Abstract
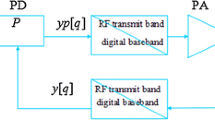
A comparison of test point selection methods using a linear matrix model based on the National Institute of Standard method and wavelet transform to reduce the number of test points, and hence, the test time, for a programmable gain amplifier (PGA) was investigated. The concept of integral nonlinearity (INL) was used to predict the performance of the PGA. It was found that the NIST method retained the original properties of the INL of the PGA. As such, the NIST method is able to predict the test responses of the PGA much more accurately than the wavelet transform method, using only 3 test points instead of the 155 test points as required in a full test.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodero V, Chiari A, Leduc Y, Pignatari C (1998) Test point selection using wavelet transform. presentation at Texas Instruments, Inc., Symposium on Test
Bohan P (1995) Modeling converter mismatch, superposition, and linearity errors. Teradyne Users Group, April
Burns M, Roberts GW (2001) An introduction to mixed-signal IC test and measurement. Oxford University Press, UK, p 260
Burns M, Roberts GW (2001) An introduction to mixed-signal IC test and measurement. Oxford University Press, UK, p 416
Carter C, Ang SS (2005) A test point selection method for data converters using Rademacher functions and Wavelet transforms. IEEE International Test Conference, paper 46.3, November 8–10, Austin
Halder A, Chatterjee A (2004) Automated test generation and test point selection for specification test of analog circuits. Quality Electronic Design, 2004 Proceedings. 5th International Symposium, pp 401–406
Kwak KC, Pedrycz W (2004) Face recognition using fuzzy integral and wavelet decomposition method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, Part B, Cybern 34(4), August
Shensa MJ (1992) The discrete wavelet transform: wedding the À trous and Mallat Algorithms. IEEE Trans Signal Process 40:2464–2482 Oct
Souders TM, Stenbakken GN (1990) A comprehensive approach for modeling and testing analog and mixed-signal device. Proceedings of the IEEE International Test conference, pp 169–174
Starzyk JA, Liu D, Liu ZH, Nelson DE, Rutkowski JO (2004) Entropy-based optimum test points selection for analog fault dictionary techniques. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 53(3):754–761 June
Young CA (1990) An enhanced method for characterizing successive approximation converters. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 39(2):335–339 April
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Texas Instruments, Inc., in the study of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: M. Sachdev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ang, S.S. & Carter, C. Comparison of NIST and Wavelet Transform Test Point Selection Methods For a Programmable Gain Amplifier. J Electron Test 24, 449–460 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-008-5070-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-008-5070-6