Abstract
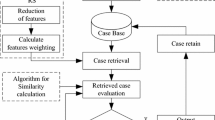
Case Based Reasoning (CBR) is a novel paradigm that uses previous cases to solve new, unseen and different problems. However, redundant features may not only dramatically increase the case memory, but also make the case retrieval more time-consuming. Furthermore, camshaft grinding process is controlled by a number of process parameters, and it is more complex comparing with the ordinary cylindrical grinding. The process conditions are achieved by skilled and professional workers. Therefore, this research combines Rough set (RS) and CBR for process conditions selection in camshaft grinding, and Genetic Algorithm (GA) is developed to discretize condition features. Through the approach an optimal subset of process conditions can be selected quickly and effectively from a large database with a lot of cases, and complexity of computation of the similarity testing is significantly reduced. Moreover, the validity of the proposed solution is verified by the application of practical experiments for the process conditions selection in camshaft grinding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamodt A., Plaza E. (1994) Case-based reasoning: foundational issues, methodological variations, and system approaches. AI Communications 7(1): 39–59
Brian Rowe W. (1996) Case-based reasoning for selection of grinding conditions. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems 9(4): 197–205
Cai R., Rowe W. B., Moruzzi J. L., Morgan M. N. (2007) Intelligent grinding assistant (IGA)—System development part i intelligent grinding database. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 35(1-2): 75–85
Chen G. (2007) Discretization method of continuous attributes in decision table based on genetic algorithm. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument 16(9): 1700–1705
Chen X., Rowe W. B., Allanson D. R., Mills B. (1999) A grinding power model for selection of dressing and grinding conditions. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, Transactions of the ASME 121(4): 632–637
Chiu C. C., Chang P. C., Chiu N. H. (2003) A case-based expert support system for due-date assignment in a wafer fabrication factory. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 14(3-4): 287–296
Choi T., Shin Y. C. (2007) Generalized intelligent grinding advisory system. International Journal of Production Research 45(8): 1899–1932
Deng Z. H., Zhang X. H., Liu W., Cao H. (2009) A hybrid model using genetic algorithm and neural network for process parameters optimization in NC camshaft grinding. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 45(9-10): 859–866
Finnie G., Sun Z. (2003) R5 model for case-based reasoning. Knowledge-Based Systems 16(1): 59–65
Geng Z., Zhu Q. (2009) Rough set-based heuristic hybrid recognizer and its application in fault diagnosis. Expert Systems with Applications 36(2 PART 2): 2711–2718
Gopal A. V., Venkateswara Rao P. (2003) Selection of optimum conditions for maximum material removal rate with surface finish and damage as constraints in SiC grinding. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 43(13): 1327–1336
Gopala Krishna A. (2007) Selection of optimal conditions in the surface grinding process using a differential evolution approach. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 221(7): 1185–1192
Gutiérrez Martínez I., Bello Pérez R. E. (2003) Making decision in case-based systems using probabilities and rough sets. Knowledge-Based Systems 16(4): 205–213
Huang C. C., Tseng T. L. (2004) Rough set approach to case-based reasoning application. Expert Systems with Applications 26(3): 369–385
Jiang Y. J., Chen J., Ruan X. Y. (2006) Fuzzy similarity-based rough set method for case-based reasoning and its application in tool selection. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 46(2): 107–113
Kwong C. K., Smith G. F., Lau W. S. (1997) Application of case based reasoning in injection moulding. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 63(1-3): 463–467
Li Y., Rowe W. B., Chen X., Mills B. (1999) Study and selection of grinding conditions. Part 2: A hybrid intelligent system for selection of grinding conditions. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 213(2): 131–142
Lin R. H., Wang Y. T., Wu C. H., Chuang C. L. (2009) Developing a business failure prediction model via RST, GRA and CBR. Expert Systems with Applications 36(2 PART 1): 1593–1600
Li J. R., Khoo L. P., Tor S. B. (2006a) A rough set based data mining prototype for the reasoning of incomplete data in condition-based fault diagnosis. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 17(1): 163–176
Li Y., Shiu S. C. K., Pal S. K., Liu J. N. K. (2006b) A rough set-based case-based reasoner for text categorization. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 41(2): 229–255
Louhi-kultanen M., Kraslawski A., Avramenko Y. (2009) Case-based reasoning for crystallizer selection using rough sets and fuzzy sets analysis. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification 48(7): 1193–1198
Nagano T., Shirase K., Wakamatsu H., Arai E. (2001) Expert system based on case-based reasoning to select cutting conditions. Seimitsu Kogaku Kaishi/Journal of the Japan Society for Precision Engineering 67(9): 1485–1489
Pawlak Z. (2002) Rough sets and intelligent data analysis. Information Sciences 147(1-4): 1–12
Riesbeck C. K., Schank R. C. (1989) Inside case-based reasoning. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillside, NJ
Sedighi M., Afshari D. (2010) Creep feed grinding optimization by an integrated GA-NN system. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 21(6): 657–663
Shin K. S., Han I. (1999) Case-based reasoning supported by genetic algorithms for corporate bond rating. Expert Systems with Applications 16(2): 85–95
Tong K. W., Kwong C. K., Chan C. Y. (2001) Initial process-parameters setting of transfer moulding in microchip encapsulation: A case-based reasoning approach. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 113(1-3): 432–438
Tsai C. Y., Chiu C. C. (2007) A case-based reasoning system for PCB principal process parameter identification. Expert Systems with Applications 32(4): 1183–1193
Watson I. (1999) Case-based reasoning is a methodology not a technology. Knowledge-Based Systems 12(5-6): 303–308
Yang S.Y., Tansel I.N., Kropas-Hughes C.V. (2003) Selection of optimal material and operating conditions in composite manufacturing. Part I: Computational tool. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 43(2): 169–173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.H., Deng, Z.H., Liu, W. et al. Combining rough set and case based reasoning for process conditions selection in camshaft grinding. J Intell Manuf 24, 211–224 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-011-0557-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-011-0557-x