Abstract
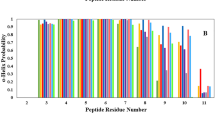
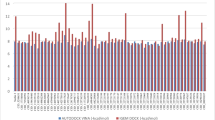
Targeting of MDM2-p53 protein–protein interaction is a current approach for the development of potent anticancer agents. The classical pharmacophore hypothesis for the design of such molecules describes the three point binding of a small molecule inhibitor to the MDM2 protein. However, this hypothesis is not confirmed when considering the activity of a number of known potent MDM2 inhibitors. Here we demonstrate the important role of the flexible N-terminal region of the MDM2 protein in the binding with small molecule compounds, which contributes to the transition from three point binding to four point binding during the development of new anticancer agents. To evaluate the contribution of the MDM2 N-terminal region to the structure–activity relationship of known MDM2 inhibitors, compounds of nutlin series, whose spatial configuration was shown to dramatically affect the target activity, were used as objects of the study. The key amino acid residues within the N-terminal region involved in the interaction with small molecule ligands were determined by means of molecular dynamics. The conformational stability of the flexible MDM2 fragment was simulated under different conditions. The effects of point mutations on the N-terminal region stability were also demonstrated.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nowsheen S, Yang ES (2012) The intersection between DNA damage response and cell death pathways. Exp Oncol 34:243–254
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M (1997) Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387:296–299
Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (1997) Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett 420:25–27
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH (1997) Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature 387:299–303
Kruse JP, Gu W (2009) Modes of p53 regulation. Cell 137:609–622
Shi D, Gu W (2012) Dual roles of MDM2 in the regulation of p53: ubiquitination dependent and ubiquitination independent mechanisms of MDM2 repression of p53 activity. Genes Cancer 3:240–248
Cordon-Cardo C, Latres E, Drobnjak M, Oliva MR, Pollack D, Woodruff JM, Marechal V, Chen J, Brennan MF, Levine AJ (1994) Molecular abnormalities of mdm2 and p53 genes in adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res 54:794–799
Marchetti A, Buttitta F, Girlando S, Dalla Palma P, Pellegrini S, Fina P, Doglioni C, Bevilacqua G, Barbareschi M (1995) Mdm2 gene alterations and mdm2 protein expression in breast carcinomas. J Pathol 175:31–38
Marchetti A, Buttitta F, Pellegrini S, Merlo G, Chella A, Angeletti CA, Bevilacqua G (1995) Mdm2 gene amplification and overexpression in non-small cell lung carcinomas with accumulation of the p53 protein in the absence of p53 gene mutations. Diagn Mol Pathol 4:93–97
Saha MN, Qiu L, Chang H (2013) Targeting p53 by small molecules in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol 6:23
Krasavin M, Gureyev MA, Dar’in D, Bakulina O, Chizhova M, Lepikhina A, Novikova D, Grigoreva T, Ivanov G, Zhumagalieva A, Garabadzhiu AV, Tribulovich VG (2018) Design, in silico prioritization and biological profiling of apoptosis-inducing lactams amenable by the Castagnoli-Cushman reaction. Bioorg Med Chem 26:2651–2673
Davidovich P, Aksenova V, Petrova V, Tentler D, Orlova D, Smirnov S, Gurzhiy V, Okorokov AL, Garabadzhiu A, Melino G, Barlev N, Tribulovich V (2015) Discovery of novel isatin-based p53 inducers. ACS Med Chem Lett 6:856–860
Grigoreva TA, Novikova DS, Gureev MA, Garabadzhiu AV, Tribulovich VG (2018) Amino acids as chiral derivatizing agents for antiproliferative substituted N-benzyl isoindolinones. Chirality 30:785–797
Ribeiro CJ, Rodrigues CM, Moreira R, Santos MM (2016) Chemical variations on the p53 reactivation theme. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 9:E25
Michelsen K, Jordan JB, Lewis J, Long AM, Yang E, Rew Y, Zhou J, Yakowec P, Schnier PD, Huang X, Poppe L (2012) Ordering of the N-terminus of human MDM2 by small molecule inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc 134:17059–17067
Grigoreva TA, Garabadzhiu AV, Tribulovich VG (2016) Diastereotopic derivatives of chiral alkoxyisoindolinones. Russ J Gen Chem 86:2454–2461
Grigoreva TA, Novikova DS, Petukhov AV, Gureev MA, Garabadzhiu AV, Melino G, Barlev NA, Tribulovich VG (2017) Proapoptotic modification of substituted isoindolinones as MDM2-p53 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:5197–5202
