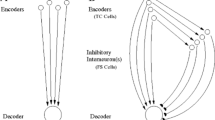
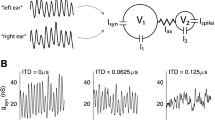
Abstract
While cells within barrel cortex respond primarily to deflections of their principal whisker (PW), they also exhibit responses to non-principal, or adjacent, whiskers (AWs), albeit responses with diminished amplitudes and longer latencies. The origin of multiwhisker receptive fields of barrel cells remains a point of controversy within the experimental literature, with three contending possibilities: (i) barrel cells inherit their AW responses from the AW responses of thalamocortical (TC) cells within their aligned barreloid; (ii) the axons of TC cells within a barreloid ramify to innervate multiple barrels, rather than only terminating within their aligned barrel; (iii) lateral intracortical transmission between barrels conveys AW responsivity to barrel cells. In this work, we develop a detailed, biologically plausible model of multiple barrels in order to examine possibility (iii); in order to isolate the dynamics that possibility (iii) entails, we incorporate lateral connections between barrels while assuming that TC cells respond only to their PW and that TC cell axons are confined to their home barrel. We show that our model is capable of capturing a broad swath of experimental observations on multiwhisker receptive field dynamics within barrels, and we compare and contrast the dynamics of this model with model dynamics from prior work in which employ a similar general modeling strategy to examine possibility (i).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agmon, A., Yang, L., Jones, E., & O’Dowd, D. (1995). Topological precision in the thalamic projection to neonatal mouse barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 15(1 Pt 2), 549–561.
Andermann, M., & Moore, C. (2006). A somatotopic map of vibrissa motion direction within a barrel column. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 543–551.
Armstrong-James, M., Fox, K., & Das-Gupta, A. (1992). Flow of excitation within rat barrel cortex on striking a single vibrissa. Journal of Neurophysiology, 68, 1345–1358.
Arnold, P., Li, C., & Waters, R. (2001). Thalamocortical arbors extend beyond single cortical barrels: an in vivo intracellular tracing study in rat. Experimental Brain Research, 136, 152–168.
Beaulieu, C. (1993). Numerical data on neocortical neurons in adult rat, with special reference to the gaba population. Brain Research, 609, 284–292.
Benowitz, L., & Karten, H. (2004). Organization of the tectofugal visual pathway in the pigeon: a retrograde transport study. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 167(4), 503–520.
Bernardo, K., & Woolsey, T. (1987). Axonal trajectories between mouse somatosensory thalamus and cortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 258, 542–564.
Blitz, D., & Regehr, W. (2005). Timing and specificity of feed-forward inhibition within the LGN. Neuron, 45, 917–928.
Brecht, M., & Sakmann, B. (2002). Dynamic representation of whisker deflection by synaptic potentials in spiny stellate and pyramidal cells in the barrels and septa of layer 4 rat somatosensory cortex. The Journal of Physiology, 543(Pt 1), 49–70.
Brecht, M., & Sakmann, B. (2002). Whisker maps of neuronal subclasses of the rat ventral posterior medial thalamus, identified by whole-cell voltage recording and morphological reconstruction. The Journal of Physiology, 538(Pt 2), 495–515.
Brumberg, J., Pinto, D., & Simons, D. (1996). Spatial gradients and inhibitory summation in the rat whisker barrel system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 76, 130–140.
Bruno, R. (2011). Synchrony in sensation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 21(5), 701–708.
Bruno, R., Khatri, V., Land, P., & Simons, D. (2003). Thalamocortical angular tuning domains within individual barrels of rat somatosensory cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 9565–9574.
Bruno, R., & Sakmann, B. (2006). Cortex is driven by weak but synchronously active thalamocortical synapses. Science, 312(5780), 1622–1627.
Bruno, R., & Simons, D. (2002). Feedforward mechanisms of excitatory and inhibitory cortical receptive fields. The Journal of Neuroscience, 22, 10966–10975.
Campagner, D., Evans, M., Loft, M., & Petersen, R. (2018). What the whiskers tell the brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 368, 95–108.
