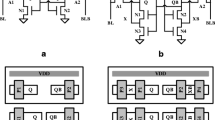
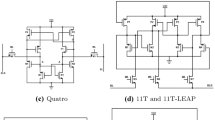
Abstract
This paper presents an SEU-resilient 12 T SRAM bitcell. Simulation results demonstrate that it has higher critical charge than the traditional 6 T cell. Alpha and proton testing results validate that it has a lower soft error rate compared to the reference designs for all data patterns and supply voltage levels. The improvement in SEU tolerance is achieved at the expense of 2X area penalty.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amusan OA, Witulski AF, Massengill LW, Bhuva BL, Fleming PR, Alles ML, Sternberg AL, Black JD, Schrimpf RD (2006) Charge collection and charge sharing in a 130 nm CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 53(6):3253–3258
Amusan OA, Massengill LW, Baze MP, Bhuva BL, Witulski AF, DasGupta S, Sternberg AL, Fleming PR, Heath CC, Alles ML (2007) Directional sensitivity of single event upsets in 90 nm CMOS due to charge sharing. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 6(54):2584–2589
Amusan OA, Massengill LW, Baze MP, Bhuva BL, Witulski AF, Black JD, Balasubramanian A, Casey MC, Black DA, Ahlbin JR, Reed RA, McCurdy MW (2009) Mitigation techniques for single-event-induced charge sharing in a 90-nm bulk CMOS process. IEEE Trans Device Mater Rel 9(2):311–317
Argyrides C, Chipana R, Vargas F, Pradhan DK (2011) Reliability analysis of H-tree random access memories implemented with built in current sensors and parity codes for multiple bit upset correction. IEEE Trans Reliab 60(3):528–537
Baeg S, Wen S, Wong R (2009) SRAM interleaving distance selection with a soft error failure model. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 56(4):2111–2118
Baumann RC (2005) Radiation-induced soft errors in advanced semiconductor technologies. IEEE Trans Device Mater Rel 5(3):305–316
Black JD, Sternberg AL, Alles ML, Witulski AF, Bhuva BL, Massengill LW, Benedetto JM, Baze MP, Wert JL, Hubert MG (2005) HBD layout isolation techniques for multiple node charge collection mitigation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 52(6):2536–2541
Blum DR, Delgado-Frias JG (2009) Delay and energy analysis of SEU and SET-tolerant pipeline latches and flip-flops. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 56(3):1618–1628
Calin T, Nicolaidis M, Velazco R (1996) Upset hardened memory design for submicron CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 43(6):2874–2878
Chen Q, Wu L, Li L, Ma X, Wang X-A (2015) Method for improving data security in register files based on multiple pipeline restart. Intern J Inform Technol Web Eng (IJITWE) 10(3):17–32
Dodd PE, Massengill LW (2003) Basic mechanisms and modeling of single-event upset in digital microelectronics. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 50(3):583–602
Dodd PE, Shaneyfelt MR, Felix JA, Schwank JR (2004) Production and propagation of single-event transients in high-speed digital logic ICs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 51(6):3278–3284
Giot D, Roche P, Gasiot G, Autran JL, Harboe-Sorensen R (2008) Heavy ion testing and 3-D simulations of multiple cell upset in 65 nm standard SRAMs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 55(4):2048
Jahinuzzaman SM, Rennie DJ, Sachdev M (2009) A soft error tolerant 10 T SRAM bit-cell with differential read capability. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 56(6):3768–3773
Li Y, Nelson B, Wirthlin M (2013) Reliability models for SEC/DED memory with scrubbing in FPGA-based designs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 60(4):2720–2727
Li L, Li Y, Wang H, Liu R, Wu Q, Newton M, Ma Y, Chen L (2015) Simulation and experimental evaluation of a soft error tolerant layout for SRAM 6 T bitcell in 65 nm technology. J Electron Test 31(5–6):561–568
Mavis DG, Eaton PH, Sibley MD, Lacoe RC, Smith EJ, Avery KA (2008) Multiple bit upsets and error mitigation in ultra-deep submicron SRAMs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 55(6):3288–3294
Ming Z, Yi X-L, Chang L, Wei Z-J (2011) Reliability of memories protected by multibit error correction codes against MBUs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 58(1):289–295
Nicolaidis M (2005) Design for soft error mitigation. IEEE Trans Device Mater Rel 5(3):405–418
Pontes J, Calazans N, Vivet P (2012) Adding temporal redundancy to delay insensitive codes to mitigate single event effects. In: Proceedings of 18th IEEE International Symposium on Asynchronous Circuits and Systems (ASYNC). IEEE, pp 142–149
Rajsuman R (2001) Design and test of large embedded memories: an overview. IEEE Des Test Comput 18(3):16–27
Reviriego P, Maestro JA, Cervantes C (2007) Reliability analysis of memories suffering multiple bit upsets. IEEE Trans Device Mater Rel 7(4):592–601
Saleh AM, Serrano JJ, Patel JH (1990) Reliability of scrubbing recovery-techniques for memory systems. IEEE Trans Reliab 39(1):114–122
Wang H-B, Li M-L, Chen L, Liu R, Baeg S, Wen S-J, Wong R, Fung R, Bi J-S (2014) Single event resilient dynamic logic designs. J Electron Test 30(6):751–761
Wu Q, Li Y, Chen L, He A, Guo G, Baeg SH, Wong R (2015) Supply voltage dependence of heavy ion induced SEEs on 65 nm CMOS bulk SRAMs. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 62(4):1898–1904
Acknowledgments
The University of Saskatchewan appreciates the support from Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and CMC Microsystems. This project is in part supported by NSFC under contract No. 61504038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V. D. Agrawal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Wang, H., Chen, L. et al. An SEU-Resilient SRAM Bitcell in 65-nm CMOS Technology. J Electron Test 32, 385–391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-016-5586-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-016-5586-0