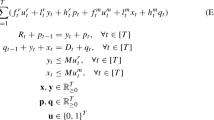Abstract
In the general lot-sizing replenishment problem, warehousing costs are considered as part of the inventory holding cost. When decision makers need warehouse space to store their products, they generally think about the warehousing cost as included in the inventory cost. In this study, we investigate an optimal lot-sizing and replenishment problem under a piecewise linear warehousing cost structure. Theoretical analysis of the optimality structure of a model of multiple stock-keeping units with joint inventory costs is conducted, and an effective search algorithm is proposed. Based on our random experiments, we demonstrate that our search algorithm outperforms the approach that the existing literature offers as solution.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballou, H. R. (1992). Business logistics management: Planning and control (3rd ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Benyoucef, L., & Tiwari, M. K. (2012). Editorial note for the special issue on ‘Advanced metaheuristics for integrated supply chain management’. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23, 1079–1082.
Chan, F. T. S., & Kumar, V. (2009). A hybrid TSSA algorithm based approach to solve warehouse scheduling problems. International Journal of Production Research, 47(4), 919–940.
Chu, C. L., & Leon, V. J. (2008). Power-of-two single-warehouse multi-buyer inventory coordination with private information. International Journal of Production Economics, 111(2), 562–574.
Cormier, C., & Gunn, E. A. (1992). A review of warehouse models. European Journal of Operational Research, 58(1), 149–154.
Cormier, C., & Gunn, E. A. (1996). Simple models and insights for warehouse sizing. Journal of Operational Research Society, 47(5), 690–696.
Cormier, G., & Gunn, E. A. (1999). Modeling and analysis for capacity expansion planning in warehousing. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 50(1), 52–59.
Goh, M., Ou, J., & Teo, C. P. (2001). Warehouse sizing to minimize inventory and storage costs. Naval Res Logistics, 48(4), 299–312.
Gu, J., Goetschalckx, M., & McGinnis, L. F. (2010). Research on warehouse design and performance evaluation: A comprehensive review. European Journal of Operational Research, 203(3), 539–549.
Huang, J. Y., & Yao, M. J. (2008). On the coordination of maintenance scheduling for transportation fleets of many branches of a logistic service provider. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 56(5), 1303–1313.
Huang, J. Y., & Yao, M. J. (2013). On the optimal lot-sizing and scheduling problem in serial-type supply chain system using a time-varying lot-sizing policy. International Journal of Production Research., 51(3), 735–750.
Ito, T., & Abadi, S. (2002). Agent-based material handling and inventory planing in warehouse. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 13(3), 201–210.
Lee, F. C., & Yao, M. J. (2003). A global optimum search algorithm for the joint replenishment problem under power-of-two policy. Computers and Operations Research, 30(9), 1319–1333.
Mason, S. J., Ribera, P. M., Farris, J. A., & Kirk, R. G. (2003). Integrating the warehousing and transportation functions of the supply chain. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 39(2), 141–159.
Minner, S. (2009). A comparison of simple heuristics for multi-product dynamic demand lot-sizing with limited warehouse capacity. International Journal of Production Economics, 118(1), 305–310.
Petinisa, V. V., Tarantilis, C. D., & Kiranoudisa, C. T. (2005). Warehouse sizing and inventory scheduling for multiple stock-keeping products. International Journal of Systems Science, 36(1), 39–47.
Rao, A. K., & Rao, M. R. (1998). Solution procedures for sizing of warehouse. European Journal Operational Research, 108(1), 16–25.
Sainathuni, B., Parikh, P. J., Zhanga, X., & Kong, N. (2014). The warehouse–inventory–transportation problem for supply chains. European Journal of Operational Research, 237(2), 690–700.
Skintzi, G., Ioannou, G., & Prastacos, G. (2008). Investigating warehousing policies. International Journal of Production Economics, 112(2), 955–970.
Wang, S. P., & Lee, W. (2013). A joint economic lot-sizing model for the hospital’s supplier with capacitated warehouse constraint. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 30(3), 202–210.
White, J. A., & Francis, R. L. (1971). Normative models for some warehouse sizing problems. AIIE Transactions, 3(3), 185–190.
Yao, M. J. (2007). Solving the joint replenishment problem with warehouse-space restrictions using a genetic algorithm. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Industrial Engineers, 24(2), 128–141.
Yao, M. J., & Chu, W. M. (2008). A genetic algorithm for determining optimal replenishment cycles to minimize maximum warehouse space. Omega: The International Journal of Management Sciences, 36(4), 619–631.
Yao, M. J., Chu, W. M., & Lin, Y. F. (2008). Determination of replenishment dates for restricted-storage, static demand, cyclic replenishment schedule. Computers and Operations Research, 35(10), 3230–3242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, MJ., Huang, JY. Optimal lot-sizing and joint replenishment strategy under a piecewise linear warehousing cost structure. J Intell Manuf 28, 791–803 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-1027-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-1027-z