Cruikshank, S., Lewis, T., & Connors, B. (2007). Synaptic basis for intense thalamocortical activation of feedforward inhibitory cells in neocortex. Nature Neuroscience, 10, 462–468.
Deng, C., & Rogers, L. (1998). Organisation of the tectorotundal and SP/IPS-rotundal projections in the chick. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 394(2), 171–185.
Fox, K. (1994). The cortical component of experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in the rat barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 14, 7665–7679.
Fox, K. (2018). Deconstructing the cortical column in the barrel cortex. Neuroscience, 368, 17–28.
Fox, K., Wright, N., Wallace, H., & Glazewski, S. (2003). The origin of cortical surround receptive fields studied in the barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 8380–8391.
Fricker, D., & Miles, R. (2000). EPSP amplification and the precision of spike timing in hippocampal neurons. Neuron, 28, 559–569.
Furuta, T., Deschenes, M., & Kaneko, T. (2011). Anisotropic distribution of thalamocortical boutons in barrels. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 6432–6439.
Gabernet, L., Jadhav, S., Feldman, D., Carandini, M., & Scanzianiemail, M. (2005). Somatosensory integration controlled by dynamic thalamocortical feed-forward inhibition. Neuron, 48(2), 315–327.
Ghazanfar, A., & Nicolelis, M. (1997). Nonlinear processing of tactile information in the thalamocortical loop. Journal of Neurophysiology, 78, 506–510.
Goldreich, D., Kyriazi, H., & Simons, D. (1999). Functional independence of layer iv barrels in rodent somatosensory cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 82, 1311–1316.
Gottlieb, J., & Keller, A. (1997). Intrinsic circuitry and physiological properties of pyramidal neurons in rat barrel cortex. Experimental Brain Research, 115, 47–60.
Harris, R., & Woolsey, T. (1983). Computer-assisted analyses of barrel neuron axons and their putative synaptic contacts. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 220, 63–79.
Hemelt, M., Kwegyir-Afful, E., Bruno, R., Simons, D., & Keller, A. (2010). Consistency of angular tuning in the rat vibrissa system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104, 3105–3112.
Higley, M., & Contreras, D. (2007). Frequency adaptation modulates spatial integration of sensory responses in the rat whisker system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 97, 3819–3824.
Jensen, K., & Killackey, H. (1987). Terminal arbors of axons projecting to the somatosensory cortex of the adult rat. i. the normal morphology of specific thalamocortical afferents. Journal of Neuroscience 7, 3529–3543.
Jortner, R., Farivar, S., & Laurent, G. (2007). A simple connectivity scheme for sparse coding in an olfactory system. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 1659–1669.
Joshi, B., & Patel, M. (2013). Encoding with synchrony: phase-delayed inhibition allows for reliable and specific stimulus detection. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 328, 26–32.
Katz, Y., Heiss, J., & Lampl, I. (2006). Cross-whisker adaptation of neurons in the rat barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 13363–13372.
Kawaguchi, Y., & Kubota, Y. (1993). Correlation of physiological subgroupings of nonpyramidal cells with parvalbumin- and calbindind28k-immunoreactive neurons in layer v of rat frontal cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 70, 387–396.
Keller, A., & Carlson, G. (1999). Neonatal whisker clipping alters intracortical, but not thalamocortical projections, in rat barrel cortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 412, 93–94.
Kida, H., Shimegi, S., & Sato, H. (2005). Similarity of direction tuning among responses to stimulation of different whiskers in neurons of rat barrel cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 94, 2004–2018.
Kremer, Y., Leger, J., Goodman, D., Brette, R., & Bourdieu, L. (2011). Late emergence of the vibrissa direction selectivity map in the rat barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 10689–10700.
Kwegyir-Afful, E., Bruno, R., Simons, D., & Keller, A. (2005). The role of thalamic inputs in surround receptive fields of barrel neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 5926–5934.
Kyriazi, H., Carvell, G., Brumberg, J., & Simons, D. (1996). Quantitative effects of gaba and bicuculline methiodide on receptive field properties of neurons in real and simulated whisker barrels. Journal of Neurophysiology, 75, 547–560.
Kyriazi, H., & Simons, D. (1993). Thalamocortical response transformations in simulated whisker barrels. The Journal of Neuroscience, 13, 1601–1615.
