Abstract
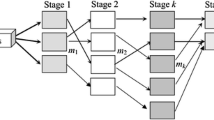
This paper addresses the scheduling problem for a multi-stage hybrid flow shop (HFS) with single processing machines and batch processing machines. Each stage consists of nonidentical machines in parallel, and only one of the stages is composed of batch processing machines. Such a variant of the HFS problem is derived from the actual manufacturing of complex products in the equipment manufacturing industry. Aiming at minimizing the maximum completion time and minimizing the total weighted tardiness, respectively, a heuristic-search genetic algorithm (HSGA) is developed in this paper, which selects assignment rules for parts, sequencing rules for machines (including single processing machines and batch processing machines), and batch formation rules for batch processing machines, simultaneously. Then parts and machines are scheduled using the obtained combinatorial heuristic rules. Since the search space composed of the heuristic rules is much smaller than that composed of the schedules, the HSGA results in lower complexity and higher computational efficiency. Computational results indicate that as compared with meta-heuristics that search for scheduling solutions directly, the HSGA has a significant advantage with respect to the computational efficiency. As compared with combinatorial heuristic rules, other heuristic-search approaches, and the CPLEX, the HSGA provides better optimizational performance and is especially suitable to solve large dimension scheduling problems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allahverdi, A., Ng, C. T., Cheng, T. C. E., & Kovalyov, M. Y. (2008). A survey of scheduling problems with setup times or costs. European Journal Of Operational Research, 187(3), 985–1032.
Barman, S. (1997). Simple priority rule combinations: An approach to improve both flow time and tardiness. International Journal of Production Research, 35(10), 2857–2870.
Behnamian, J., Ghomi, S. M. T. F., Jolai, F., & Amirtaheri, O. (2012). Realistic two-stage flowshop batch scheduling problems with transportation capacity and times. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 36(2), 723–735.
Damodaran, P., Rao, A. G., & Mestry, S. (2013). Particle swarm optimization for scheduling batch processing machines in a permutation flowshop. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 64(5–8), 989–1000.
Dorndorf, U., & Pesch, E. (1995). Evolution based learning in a job-shop scheduling environment. Computers & Operations Research, 22(1), 25–40.
Fayad, C., & Petrovic, S. (2005). A fuzzy genetic algorithm for real-world job shop scheduling. Innovations in Applied Artificial Intelligence, 3533, 524–533.
Feng, H. D., Lu, S. P., & Li, X. Q. (2009). Genetic algorithm for hybrid flow-shop scheduling with parrel batch processors. In 2009 Wase international conference on information engineering, Icie 2009, Vol Ii, 9–13.
Hu, H., & Li, Z. (2009). Modeling and scheduling for manufacturing grid workflows using timed Petri nets. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 42(5–6), 553–568.
Kim, Y. D., Joo, B. J., & Shin, J. H. (2009). Heuristics for a two-stage hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with ready times and a product-mix ratio constraint. Journal of Heuristics, 15(1), 19–42.
Laforge, R. L., & Barman, S. (1989). Performance of simple priority rule combinations in a flow dominant shop. Production & Inventory Management Journal, 30(3), 1–4.
Liu, Y., & Karimi, I. A. (2008). Scheduling multistage batch plants with parallel units and no interstage storage. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 32(4–5), 671–693.
Luo, H., Huang, G. Q., Zhang, Y. F., & Dai, Q. Y. (2011). Hybrid flowshop scheduling with batch-discrete processors and machine maintenance in time windows. International Journal of Production Research, 49(6), 1575–1603.
Mathirajan, M., Bhargav, V., & Ramachandran, V. (2010). Minimizing total weighted tardiness on a batch-processing machine with non-agreeable release times and due dates. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 48(9–12), 1133–1148.
Mirsanei, H. S., Zandieh, M., Moayed, M. J., & Khabbazi, M. R. (2011). A simulated annealing algorithm approach to hybrid flow shop scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22(6), 965–978.
Montgomery, D. C. (2000). Design and analysis of experiments (5th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Park, S. C., Raman, N., & Shaw, M. J. (1997). Adaptive scheduling in dynamic flexible manufacturing systems: A dynamic rule selection approach. Ieee Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 13(4), 486–502.
Ponnambalam, S. G., Ramkumar, V., & Jawahar, N. (2001). A multiobjective genetic algorithm for job shop scheduling. Production Planning & Control, 12(8), 764–774.
Potts, C. N., & Kovalyov, M. Y. (2000). Scheduling with batching: A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 120(2), 228–249.
Rossi, A., & Dini, G. (2007). Flexible job-shop scheduling with routing flexibility and separable setup times using ant colony optimisation method. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 23(5), 503–516.
Ruiz, R., & Maroto, C. (2006). A genetic algorithm for hybrid flowshops with sequence dependent setup times and machine eligibility. European Journal of Operational Research, 169(3), 781–800.
Ruiz, R., Serifoglu, F. S., & Urlings, T. (2008). Modeling realistic hybrid flexible flowshop scheduling problems. Computers & Operations Research, 35(4), 1151–1175.
Ruiz, R., & Vazquez-Rodriguez, J. A. (2010). The hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. European Journal Of Operational Research, 205(1), 1–18.
Sarper, H., & Henry, M. C. (1996). Combinatorial evaluation of six dispatching rules in a dynamic two-machine flow shop. Omega, 24(1), 73–81.
Su, L. H., & Chen, J. C. (2010). Sequencing two-stage flowshop with nonidentical job sizes. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 47(1–4), 259–268.
Sung, C. S., Kim, Y. H., & Yoon, S. H. (2000). A problem reduction and decomposition approach for scheduling for a flowshop of batch processing machines. European Journal of Operational Research, 121(1), 179–192.
Vazquez-Rodriguez, J. A., & Petrovic, S. (2010). A new dispatching rule based genetic algorithm for the multi-objective job shop problem. Journal of Heuristics, 16(6), 771–793.
Wang, I. L., Yang, T. H., & Chang, Y. B. (2012). Scheduling two-stage hybrid flow shops with parallel batch, release time, and machine eligibility constraints. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(6), 2271–2280.
Yang, T., Kuo, Y., & Cho, C. (2007). A genetic algorithms simulation approach for the multi-attribute combinatorial dispatching decision problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 176(3), 1859–1873.
Yao, F. S., Zhao, M., & Zhang, H. (2012). Two-stage hybrid flow shop scheduling with dynamic job arrivals. Computers & Operations Research, 39(7), 1701–1712.
Zandieh, M., Mozaffari, E., & Gholami, M. (2010). A robust genetic algorithm for scheduling realistic hybrid flexible flow line problems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 21(6), 731–743.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (4122069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Meng, X., Liang, Q. et al. A heuristic-search genetic algorithm for multi-stage hybrid flow shop scheduling with single processing machines and batch processing machines. J Intell Manuf 26, 873–890 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0874-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0874-y