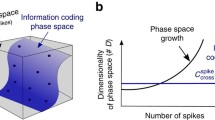
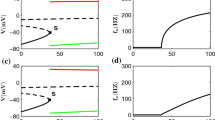
Abstract
The linear-nonlinear cascade model (LN model) has proven very useful in representing a neural system’s encoding properties, but has proven less successful in reproducing the firing patterns of individual neurons whose behavior is strongly dependent on prior firing history. While the cell’s behavior can still usefully be considered as feature detection acting on a fluctuating input, some of the coding capacity of the cell is taken up by the increased firing rate due to a constant “driving” direct current (DC) stimulus. Furthermore, both the DC input and the post-spike refractory period generate regular firing, reducing the spike-timing entropy available for encoding time-varying fluctuations. In this paper, we address these issues, focusing on the example of motoneurons in which an afterhyperpolarization (AHP) current plays a dominant role regularizing firing behavior. We explore the accuracy and generalizability of several alternative models for single neurons under changes in DC and variance of the stimulus input. We use a motoneuron simulation to compare coding models in neurons with and without the AHP current. Finally, we quantify the tradeoff between instantaneously encoding information about fluctuations and about the DC.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguera y Arcas, B., & Fairhall, A. L. (2003). What causes a neuron to spike? Neural Computation, 15, 1789–1807.
Aguera y Arcas, B., Fairhall, A. L., & Bialek, W. (2003). Computation in a single neuron: Hodgkin and Huxley revisited. Neural Computation, 15, 1715–1749.
Berry, M. J., & Meister, M. (1998). Refractoriness and neural precision. Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 2200–2211.
Binder, M. D., Poliakov, A. V., & Powers, R. K. (1999). Functional identification of the input–output transforms of mammalian motoneurones. Journal of Physiology, Paris, 93, 29–42.
Brenner, N., Bialek, W., & de van Ruyter Steveninck, R. R. (2000a). Adaptive rescaling maximizes information transmission. Neuron, 26, 695–702.
Brenner, N., Strong, S. P., Koberle, R., Bialek, W., & de van Ruyter Steveninck, R. R. (2000b). Synergy in a neural code. Neural Computation, 12, 1531–1552.
Brosh, I., Rosenblum, K., & Barkai, E. (2007). Learning-induced modulation of SK channels-mediated effect on synaptic transmission. European Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 3253–3260.
Bryant, H. L., & Segundo, J. P. (1976). Spike initiation by transmembrane current: a white-noise analysis. Journal of Physiology, 260, 279–314.
Cover, T. M., & Thomas, J. A. (1991). Elements of Information Theory. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience.
de Boer, R., & Kuyper, P. (1968). Triggered correlation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 15, 169–179.
de van Ruyter Steveninck, R. R., & Bialek, W. (1988). Real-time performance of a movement-sensitive neuron in the blowfly visual system: coding and information transmission in short spike sequences. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B, 234, 379–414.
Diaz-Quesada, M., & Maravall, M. (2008). Intrinsic mechanisms for adaptive gain rescaling in barrel cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 696–710.
Escabi, M. A., Nassiri, R., Miller, L. M., Schreiner, C. E., & Read, H. L. (2005). The contribution of spike threshold to acoustic feature selectivity, spike information content, and information throughput. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 9524–9534.
Fairhall, A. L., Lewen, G. D., Bialek, W., & de Ruyter Van Steveninck, R. R. (2001). Efficiency and ambiguity in an adaptive neural code. Nature, 412(6849), 787–792.
Fairhall, A. L., Burlingame, C. A., Narasimhan, R., Harris, R. A., Puchalla, J. L., & Berry, M. J. (2006). Selectivity for multiple stimulus features in retinal ganglion cells. Journal of Neurophysiology, 96, 2724–2738.
Famulare, M., & Fairhall, A. (2010). Feature selection in simple neurons: how coding depends on spiking dynamics. Neural Computation, 22, 581–598.
Famulare M, Fairhall A (2011). Adaptive probabilistic neural coding from deterministic spiking neurons: analysis from first principles. Eprint arxivorg/abs/11110097.
Fellous, J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (2003). Regulation of persistent activity by background inhibition in an in vitro model of a cortical microcircuit. Cerebral Cortex, 13, 1232–1241.
Gerstein, G. L., & Mandelbrot, B. (1964). Random walk models for the spike activity of a single neuron. Biophysical Journal, 4, 41–68.
