Abstract
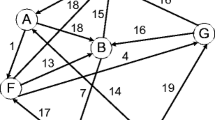
In this paper, a hierarchical multi-agent based routing has been introduced. In dynamic situations, the previously planned entire optimum path may not stay optimum over time. Thus the approach in this paper routes a job to the next optimum neighboring node from the current position, instead of deciding over the entire path before the journey begins. Whenever there is a need to choose the next optimum node for routing or whenever a job enters the system, the master agent calls the worker agents. The worker agents run in parallel and return the results to the master agent. The worker agents are killed after their tasks are completed. The master agent takes decision based on the data delivered by the worker agents through a multi-criteria decision analysis technique known as PROMETHEE. A total of five worker agents are used for seven criteria and fuzzy approach is applied in a fuzzy shortest path algorithm performed by a worker agent and in fuzzy weight calculation in PROMETHEE. Three examples with three different kinds of networks have been used to show the effectiveness of the entire approach. The motivation of the idea introduced in this paper has come from the mating behavior of a spider known as Tarantula where the female spider sometimes eats the male spider just after mating.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aissani, N., Bekrar, A., Trentesaux, D., & Beldjilali, B. (2012). Dynamic scheduling for multi-site companies: A decisional approach based on reinforcement multi-agent learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(6), 2513–2529.
Al-Mutawah, K., Lee, V., & Cheung, Y. (2009). A new multi-agent system framework for tacit knowledge management in manufacturing supply chains. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 20(5), 593–610.
Anand, N., Yang, M., van Duin, J. H. R., & Tavasszy, L. (2012). GenCLOn: An ontology for city logistics. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(15), 11944–11960.
Asadzadeh, L., & Zamanifar, K. (2010). An agent-based parallel approach for the job shop scheduling problem with genetic algorithms. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 52(11–12), 1957–1965.
Bahrammirzaee, A., Chohra, A., & Madani, K. (2011). An artificial negotiating agent modeling approach embedding dynamic offer generating and cognitive layer. Neurocomputing, 74(16), 2698–2709.
Barbucha, D. (2012). Agent-based guided local search. Expert Systems with Applications. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2012.03.074.
Brans, J.-P., & Mareschal, B. (2005). Multiple criteria decision analysis: State of the art surveys. In F. José, G. Salvatore, & E. Matthias (Eds.), PROMETHEE method (pp. 200–232). Boston: Springer.
Bresciani, P., Giorgini, P., Giunchiglia, F., Mylopoulos, J., & Perini, A. (2004). Tropos: An agent-oriented software development methodology. Journal of Autonomous Agents and Software Development Methodologies, 8, 203–236.
Burrafato, P., & Cossentino, M. (2002). Designing a multi-agent solution for a bookstore with the PASSI methodology. In Proceedings of the fourth international bi-conference workshop on agent-oriented information systems (AOIS-2002), Toronto, 2002. http://mozart.csai.unipa.it/passi/.
Chen, B., Cheng Harry, H., & Palen, J. (2009). Integrating mobile agent technology with multi-agent systems for distributed traffic detection and management systems. Transportation Research Part C, 17(1), 1–10.
Cheshmehgaz, H. R., Desa, M. I., & Wibowo, A. (2011). A flexible three-level logistic network design considering cost and time criteria with a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0584-7.
Chirn, J., & McFarlane, D. (2000). A component-based approach to the holonic control of a robot assembly cell. In Proceedings of the IEEE 17th international conference on robotics and automation, ICRA 2000.
Choi, H. S., & Park, K. H. (1997). Shop-floor scheduling at shipbuilding yards using the multiple intelligent agent system. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 8(6), 505–515.
Coleman, D., Arnold, P., Bodoff, S., Gilchrist, H., Hayes, F., & Jeremaes, P. (1994). Object-oriented development: The FUSION method. Hemel Hempstead: Prentice Hall.
Demircan, S., Aydin, M., & Durduran, S. S. (2011). Finding optimum route of electrical energy transmission line using multi-criteria with Q-learning. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), 3477–3482.
Deng, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., & Mahadevan, S. (2012). Fuzzy Dijkstra algorithm for shortest path problem under uncertain environment. Applied Soft Computing, 12(3), 1231–1237.
