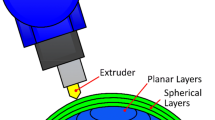
Abstract
AM, generally known as 3D printing, is a promising technology. Robotic AM enables the direct fabrication of products possessing complex geometry and high performance without extra support structures. Process planning of slicing and tool path generation has been a challenging issue due to geometric complexity, material property, etc. Simple and robust planar slicing has been widely researched and applied. However, support structures usually result in time-consuming and cost-expensive. Notwithstanding multi-direction slicing and non-planar slicing (curved layer slicing) have been proposed respectively to decrease support structures, capture some minute but critical features and improve the surface quality and part strength. There is no slicing method aiming at features of part’s sub-volumes. A comprehensive literature review is given first to illustrate the problems and features of available slicing methods better. Then, in order to combine the merits of planar and non-planar slicing to realize intelligent manufacturing further, this paper reports the concept and implementation of a mixed-layer adaptive slicing method for robotic AM. Different from applying planar slicing in any cases or adopting the decomposing and regrouping based multi-direction planar slicing for finding the optimal slicing directions, the proposed method mainly focuses on how to apply planar and non-planar slicing for each sub-volume according to the geometrical features. Additionally, the requirements for robotic AM equipment in possessing multi-mode of printing and slicing are investigated.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AM:
-
Additive Manufacturing
- ADfAM:
-
Advanced design for Additive Manufacturing
- BSP:
-
Binary Space Partitioning
- CAM:
-
Computer-aided manufacturing
- CLAS:
-
Curved layer adaptive slicing
- CLFD:
-
Curved layer fused deposition
- CLFDM:
-
Curved layer fused deposition modeling
- CLFFF:
-
Curved layer fused filament fabrication
- DOF:
-
Degree of Freedom
- EL:
-
Extruder location
- FDM:
-
Fused Deposition Modelling
- FT:
-
Filament target
- FVCP:
-
Four Vector Cross Product
- LOM:
-
Laminated Object Manufacturing
- MFR:
-
Manufacturing feature recognition
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis
- RSS:
-
Reference Slicing Surface
- SFF:
-
Solid Freeform Fabrication
- SM:
-
Subtractive Manufacturing
- WAAM:
-
Welding Arc Additive Manufacturing
References
Allen, R. J., & Trask, R. S. (2015). An experimental demonstration of effective Curved Layer Fused Filament Fabrication utilising a parallel deposition robot. Additive Manufacturing, 8, 78–87.
Campana, G., & Mele, M. (2018). An application to Stereolithography of a feature recognition algorithm for manufacturability evaluation. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1441-8.
Chakraborty, D., Aneesh Reddy, B., & Roy Choudhury, A. (2008). Extruder path generation for curved layer fused deposition modeling. Computer-Aided Design,40(2), 235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2007.10.014.
Chan, C. K., & Tan, S. T. (2005). Volume decomposition of CAD models for rapid prototyping technology. Rapid Prototyping Journal,11(4), 221–234. https://doi.org/10.1108/13552540510612910.
Diegel, O., Singamneni, S., Huang, B., & Gibson, I. (2011). Getting rid of the wires: Curved layer fused deposition modeling in conductive polymer additive manufacturing. In D. Zeng (Ed.), Key engineering materials (Vol. 467-469, p. 662). Stafa-Zurich: Trans Tech Publishing.
Ding, Y., Dwivedi, R., & Kovacevic, R. (2017). Process planning for 8-axis robotized laser-based direct metal deposition system: A case on building revolved part. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing,44, 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2016.08.008.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., & Li, H. (2015). Process planning for robotic wire and arc additive manufacturing.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., Li, H., & Duin, S. V. (2016a). Advanced design for Additive Manufacturing: 3D slicing and 2D path planning.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., Li, H., Larkin, N., & Duin, S. V. (2015). Multi-direction slicing of stl models for robotic wire-feed additive manufacturing. In International solid freeform fabrication symposium.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., Li, H., Larkin, N., & van Duin, S. (2016b). Automatic multi-direction slicing algorithms for wire based additive manufacturing. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing,37, 139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2015.09.002.
Gohari, H., Barari, A., & Kishawy, H. (2016). Using Multistep methods in slicing 2½ dimensional parametric surfaces for Additive Manufacturing applications. IFAC-PapersOnLine,49(31), 67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.12.163.
Grutle, Ø. K. (2015). 5-axis 3D printer.
Huang, B. (2009). Development of a software procedure for curved layered fused deposition modelling (CLFDM). Master thesis. Auckland University of Technology.
Huang, B., & Singamneni, S. (2013). Curved layer fused deposition modeling with varying raster orientations. Applied Mechanics and Materials,446–447, 263–269. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.446-447.263.
Huang, B., & Singamneni, S. B. (2015a). Curved layer adaptive slicing (CLAS) for fused deposition modelling. Rapid Prototyping Journal,21(4), 354–367. https://doi.org/10.1108/rpj-06-2013-0059.
Huang, B., & Singamneni, S. (2015b). A mixed-layer approach combining both flat and curved layer slicing for fused deposition modelling. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture,229(12), 2238–2249. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414551076.