Land, P., Buffer, S., & Yaskosky, J. (1995). Barreloids in adult rat thalamus: three dimensional architecture and relationship to somatosensory cortical barrels. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 355, 573–588.
Le Cam, J., Estebanez, L., Jacob, V., & Shulz, D. (2011). Spatial structure of multiwhisker receptive fields in the barrel cortex is stimulus dependent. Journal of Neurophysiology, 106, 986–998.
Lee, S., Friedberg, M., & Ebner, F. (1994). The role of gaba-mediated inhibition in the rat ventral posterior medial thalamus. i. assessment of receptive field changes following thalamic reticular nucleus lesions. Journal of Neurophysiology 71, 1702–1715.
Lee, S., & Simons, D. (2004). Angular tuning and velocity sensitivity in different neuron classes within layer 4 of rat barrel cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 91, 223–229.
Leitch, B., Laurent, G., et al. (1996). GABAergic synapses in the antennal lobe and mushroom body of the locust olfactory system. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 372, 487–514.
Liu, R., Patel, M., & Joshi, B. (2014). Encoding whisker deflection velocity within the rodent barrel cortex using phase-delayed inhibition. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 37, 387–401.
Lubke, J., Egger, V., Sakmann, B., & Feldmeyer, D. (2000). Columnar organization of dendrites and axons of single and synaptically coupled excitatory spiny neurons in layer 4 of the rat barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 5300–5311.
Mittmann, W., Koch, U., & Häusser, M. (2005). Feed-forward inhibition shapes the spike output of cerebellar purkinje cells. The Journal of Physiology, 563, 369–378.
Patel, M. (2018). Effects of adaptation on discrimination of whisker deflection velocity and angular direction in a model of the barrel cortex. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 12, 45–60.
Patel, M. (2018). Spiking and excitatory/inhibitory input dynamics of barrel cells in response to whisker deflections of varying velocity and angular direction. The Journal of Neuroscience, 369, 15–28.
Patel, M. (2019). Analysis of feedforward mechanisms of multiwhisker receptive field generation in a model of the rat barrel cortex. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 477, 51–62.
Patel, M., & Joshi, B. (2013). Decoding synchronized oscillations within the brain: phase-delayed inhibition provides a robust mechanism for creating a sharp synchrony filter. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 334, 13–25.
Patel, M., & Reed, M. (2013). Stimulus encoding within the barn owl optic tectum using gamma oscillations vs. spike rate: A modeling approach. Network: Computation in Neural Systems, 24, 2, 52–74.
Perez-Orive, J., Mazor, O., Turner, G., Cassenaer, S., Wilson, R., & Laurent, G. (2002). Oscillations and sparsening of odor representations in the mushroom body. Science, 297, 359–365.
Petersen, C. (2007). The functional organization of the barrel cortex. Neuron, 56(2), 339–355.
Petersen, C., & Sakmann, B. (2000). The excitatory neuronal network of rat layer 4 barrel cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 7579–7586.
Petersen, C., & Sakmann, B. (2001). Functionally independent columns of rat somatosensory barrel cortex revealed with voltage-sensitive dye imaging. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 8435–8446.
Pinto, D., Brumberg, J., & Simons, D. (2000). Circuit dynamics and coding strategies in rodent somatosensory cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 83(3), 1158–1166.
Pouille, F., & Scanziani, M. (2001). Enforcement of temporal fidelity in pyramidal cells by somatic feed-forward inhibition. Science, 293, 1159–1163.
Puccini, G., Compte, A., & Maravall, M. (2006). Stimulus dependence of barrel cortex directional selectivity. PLoS One, 1.
Roy, N., Bessaih, T., & Contreras, D. (2011). Comprehensive mapping of whisker-evoked responses reveals broad, sharply tuned thalamocortical input to layer 4 of barrel cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 105, 2421–2437.
Schubert, D., Kotter, R., & Staiger, J. (2007). Mapping functional connectivity in barrel-related columns reveals layer- and cell type-specific microcircuits. Brain Structure and Function, 212, 107–119.