Eltarras, R., & Eltoweissy, M. (2011). Associative routing for wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 34(18), 2162–2173.
Figueira, J., Greco, S., & Ehrgott, M. (Eds.). (2005). Multiple criteria decision analysis: State of the art surveys. Boston: Springer.
Gao, L., & Hailu, A. (2012). Ranking management strategies with complex outcomes: An AHP-fuzzy evaluation of recreational fishing using an integrated agent-based model of a coral reef ecosystem. Environmental Modelling & Software, 31, 3–18.
Geoff, B., Stephen, C., & Martin, P. (2001). The Styx agent methodology. The Information Science Discussion Paper Series 2001/02, Department of Information Science, University of Otago, New Zealand, 2001. http://divcom.otago.ac.nz/infosci.
Gómez-Gasquet, P., Andrés, C., & Lario, F.-C. (2012). An agent-based genetic algorithm for hybrid flowshops with sequence dependent setup times to minimise makespan. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(9), 8095–8107.
Hassanein, H., & Zhou, A. (2003). Load-aware destination-controlled routing for MANETs. Computer Communications, 26(14), 1551–1559.
Holmgren, J., Davidsson, P., & Ramstedt, L. (2012). TAPAS: A multi-agent-based model for simulation of transport chains. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 23, 1–18.
Hsieh, F.-S. (2010). Design of reconfiguration mechanism for holonic manufacturing systems based on formal models. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 23(7), 1187–1199.
Ilie, S, & Bădică, C. (2011). Multi-agent approach to distributed ant colony optimization. Science of Computer Programming. doi:10.1016/j.scico.2011.09.001.
Jennings, N. R., Corera, J., Laresgoiti, I., Mamdani, E. H., Perriolat, F., Skarek, P., et al. (1996a). Varga. Using ARCHON to develop real-world DAI applications for electricity transportation management and particle acceleration control. IEEE Expert, 11(6), 60–88.
Jennings, N. R., Faratin, P., Johnson, M. J., Norman, T. J., O’Brien, P., Wiegand, M., et al. (1996b). Agent-based business process management. International Journal of Cooperative Information Systems, 5(2–3), 105–130.
Juan, T., Pearce, A., & Sterling, L. (2002). ROADMAP: Extending the Gaia methodology for complex open systems. In M. Gini, T. Ishida, C. Castelfranchi, & W. L. Johnson (Eds.), Proceedings of the first international joint conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems (AAMAS’02) (pp. 3–10). ACM Press, 2002.
Kanaga, E. G. M., & Valarmathi, M. L. (2012). Multi-agent based patient scheduling using particle swarm optimization. Procedia Engineering, 30, 386–393.
Kim, H. S., & Cho, J. H. (2010). Supply chain formation using agent negotiation. Decision Support Systems, 49(1), 77–90.
Kouiss, K., Pierreval, H., & Mebarki, N. (1997). Using multi-agent architecture in FMS for dynamic scheduling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 8(1), 41–47.
Lee, W.-C., Chen, S-k, & Wu, C.-C. (2010). Branch-and-bound and simulated annealing algorithms for a two-agent scheduling problem. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(9), 6594–6601.
Lee, Y. H., Kumara, S. R. T., & Chatterjee, K. (2003). Multi-agent-based dynamic resource scheduling for distributed multiple projects using a market mechanism. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 14(5), 471–484.
Leitaõ, P., Colombo, A., & Restivo, F. (2005). ADACOR: A collaborative production automation and control architecture. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 20(1), 58–66.
Leung, C. W., Wong, T. N., Mak, K. L., & Fung, R. Y. K. (2010). Integrated process planning and scheduling by an agent-based ant colony optimization. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 59(1), 166–180.
Li, C., & Li, L. (2007). Utility-based QoS optimisation strategy for multi-criteria scheduling on the grid. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 67(2), 142–153.
Li, G., & Shi, J. (2012). Agent-based modeling for trading wind power with uncertainty in the day-ahead wholesale electricity markets of single-sided auctions. Applied Energy, 99, 13–22.
Li, X., Gao, L., & Shao, X. (2012). Anactive learning genetic algorithm for integrated process planning and scheduling. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(8), 6683–6691.