Jin, Y., Du, J., He, Y., & Fu, G. (2017). Modeling and process planning for curved layer fused deposition. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,91(1–4), 273–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9743-5.
Jin, Y., Li, H., He, Y., & Fu, J. (2015). Quantitative analysis of surface profile in fused deposition modelling. Additive Manufacturing,8, 142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2015.10.001.
Jung, J. Y., & Ahluwalia, R. S. (2005). NC tool path generation for 5-axis machining of free formed surfaces. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,16(1), 115–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-005-4828-2.
Kalmanovich, G., Dodin, L., & Tu, S. (1997). Curved-layer laminated object manufacturing. In International conference on rapid prototyping.
Kerschbaumer, M., Ernst, G., & O’Leary, P. (2005). Tool path generation for 3D laser cladding using adaptive slicing technology. Journal of Laser Applications. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5060506.
Lee, W., Wei, C., & Chung, S. (2014). Development of a hybrid rapid prototyping system using low-cost fused deposition modeling and five-axis machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,214(11), 2366–2374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.05.004.
Lim, S., Buswell, R. A., Valentine, P. J., Piker, D., Austin, S. A., & De Kestelier, X. (2016). Modelling curved-layered printing paths for fabricating large-scale construction components. Additive Manufacturing,12, 216–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2016.06.004.
Luo, L., Baran, I., Rusinkiewicz, S., & Matusik, W. (2012). Chopper: Partitioning models into 3D-printable parts. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),31(6), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1145/2366145.2366148.
Oh, Y., Zhou, C., & Behdad, S. (2018). Part decomposition and assembly-based (Re) design for additive manufacturing: A review. Additive Manufacturing,22, 230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.04.018.
Osborne, N. R., Bezeredi, A., Han, G., Klosterman, D. A., Chartoff, R. P., Rodrigues, S., et al. (1999). Development of a curved layer LOM process for monolithic ceramics and ceramic matrix composites. Rapid Prototyping Journal,5(5), 61–71. https://doi.org/10.1108/13552549910267362.
Panchagnula, J. S., & Simhambhatla, S. (2016). Inclined slicing and weld-deposition for additive manufacturing of metallic objects with large overhangs using higher order kinematics. Virtual and Physical Prototyping,11(2), 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2016.1163766.
Patel, Y., Kshattriya, A., Singamneni, S. B., & Choudhury, A. R. (2015). Application of curved layer manufacturing for preservation of randomly located minute critical surface features in rapid prototyping. Rapid Prototyping Journal,21(6), 725–734. https://doi.org/10.1108/rpj-07-2013-0073.
Ren, L., Sparks, T., Ruan, J., & Liou, F. (2008). Process planning strategies for solid freeform fabrication of metal parts. Journal of Manufacturing Systems,27(4), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2009.02.002.
Shen, H., Diao, H., Yue, S., & Fu, J. (2018). Fused deposition modeling five-axis additive manufacturing: machine design, fundamental printing methods and critical process characteristics. Rapid Prototyping Journal,24(3), 548–561. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-05-2017-0096.
Sommerville, M. G. L., Clark, D. E. R., & Corney, J. R. (2001). Viewer-centered geometric feature recognition. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,12(4), 359–375. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1011219517642.
Tsao, C., Chang, H., Liu, M., Chen, H., Hsu, Y., Lin, P., et al. (2018). Freeform additive manufacturing by vari-directional vari-dimensional material deposition. Rapid Prototyping Journal,24(2), 379–394. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-01-2017-0014.
Wei, X., Qiu, S., Zhu, L., Feng, R., Tian, Y., Xi, J., et al. (2018). Toward support-free 3D printing: A skeletal approach for partitioning models. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics,24(10), 2799–2812. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2017.2767047.
Xiangping, W., Haiou, Z., & Guilan, W. (2016). Adaptive slicing for WAAM to fabricate large overhang without support. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology-Natural Sciences Edition. https://doi.org/10.13245/j.hust.160112.
Xu, J., Gu, X., Ding, D., Pan, Z., & Chen, K. (2018). A review of slicing methods for directed energy deposition based additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyping Journal. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-10-2017-0196.
Zeng, L., Lai, L. M., Qi, D., Lai, Y., & Yuen, M. M. (2011). Efficient slicing procedure based on adaptive layer depth normal image. Computer-Aided Design,43(12), 1577–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2011.06.007.
Zhao, D., & Guo, W. (2018). Research on curved layer fused deposition modeling (CLFDM) with variable extruded filament (VEF). In ASME 2018 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, 2018 American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection.
Zhao, G., Ma, G., Feng, J., & Xiao, W. (2018). Nonplanar slicing and path generation methods for robotic additive manufacturing. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,96(9–12), 3149–3159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1772-9.
Zhu, Z., Dhokia, V., & Newman, S. T. (2017). A novel decision-making logic for hybrid manufacture of prismatic components based on existing parts. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,28(1), 131–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0966-8.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the partial financial support under the project from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51735009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Guo, W. Mixed-layer adaptive slicing for robotic Additive Manufacturing (AM) based on decomposing and regrouping. J Intell Manuf 31, 985–1002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01490-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01490-z