Parks DJ, LaFrance LV, Calvo RR, Milkiewicz KL, Marugán JJ, Raboisson P, Schubert C, Koblish HK, Zhao S, Franks CF, Lattanze J, Carver TE, Cummings MD, Maguire D, Grasberger BL, Maroney AC, Lu T (2006) Enhanced pharmacokinetic properties of 1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-dione antagonists of the HDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction through structure-based drug design. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:3310–3314
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, Fotouhi N, Liu EA (2004) In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303:844–848
Anil B, Riedinger C, Endicott JA, Noble ME (2013) The structure of an MDM2-Nutlin-3a complex solved by the use of a validated MDM2 surface-entropy reduction mutant. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69:1358–1366
Jones G, Willett P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R (1997) Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol 267:727–748
Jacobson MP, Pincus DL, Rapp CS, Day TJ, Honig B, Shaw DE, Friesner RA (2004) A hierarchical approach to all-atom protein loop prediction. Proteins 55:351–367
Jacobson MP, Friesner RA, Xiang Z, Honig B (2002) On the role of the crystal environment in determining protein side-chain conformations. J Mol Biol 320:597–608
Harder E, Damm W, Maple J, Wu C, Reboul M, Xiang JY, Wang L, Lupyan D, Dahlgren MK, Knight JL, Kaus JW, Cerutti DS, Krilov G, Jorgensen WL, Abel R, Friesner RA (2016) OPLS3: A force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. J Chem Theory Comput 12:281–296
Toukan K, Rahman A (1985) Molecular-dynamics study of atomic motions in water. Phys Rev B 31:2643–2648
Bueren-Calabuig JA, Michel J (2016) Impact of Ser17 phosphorylation on the conformational dynamics of the oncoprotein MDM2. Biochemistry 55:2500–2509
Zheng J, Lang Y, Zhang Q, Cui D, Sun H, Jiang L, Chen Z, Zhang R, Gao Y, Tian W, Wu W, Tang J, Chen Z (2015) Structure of human MDM2 complexed with RPL11 reveals the molecular basis of p53 activation. Genes Dev 29:1524–1534
Uhrinova S, Uhrin D, Powers H, Watt K, Zheleva D, Fischer P, McInnes C, Barlow PN (2005) Structure of free MDM2 N-terminal domain reveals conformational adjustments that accompany p53-binding. J Mol Biol 350:587–598
Shin JS, Ha JH, Lee DH, Ryu KS, Bae KH, Park BC, Park SG, Yi GS, Chi SW (2015) Structural convergence of unstructured p53 family transactivation domains in MDM2 recognition. Cell Cycle 14:533–543
Worrall EG, Wawrzynow B, Worrall L, Walkinshaw M, Ball KL, Hupp TR (2009) Regulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of MDM2 by an N-terminal pseudo-substrate motif. J Chem Biol 2:113–129
Dastidar SG, Raghunathan D, Nicholson J, Hupp TR, Lane DP, Verma CS (2011) Chemical states of the N-terminal “lid” of MDM2 regulate p53 binding: simulations reveal complexities of modulation. Cell Cycle 10:82–89
Verkhivker GM (2012) Simulating molecular mechanisms of the MDM2-mediated regulatory interactions: a conformational selection model of the MDM2 lid dynamics. PLoS ONE 7:e40897
Zhan C, Varney K, Yuan W, Zhao L, Lu W (2012) Interrogation of MDM2 phosphorylation in p53 activation using native chemical ligation: the functional role of Ser17 phosphorylation in MDM2 reexamined. J Am Chem Soc 134:6855–6864
Showalter SA, Bruschweiler-Li L, Johnson E, Zhang F, Brüschweiler R (2008) Quantitative lid dynamics of MDM2 reveals differential ligand binding modes of the p53-binding cleft. J Am Chem Soc 130:6472–6478
Thompson T, Andreeff M, Studzinski GP, Vassilev LT (2010) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances the apoptotic activity of MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3a in acute myeloid leukemia cells expressing wild-type p53. Mol Cancer Ther 9:1158–1168
Fry DC, Wartchow C, Graves B, Janson C, Lukacs C, Kammlott U, Belunis C, Palme S, Klein C, Vu B (2013) Deconstruction of a nutlin: dissecting the binding determinants of a potent protein-protein interaction inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 4:660–665
Fedorova O, Daks A, Petrova V, Petukhov A, Lezina L, Shuvalov O, Davidovich P, Kriger D, Lomert E, Tentler D, Kartsev V, Uyanik B, Tribulovich V, Demidov O, Melino G, Barlev NA (2018) Novel isatin-derived molecules activate p53 via interference with Mdm2 to promote apoptosis. Cell Cycle 17:1917–1930
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 16-13-10358).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gureev, M., Novikova, D., Grigoreva, T. et al. Simulation of MDM2 N-terminal domain conformational lability in the presence of imidazoline based inhibitors of MDM2-p53 protein–protein interaction. J Comput Aided Mol Des 34, 55–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-019-00260-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-019-00260-6