Lin, L., Hao, X.-C., Gen, M., & Jo, J.-B. (2012a). Network modeling and evolutionary optimization for scheduling in manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Mnaufacturing, 23(6), 2237–2253.
Lin, Y.-I., Chou, Y.-W., Shiau, J.-Y., & Chu, C.-H. (2011). Multi-agent negotiation based on price schedules algorithm for distributed collaborative design. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0609-2.
Lin, Y.-I., Tien, K.-W., & Chu, C.-H. (2012b). Multi-agent hierarchical negotiation based on augmented price schedules decomposition for distributed design. Computers in Industry, 63(6), 597–609.
López-Ortega, O., & Villar-Medina, I. (2009). A multi-agent system to construct production orders by employing an expert system and a neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(2), 2937–2946.
Mahdjoub, M., Monticolo, D., Gomes, S., & Sagot, J.-C. (2010). A collaborative design for usability approach supported by virtual reality and a multi-agent system embedded in a PLM environment. Computer-Aided Design, 42(5), 402–413.
Maione, G., & Naso, D. (2003). A soft computing approach for task contracting in multi-agent manufacturing control. Computers in Industry, 52(3), 199–219.
Mikler Armin, R., Honavar, V., & Wong, J. S. K. (2001). Autonomous agents for coordinated distributed parameterized heuristic routing in large dynamic communication networks. The Journal of Systems and Software, 56, 231–246.
Miyashita, K. (1998). CAMPS: A constraint-based architecture for multiagent planning and scheduling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 9(2), 147–154.
Padgham, L., & Winikoff, M. (2004). Developing intelligent agent systems—A practical guide. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-470-86120-7.
Shao, X., Li, X., Gao, L., & Zhang, C. (2009). Integration of process planning and scheduling-Amodified genetic algorithm-based approach. Computers & Operations Research, 36(6), 2082–2096.
Shen, W., Maturana, F., & Norrie, D. H. (2000). Enhancing the performance of an agent-based manufacturing system through learning and forecasting. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 11(4), 365–380.
Shi, X., & Qian, F. (2011). A multi-agent immune network algorithm and its application to murphree efficiency determination for the distillation column. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 8(2), 181–190.
Sinha, A. K., Aditya, H. K., Tiwari, M. K., & Chan, F. T. S. (2011). Agent oriented petroleum supply chain coordination: Co-evolutionary Particle Swarm Optimization based approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(5), 6132–6145.
Soroor, J., Tarokh, M. J., Khoshalhan, F., & Sajjadi, S. (2012). Intelligent evaluation of supplier bids using a hybrid technique in distributed supply chains. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 31(2), 240–252.
Su, C. J. (2008). Mobile multi-agent based, distributed information platform (MADIP) for wide-area e-health monitoring. Computers in Industry, 59(1), 55–68.
Trappey, C. V., Trappey, A. J. C., Huang, C.-J., & Ku, C. C. (2009). The design of a JADE-based autonomous workflow management system for collaborative SoC design. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(2), 2659–2669.
Van Brussel, H., Wyns, J., Valckenaers, P., & Bongaerts, L. (1998). Reference architecture for holonic manufacturing systems: PROSA. Computers in Industry, 37(3), 255–274.
Vasudevan, K., & Son, Y.-J. (2011). Concurrent consideration of evacuation safety and productivity in manufacturing facility planning using multi-paradigm simulations. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 61(4), 1135–1148.
Wang, L., Tang, D.-B., Gu, W.-B., Zheng, K., Yuan, W.-D., & Tang, D.-S. (2012). Pheromone-based coordination for manufacturing system control. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(3), 747–757.
Wooldridge, M., Jennings, N. R., & Kinny, D. (2000). The Gaia methodology for agent-oriented analysis and design. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 3(3), 285–312.
Zhao, J., Mazhari, E., Celik, N., & Son, Y.-J. (2011). Hybrid agent-based simulation for policy evaluation of solar power generation systems. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 19, 2189–2205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandyopadhyay, S., Bhattacharya, R. Finding optimum neighbor for routing based on multi-criteria, multi-agent and fuzzy approach. J Intell Manuf 26, 25–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0758-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0758-6