Hille B (2001). Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes: Sinauer Associates.
Hodgkin, A. L., & Huxley, A. F. (1952). Propagation of electrical signals along giant nerve fibers. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 140, 177–183.
Hong, S., Aguera y Arcas, B., & Fairhall, A. L. (2007). Single neuron computation: from dynamical system to feature detector. Neural Computation, 19, 3133–3172.
Jackson, M. B. (1992). Cable analysis with the whole-cell patch clamp. Theory and experiment. Biophysics Journal, 61(3), 756–766.
Ji, H., Hougaard, C., Herrik, K. F., Strobaek, D., Christophersen, P., & Shepard, P. D. (2009). Tuning the excitability of midbrain dopamine neurons by modulating the Ca2+ sensitivity of SK channels. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 1883–1895.
Joeken, S., Schwegler, H., & Richter, C. P. (1997). Modeling stochastic spike train responses of neurons: an extended Wiener series analysis of pigeon auditory nerve fibers. Biological Cybernetics, 76, 153–162.
Keat, J., Reinagel, P., Reid, R. C., & Meister, M. (2001). Predicting every spike: a model for the responses of visual neurons. Neuron, 30, 803–817.
Kim, K. J., & Rieke, F. (2001). Temporal contrast adaptation in the input and output signals of salamander retinal ganglion cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 287–299.
Kistler, W., Gerstner, W., & van Hemmen, J. L. (1997). Reduction of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations to a single-variable threshold model. Neural Computation, 9, 1015–1045.
Koch, C. (1999). Biophysics of computation: information processing in single neurons. New York: Oxford University Press.
Korenberg, M., & Hunter, I. (1986). The identification of nonlinear biological systems: LNL cascade models. Biological Cybernetics, 55, 125–134.
Mainen, Z. F., Joerges, J., Huguenard, J. R., & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). A model of spike initiation in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron, 15, 1427–1439.
Maingret, F., Coste, B., Hao, J., Giamarchi, A., Allen, D., Crest, M., et al. (2008). Neurotransmitter modulation of small-conductance Ca2+ −activated K+ channels by regulation of Ca2+ gating. Neuron, 59, 439–449.
Maravall, M., Petersen, R. S., Fairhall, A. L., Arabzadeh, E., & Diamond, M. E. (2007). Shifts in coding properties and maintenance of information transmission during adaptation in barrel cortex. PLoS Biology, 5, e19.
Marmarelis, P., & Marmarelis, V. Z. (1968). Analysis of Physiological Systems: The White Noise Approach. York New: Plenum Press.
Matthews, P. B. (1996). Relationship of firing intervals of human motor units to the trajectory of post-spike after-hyperpolarization and synaptic noise. Journal of Physiology, 492(2), 597–628.
Mease, R. A., Famulare, M., Gjorgjieva, J., Moody, W. J., & Fairhall, A. L. (2013). Emergence of adaptive computation by single neurons in the developing cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(30), 12154–12170.
Paninski, L., Pillow, J., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2004). Maximum likelihood estimation of a stochastic integrate-and-fire neural encoding model. Neural Computation, 16, 2533–2561.
Pedarzani, P., & Stocker, M. (2008). Molecular and cellular basis of small- and intermediate-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channel function in the brain. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 65, 3196–3217.
Pillow, J. W., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2003). Biases in white noise analysis due to non-Poisson spike generation. Neurocomputing, 52–54, 109–115.
Pillow, J. W., Shlens, J., Paninski, L., Sher, A., Litke, A. M., Chichilnisky, E. J., et al. (2008). Spatio-temporal correlations and visual signalling in a complete neuronal population. Nature, 454(7207), 995–999.
Poliakov, A. V., Powers, R. K., & Binder, M. D. (1997). Functional identification of the input–output transforms of motoneurones in the rat and cat. Journal of Physiology, 504(2), 401–424.
Powers, R. K. (1993). A variable-threshold motoneuron model that incorporates time- and voltage-dependent potassium and calcium conductances. Journal of Neurophysiology, 70, 246–262.
Powers, R. K., & Binder, M. D. (2000). Relationship between the time course of the afterhyperpolarization and discharge variability in cat spinal motoneurones. Journal of Physiology, 528, 131–150.
Powers, R., Dai, Y., Bell, B., Percival, D., & Binder, M. (2005). Contributions of the input signal and prior activation history to the discharge behaviour of rat motoneurones. Journal of Physiology, 562, 707–724.