Schubert, D., Kotter, R., Zilles, K., Luhmann, H., & Staiger, J. (2003). Cell type-specific circuits of cortical layer iv spiny neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 2961–2970.
Sharp, T., Petersen, R., & Furber, S. (2014). Real-time million-synapse simulation of rat barrel cortex. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 8, 1–9.
Shimegi, S., Ichikawa, T., Akasaki, T., & Sato, H. (1999). Temporal characteristics of response integration evoked by multiple whisker stimulations in the barrel cortex of rats. The Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 10164–10175.
Simons, D. (1985). Temporal and spatial integration in the rat si vibrissa cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 54, 615–635.
Simons, D., & Carvell, G. (1989). Thalamocortical response transformation in the rat vibrissa/barrel system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 61, 311–330.
Simons, D., & Woolsey, T. (1984). Morphology of golgi-cox impregnated barrel neurons in rat smi cortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 230, 119–132.
Sridharan, D., Boahen, K., & Knudsen, E. (2011). Space coding by gamma oscillations in the barn owl optic tectum. Journal of Neurophysiology, 105, 2005–2017.
Staiger, J., Loucif, A., Schubert, D., & Mock, M. (2016). Morphological characteristics of electrophysiologically characterized layer vb pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex. PLoS One, 11, 10.
Staiger, J., Zuschratter, W., Luhmann, H., & Schubert, D. (2009). Local circuits targeting parvalbumin-containing interneurons in layer iv of rat barrel cortex. Brain Structure and Function, 214, 1–13.
Sun, Q., Huguenard, J., & Prince, D. (2006). Barrel cortex microcircuits: Thalamocortical feedforward inhibition in spiny stellate cells is mediated by a small number of fast-spiking interneurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(4), 1219–1230.
Swadlow, H., & Gusev, A. (2002). Receptive-field construction in cortical inhibitory interneurons. Nature Neuroscience, 5, 403–404.
Tao, L., Shelley, M., McLaughlin, D., & Shapley, R. (2004). An egalitarian network model for the emergence of simple and complex cells in visual cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 366.
Temereanca, S., Brown, E., & Simons, D. (2008). Rapid changes in thalamic firing synchrony during repetitive whisker stimulation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 11153–11164.
Temereanca, S., & Simons, D. (2003). Local field potentials and the encoding of whisker deflections by population firing synchrony in thalamic barreloids. Journal of Neurophysiology, 89, 2137–2145.
Thomson, A., West, D., Wang, Y., & Bannister, A. (2002). Synaptic connections and small circuits involving excitatory and inhibitory neurons in layers 2–5 of adult rat and cat neocortex: triple intracellular recordings and biocytin labelling in vitro. Cerebral Cortex, 12, 936–953.
Timofeeva, E., Lavallee, P., Arsenault, D., & Deschenes, M. (2004). Synthesis of multiwhisker-receptive fields in subcortical stations of the vibrissa system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 91, 1510–1515.
Timofeeva, E., Merette, C., Emond, C., Lavallee, P., & Deschenes, M. (2003). A map of angular tuning preference in thalamic barreloids. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 10717–10723.
Wehr, M., & Zador, A. (2003). Balanced inhibition underlies tuning and sharpens spike timing in auditory cortex. Nature, 426, 442–446.
Welker, C., & Woolsey, T. (1974). Structure of layer iv in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat: description and comparison with the mouse. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 158, 437–453.
Wilent, W., & Contreras, D. (2005). Dynamics of excitation and inhibition underlying stimulus selectivity in rat somatosensory cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 8, 1364–1370.
Wilson, S., Law, J., Mitchinson, B., Prescott, T., & Bednar, J. (2010). Modeling the emergence of whisker direction maps in rat barrel cortex. PLoS One, 5.
Zhu, J., & Connors, B. (1999). Intrinsic firing patterns and whisker-evoked synaptic responses of neurons in the rat barrel cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 81, 1171–1183.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the College of William and Mary Department of Mathematics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Action Editor: Simon R Schultz
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Patel, M. A model of lateral interactions as the origin of multiwhisker receptive fields in rat barrel cortex. J Comput Neurosci 50, 181–201 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-021-00804-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-021-00804-6