Abstract
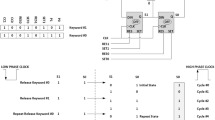
Phase shifters are used in conjunction with Linear Feedback Shift Registers and Cellular Automata in order to impose sufficient channel separations on the bit sequences produced by their successive cells. The aim is to reduce structural correlations and/or linear dependencies that are problematic for pseudorandom and pseudoexhaustive built-in test pattern generation (TPG). In this paper we present a synthesis approach that merges the logic of the original TPG mechanism with that of the required phase shifter network and yields a new compact structure that can offer lower area overhead and improved frequency of operation than the existing approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abramovici, M.A. Breuer, and A.D. Friedman, Digital Systems Testing and Testable Design, New York: Computer Science Press, 1990.
P.H. Bardell, “Calculating the Effects of Linear Dependencies in m–Sequences as Test Stimuli,” IEEE Transactions on CAD/ICAS, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 83–85, 1992.
P.H. Bardell, W.H. McAnney, and J. Savir, Built-in Test for VLSI, New York: Wiley, 1987.
C. Cattell and J.C. Muzio, “Synthesis of One-Dimensional Linear Hybrid Cellular Automata,” IEEE Transactions on CAD/ICAS, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 325–335, 1996.
D. Kagaris, “Built-in TPG with Designed Phaseshifts,” in IEEE VLSI Test Symposium, April 2003, pp. 365–370.
D. Kagaris, “A Unified Method for Phase Shifter Computation,” ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 157–167, 2005.
G. Mrugalski, J. Rajski, and J. Tyszer, “Comparative Study of CA-based PRPGs and LFSRs with Phase Shifters,” in Proc. VLSI Test Symp., 1999, pp. 236–245.
G. Mrugalski, J. Rajski, and J. Tyszer, “Cellular Automata–Based Test Pattern Generators with Phase Shifters,” IEEE Transactions on CAD/ICAS, vol. 19, no. 8, pp. 878–893, 2000.
J. Rajski, N. Tamarapalli, and J. Tyszer, “Automated Synthesis of Phase Shifters for Built-in Self-Test Applications,” IEEE Transactions on CAD/ICAS, vol. 19, no. 10, pp. 1175–1188, 2000.
H.S. Stone, Discrete Mathematical Structures and Their Applications, Science Research Associates, Chicago, IL, 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dimitri Kagaris received the Diploma degree in Computer Engineering and Informatics from the University of Patras, Greece, in 1988, and the M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in Computer Science from Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire, in 1991 and 1994, respectively. He is currently an Associate Professor in the Electrical & Computer Engineering Department, Southern Illinois University at Carbondale. His research interests include digital design automation, test pattern generation and design for testability, and computer networks.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kagaris, D. Phase Shifter Merging. J Electron Test 21, 161–168 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-005-6145-2
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-005-6145-2