Purvis, L. K., & Butera, R. J. (2005). Ionic current model of a hypoglossal motoneuron. Journal of Neurophysiology, 93, 723–733.
Rieke F, Warland D, de Ruyter van Steveninck, Rob R., Bialek W (1997). Spikes: Exploring the Neural Code: The MIT Press.
Ringach, D. L., & Malone, B. J. (2007). The operating point of the cortex: neurons as large deviation detectors. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 7673–7683.
Rust, N., Schwartz, O., Movshon, J., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2005). Spatiotemporal elements of macaque V1 receptive fields. Neuron, 46, 945–956.
Sah, P. (1996). Ca(2+)-activated K + currents in neurones: types, physiological roles and modulation. Trends in Neurosciences, 19, 150–154.
Sawczuk, A., Powers, R. K., & Binder, M. D. (1995). Spike frequency adaptation studied in hypoglossal motoneurons of the rat. Journal of Neurophysiology, 73, 1799–1810.
Sawczuk, A., Powers, R. K., & Binder, M. D. (1997). Contribution of outward currents to spike-frequency adaptation in hypoglossal motoneurons of the rat. Journal of Neurophysiology, 78, 2246–2253.
Sharpee, T., Rust, N. C., & Bialek, W. (2004). Analyzing neural responses to natural signals: maximally informative dimensions. Neural Computation, 16(2), 223–250.
Simoncelli EP, Pillow J, Paninski L, Schwartz O (2004). Characterization of neural responses with stochastic stimuli. (Gazzaniga, M., ed): MIT Press.
Slee, S. J., Higgs, M. H., Fairhall, A. L., & Spain, W. J. (2005). Two-dimensional coding in the auditory brainstem. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 9978–9988.
Svirskis, G., Kotak, V., Sanes, D. H., & Rinzel, J. (2002). Enhancement of signal-to-noise ratio and phase locking for small inputs by a low-threshold outward current in auditory neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 22, 11019–11025.
Svirskis, G., Kotak, V., Sanes, D. H., & Rinzel, J. (2004). Sodium along with low-threshold potassium currents enhance coincidence detection of subthreshold noisy signals in MSO neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 91, 2465–2473.
Touryan, J., Felsen, G., & Dan, Y. (2005). Spatial structure of complex cell receptive fields measured with natural images. Neuron, 45, 781–791.
Truccolo, W., Eden, U. T., Fellows, M. R., Donoghue, J. P., & Brown, E. N. (2005). A point process framework for relating neural spiking activity to spiking history, neural ensemble, and extrinsic covariate effects. Journal of Neurophysiology, 93(2), 1074–1089.
van Rossum, M. C. (2001). A novel spike distance. Neural Computation, 13, 751–763.
Viana, F., Bayliss, D. A., & Berger, A. J. (1995). Repetitive firing properties of developing rat brainstem motoneurones. Journal of Physiology, 486(3), 745–761.
Victor, J. D., & Purpura, K. P. (1996). Nature and precision of temporal coding in visual cortex: a metric-space analysis. Journal of Neurophysiology, 76, 1310–1326.
Victor, J. D., & Purpura, K. (1997). Metric-space analysis of spike trains: theory, algorithms, and application. Network, 8, 127–164.
Wark, B., Lundstrom, B. N., & Fairhall, A. (2007). Sensory adaptation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 17, 423–429.
Zeng, J., Powers, R. K., Newkirk, G., Yonkers, M., & Binder, M. D. (2005). Contribution of persistent sodium currents to spike-frequency adaptation in rat hypoglossal motoneurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 93, 1035–1041.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health: NS 26840 and NS 077863 (M.D.B.), NS 062200 (R.K.P), an Institutional Grant for Neurobiology T32 GM07108–35 (R.A.M.), and a Ruth L. Kirschstein Postdoctoral NRSA (A.T.M.); as well as the Burroughs-Wellcome Fund and the McKnight Endowment Fund for Neuroscience (A.L.F), and National Science Foundation grant EF0928251 (A.L.F. and S.L.). We would like to thank Paul Newman for expert technical assistance with the experimental portion of the work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: Mark van Rossum
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mease, R.A., Lee, S., Moritz, A.T. et al. Context-dependent coding in single neurons. J Comput Neurosci 37, 459–480 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-014-0513-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-014-0513-9