targets for therapy. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:308–313
Arap W, Haedicke W, Bernasconi M, Kain R, Rajotte D, Krajewski S, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (2002) Targeting the prostate for destruction through a vascular address. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1527–1531
Durr E, Yu J, Krasinska KM, Carver LA, Yates JR, Testa JE, Oh P, Schnitzer JE (2004) Direct proteomic mapping of the lung microvascular endothelial cell surface in vivo and in cell culture. Nat Biotechnol 22:985–992
Oh P, Li Y, Yu J, Durr E, Krasinska K, Carver LA, Testa JE, Schnitzer JE (2004) Subtractive proteomic mapping of the endothelial surface in lung and solid tumours for tissue-specific therapy. Nature 429:629–635
Majumdar S, Siahaan TJ (2010) Peptide-mediated targeted drug delivery. Med Res Rev. doi:10.1002/med.20225
Binétruy-Tournaire R, Demangel C, Malavaud B, Vassy R, Rouyre S, Kraemer M, Plouët J, Derbin C, Perret G, Mazié JC (2000) Identification of a peptide blocking vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis. EMBO J 19:1525–1533
Askoxylakis V, Zitzmann S, Mier W, Graham K, Krämer S, von Wegner F, Fink RH, Schwab M, Eisenhut M, Haberkorn U (2005) Preclinical evaluation of the breast cancer cell-binding peptide, p160. Clin Cancer Res 11:6705–6712
Zang L, Shi L, Guo J, Pan Q, Wu W, Pan X, Wang J (2009) Screening and identification of a peptide specifically targeted to NCI-H1299 from a phage display peptide library. Cancer Lett 281:64–70
Yanofsky SD, Baldwin DN, Butler JH, Holden FR, Jacobs JW, Balasubramanian P, Chinn JP, Cwirla SE, Peters-Bhatt E, Whitehorn EA, Tate EH, Akeson A, Bowlin TL, Dower WJ, Barrett RW (1996) High affinity type I interleukin 1 receptor antagonists discovered by screening recombinant peptide libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7381–7386
Tian W, Bai G, Li ZH, Yang WB (2006) Antagonist peptides of human interferon-alpha2b isolated from phage display library inhibit interferon induced antiviral activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:1044–1050
Kang SK, Woo JH, Kim MK, Woo SS, Choi JH, Lee HG, Lee NK, Choi YJ (2008) Identification of a peptide sequence that improves transport of macromolecules across the intestinal mucosal barrier targeting goblet cells. J Biotechnol 135:210–216
Chen Y, Shen Y, Guo X, Zhang C, Yang W, Ma M, Liu S, Zhang M, Wen LP (2006) Transdermal protein delivery by a coadministered peptide identified via phage display. Nat Biothechnol 24:455–460
Wan XM, Chen YP, Xu WR, Yang WJ, Wen LP (2009) Identification of nose-to-brain homing peptide through phage display. Peptides 30:343–350
Zhang L, Hoffman JA, Ruoslahti E (2005) Molecular profiling of heart endothelial cells. Circulation 112:1601–1611
Pasqualini R, Koivunen E, Ruoslahti E (1997) Alpha v integrins as receptors for tumor targeting by circulating ligands. Nat Biotechnol 15:542–546
Burg MA, Pasqualini R, Arap W, Ruoslahti E, Stallcup WB (1999) NG2 proteoglycan-binding peptides target tumor neovasculature. Cancer Res 59:2869–2874
Laakkonen P, Akerman ME, Biliran H, Yang M, Ferrer F, Karpanen T, Hoffman RM, Ruoslahti E (2004) Antitumor activity of a homing peptide that targets tumor lymphatics and tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9381–9386
Arap W, Kolonin MG, Trepel M, Lahdenranta J, Cardó-Vila M, Giordano RJ, Mintz PJ, Ardelt PU, Yao VJ, Vidal CI, Chen L, Flamm A, Valtanen H, Weavind LM, Hicks ME, Pollock RE, Botz GH, Bucana CD, Koivunen E, Cahill D, Troncoso P, Baggerly KA, Pentz RD, Do KA, Logothetis CJ, Pasqualini R (2002) Steps toward mapping the human vasculature by phage display. Nat Med 8:121–127
Ellerby HM, Arap W, Ellerby LM, Kain R, Andrusiak R, Rio GD, Krajewski S, Lombardo CR, Rao R, Ruoslahti E. Bredesen DE, Pasqualini R (1999) Anti-cancer activity of targeted pro-apoptotic peptides. Nat Med 5:1032–1038
Chen Y, Xu X, Hong S, Chen J, Liu N, Underhill CB, Creswell K, Zhang L (2001) RGD-tachyplesin inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Res 61:2434–2438
