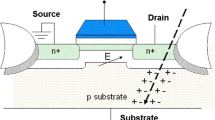
Abstract
This paper describes a tunable transient filter (TTF) design for soft error rate reduction in combinational logic circuits. TTFs can be inserted into combinational circuits to suppress propagated single-event transients (SETs) before they can be captured in latches or flip-flops. TTFs are tuned by adjusting the maximum width of the propagated SET that can be suppressed. A TTF requires 6–14 transistors, making it an attractive cost-effective option to reduce the soft error rate in combinational circuits. A global optimization approach based on geometric programming that integrates TTF insertion with dual-V DD and gate sizing is described. Simulation results for the 65 nm process technology indicate that a 17–48× reduction in the soft error rate can be achieved with this approach.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal V (1997) Low-power design by hazard filtering. In: Proc intl conference on VLSI design, Hyderabad, 4–7 January 1997, pp 193–197
Almukhaizim S, et al (2006) Seamless integration of SER in rewiring-based design space exploration. In: Proc intl test conference, Santa Clara, 24–26 October 2006
Baumann R (2004) Soft errors in advanced computer systems. IEEE Des Test Comput 22:258–266
Boyd S et al (2005) Digital circuit optimization via geometric programming. Oper Res 53:899–932
Boyd S et al (2007) A tutorial on geometric programming. Optim Eng 8:67–127
Cao Y et al (2000) New paradigm of predictive MOSFET and interconnect modeling for early circuit design. In: Proc custom integrated circuits conference, Orlando, 21–24 May 2000, pp 201–204
Cazeaux JM et al (2005) On transistor level gate sizing for increased robustness to transient faults. In: Proc intl on-line testing symposium, Saint Raphael, 6–8 July 2005, pp 23–28
Choudhury MR, Zhou Q, Mohanram K (2006) Design optimization for single-event upset robustness using simultaneous dual-V DD and sizing techniques. In: Proc intl conference computer-aided design, San Jose, 5–9 November 2006, pp 204–209
Deogun HS, Sylvester D, Blaauw D (2005) Gate-level mitigation techniques for neutron-induced soft error rate. In: Proc intl symposium on quality electronic design, San Jose, 21–23 March 2005, pp 175–180
Dhillon YS et al (2005) Load and logic co-optimization for design of soft-error resistant nanometer CMOS circuits. In: Proc intl on-line testing symposium, Saint Raphael, 6–8 July 2005, pp 35–40
Dodd PE, Massengill LW (2003) Basic mechanisms and modeling of single-event upset in digital microelectronics. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 50:583–602
Garg R et al (2006) A design approach for radiation-hard digital electronics. In: Proc design automation conference, Anaheim, 24–28 July 2006, pp 773–778
Gill BS et al (2005) Node sensitivity analysis for soft errors in CMOS logic. In: Proc intl test conference, pp 1–9
Hazucha P, Svensson C (2000) Impact of CMOS technology scaling on the atmospheric neutron soft error rate. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 47:2586–2594
Karnik T et al (2002) Selective node engineering for chip-level soft error rate improvement. In: Symp. on VLSI circuits digest of technical papers, pp 204–205
Krishnamohan S, Mahapatra NR (2005) Combining error masking and error detection plus recovery to combat soft errors in static CMOS circuits. In: Proc intl conference on dependable systems and networks, pp 40–49
Kumar J et al (2005) Use of pass transistor logic to minimize the impact of soft errors in combinational circuits. In: Proc of workshop on SELSE
Lawler EL, Wood DE (1966) Branch-and-bound methods: a survey. Oper Res 14:699–719
Lazzari C et al (2005) On implementing a soft error hardening technique by using an automatic layout generator: case study. In: Proc intl on-line testing symposium, pp. 29–34
Mavis DG, Eaton PH (2002) Soft error rate mitigation techniques for modern microcircuits. In: Proc intl reliability physics symposium, pp 216–225
Mitra S et al (2005) Robust system design with built-in soft error resilience. IEEE Comput 38:43–52
Mitra S et al (2006) Combinational logic soft error correction. In: Proc intl test conference, pp 1–9
Mohanram K, Touba NA (2003) Cost-effective approach for reducing soft error failure rate in logic circuits. In: Proc intl test conference, pp 893–901
MOSEK ApS (2008) MOSEK ApS homepage. http://www.mosek.com/
Nicolaidis M (1999) Time redundancy based soft-error tolerance to rescue nanometer technologies. In: Proc VLSI test symposium, pp 86–94
Omana M, Rossi D, Metra C (2007) Latch susceptibility to transient faults and new hardening approach. IEEE Trans Comput 56(9):1255–1268
Rao RR, Blaauw D, Sylvester D (2006) Soft error reduction in combinational logic using gate resizing and flip-flop selection. In: Proc intl conference computer-aided design, pp 502–509
Sapatnekar S (2004) Timing. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht
Sasaki Y et al (2008) Circuit and latch capable of masking soft errors with schmitt trigger. J Electron Test 1–3(24):11–19
Tang HHK, Rodbell KP (2003) Single-event upsets in microelectronics: fundamental physics and issues. Mater Res Soc Bull 28:111–116
Walstra SV, Dai C (2005) Circuit-level modeling of soft errors in integrated circuits. IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab 5:358–364
Wu K-C et al (2008) Soft error rate reduction using redundancy addition and removal. In: Proc Asia and South Pacific design automation conference, pp 559–564
Yang S (1991) Logic synthesis and optimization benchmarks user guide. Tech. rep. 1991-IWLS-UG-Saeyang, MCNC, Research Triangle Park
Zhou Q, Choudhury MR, Mohanram K (2008) Tunable transient filters for soft error rate reduction in combinational circuits. In: Proc European test symposium, pp 179–184
Zhou Q, Mohanram K (2004) Transistor sizing for radiation hardening. In: Proc intl reliability physics symposium, pp 310–315
Zhou Q, Mohanram K (2004) Cost-effective radiation hardening technique for logic circuits. In: Proc intl conference computer-aided design, pp 100–106
Zhou Q, Mohanram K (2006) Gate sizing to radiation harden combinational logic. IEEE Trans Comput-Aided Des 25:155–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: S. Hellebrand
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation CAREER Award CCF-0746850.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhury, M.R., Zhou, Q. & Mohanram, K. Soft Error Rate Reduction Using Circuit Optimization and Transient Filter Insertion. J Electron Test 25, 197–207 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-009-5103-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-009-5103-9