Yoneda Y, Steiniger SC, Capková K, Mee JM, Liu Y, Kaufmann GF, Janda KD (2008) A cell-penetrating peptidic GRP78 ligand for tumor cell-specific prodrug therapy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:1632–1636
Curnis F, Sacchi A, Borgna L, Magni F, Gasparri A, Corti A (2000) Enhancement of tumor necrosis factor α antitumor immunotherapeutic properties by targeted delivery to aminopeptidase N (CD13). Nat Biotechnol 18:1185–1190
Curnis F, Arrigoni G, Sacchi A, Fischetti L, Arap W, Pasqualini R, Corti A (2002) Differential binding of drugs containing the NGR motif to CD13 isoforms in tumor vessels, epithelia, and myeloid cells. Cancer Res 62:867–874
Jung E, Kim J, Kim M, Jung DH, Rhee H, Shin JM, Choi K, Kang SK, Kim MK, Yun CH, Choi YJ, Choi SH (2007) Artificial neural network models for prediction of intestinal permeability of oligopeptides. BMC Bioinformat 8:245
Jung E, Kim J, Choi SH, Kim M, Rhee H, Shin JM, Choi K, Kang SK, Lee NK, Choi YJ, Jung DH (2010) Artificial neural network study on organ-targeting peptides. J Comput Aided Mol Des 24:49–56
Jung E, Choi SH, Lee NK, Kang SK, Choi YJ, Shin JM, Choi K, Jung DH (2011) Machine learning study for the prediction of transdermal peptide. J Comput Aided Mol Des 25:339–347
Inaba K, Inaba M, Romani N, Aya H, Deguchi M, Ikehara S, Muramatsu S, Steinman RM (1992) Generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cultures supplemented with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med 176:1693–1702
Shepherd DM, Steppan LB, Hedstrom OR, Kerkvliet NI (2001) Anti-CD40 treatment of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-exposed C57BL/6 mice induces activation of antigen presenting cells yet fails to overcome TCDD-induced suppression of allograft immunity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 170:10–22
McCaldon P, Argos P (1988) Proteins 4:99–122
Mei H, Lian ZH, Zhou Y, Li SZ (2005) A new set of amino acid descriptors and its application in peptide QSARs. Biopolymer (Peptide Science) 80:775–786
Pipeline Pilot 8.0 (http://accelrys.com/products/pipeline-pilot/)
The R Project for Statistical Computing (http://www.r-project.org/)
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Discovery Studio 3.1 (http://accelrys.com/products/discovery-studio/)
Henikoff S, Henikoff JG (1992) Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10915–10919
Gauthier MA, Klok HA (2008) Peptide/protein–polymer conjugates: synthetic strategies and design concepts. Chem Commun 23:2591–2611
Molek P, Strukelj B, Bratkovic T (2011) Peptide phage display as a tool for drug discovery: targeting membrane receptors. Molecules 16:857–887
Rajotte D, Ruoslahti E (1999) Membrane dipeptidase is the receptor for a lung-targeting peptide identified by in vivo phage display. J Biol Chem 274:11593–11598
Kolonin MG, Saha PK, Chan L, Pasqualini R, Arap W (2004) Reversal of obesity by targeted ablation of adipose tissue. Nat Med 10:625–632
Bhattacharya SK, Peachey NS, Crabb JW (2005) Cochlin and glaucoma: a mini-review. Vis Neurosci 22:605–613
Tuma PL, Hubbard AL (2003) Transcytosis: crossing cellular barriers. Physiol Rev 83:871–932
Favier B, Alam A, Barron P, Bonnin J, Laboudie P, Fons P, Mandron M, Herault JP, Neufeld G, Savi P, Herbert JM, Bono F (2006) Neuropilin-2 interacts with VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 and promotes human endothelial cell survival and migration. Blood 108:1243–1250
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), Korea government (MEST) (Project No. 2011-0029416). We thank Accelrys Korea for the support of SciTegic Pipeline Pilot and Discovery Studio software, and acknowledge the assistance of BioMedES (http://www.biomedes.co.uk/home).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, E., Lee, N.K., Kang, SK. et al. Identification of tissue-specific targeting peptide. J Comput Aided Mol Des 26, 1267–1275 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-012-9614-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-012-9614-6