Abstract
In this study, the innovative compact heat exchanger (CHE) newly designed and manufactured using metal additive manufacturing technology were numerically and experimentally investigated. Some experiments were carried out to determine the hot water (\(hw\)) and cold water (\(cw\)) outlet temperatures of CHE. As a result of the CFD analysis, the average outlet temperatures of the \(hw\) and \(cw\) flow loops on the CHE were calculated as 48.24 and 35.38 °C, respectively. On the other hand, the experimental outlet temperatures were measured as being 48.50 and 35.72 °C, respectively. The studies showed that the numerical and experimental results of the CHE are compliant at the given boundary conditions. Furthermore, it was observed that the heat transfer rate of the CHE with lower volume is approximately 47.7% higher than that of standard brazed plate heat exchangers (BPHEs) produced by traditional methods. More experiments conducted on the CHE will inevitably have a negative effect on its manufacture time and cost. Thus, various models were developed to predict the results of unperformed experiments using the machine learning methods, ANN, MLR and SVM. In the models developed for each experiment, the source and inlet temperatures of \(hw\) and \(cw\), respectively, and the volumetric flow rate of \(cw\) were selected as input parameters for the machine learning methods. Thus, the \(hw\) and \(cw\) outlet temperatures of the CHE were estimated on the basis of these input parameters. The best performance was achieved by ANN. In addition, there is no significant performance difference between other methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ghobari, H. M., El-Marazky, M. S., Dewidar, A. Z., & Mattar, M. A. (2018). Prediction of wind drift and evaporation losses from sprinkler irrigation using neural network and multiple regression techniques. Agricultural Water Management, 195, 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.10.005.
Bai, Y., Chaudhari, A., & Wang, H. (2020). Investigation on the microstructure and machinability of ASTM A131 steel manufactured by directed energy deposition. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 276, 116410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116410.
Bhatt, P. M., Kabir, A. M., Peralta, M., Bruck, H. A., & Gupta, S. K. (2019). A robotic cell for performing sheet lamination-based additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 27, 278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.02.002.
Bineli, A. R. R., Peres, A. P. G., Jardini, A. L., & Maciel Filho, R. (2011) Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS): Technology for design and construction of microreactors. In 6th Brazilian Conference of Manufacturing Engineerin, Caxias do Sul, RS, Brazi, April 11–15 2011
Bollegala, D. (2017). Dynamic feature scaling for online learning of binary classifiers. Knowledge-Based Systems, 129, 97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.05.010.
Brooks, H., & Molony, S. (2016). Design and evaluation of additively manufactured parts with three dimensional continuous fibre reinforcement. Materials & Design, 90, 276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.123.
Chabot, A., Laroche, N., Carcreff, E., Rauch, M., & Hascoët, J.-Y. (2019). Towards defect monitoring for metallic additive manufacturing components using phased array ultrasonic testing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31, 1191–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01505-9.
Chemingui, H. (2013). Resistance, motivations, trust and intention to use mobile financial services. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 31(7), 574–592. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-12-2012-0124.
Chollet, F. (2017). Deep learning with Python. Shelter Island: Manning Publications.
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20(3), 273–297.
Cui, J., & Cui, Y. (2015). Effects of surface wettability and roughness on the heat transfer performance of fluid flowing through microchannels. Energies, 8(6), 5704–5724. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8065704.
Dinovitzer, M., Chen, X., Laliberte, J., Huang, X., & Frei, H. (2019). Effect of wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) process parameters on bead geometry and microstructure. Additive Manufacturing, 26, 138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.12.013.
Domingos, P. (2015). The master algorithm: How the quest for the ultimate learning machine will remake our world. United States: Basic Books.
Dong, L., Makradi, A., Ahzi, S., & Remond, Y. (2007) Finite element analysis of temperature and density distributions in selective laser sintering process. In Materials science forum, 2007 (Vol. 553, pp. 75–80): Trans Tech Publ
Ebrahimzadeh, E., Wilding, P., Frankman, D., Fazlollahi, F., & Baxter, L. L. (2016). Theoretical and experimental analysis of dynamic plate heat exchanger: non-retrofit configuration. Applied Thermal Engineering, 93, 1006–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.10.017.
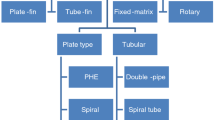
Erbay, L. B., Uğurlubilek, N., Altun, Ö., & Doğan, B. (2013). Compact heat exchangers. Engineer & The Machinery Magazine, 54(646), 37–48.
Ermis, K. (2008). ANN modeling of compact heat exchangers. International Journal of Energy Research, 32(6), 581–594.
Fluent, A. (2015). Ansys Fluent R16.1 Theory guide. Canonsburg, PA: Ansys Inc.
Foroozmehr, A., Badrossamay, M., Foroozmehr, E., & Golabi, S. I. (2016). Finite element simulation of selective laser melting process considering optical penetration depth of laser in powder bed. Materials & Design, 89, 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.002.
Fragkaki, A., Farmaki, E., Thomaidis, N., Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A., Angelis, Y., Koupparis, M., et al. (2012). Comparison of multiple linear regression, partial least squares and artificial neural networks for prediction of gas chromatographic relative retention times of trimethylsilylated anabolic androgenic steroids. Journal of Chromatography A, 1256, 232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.064.
Garg, A., Panda, B., Zhao, D., & Tai, K. (2016a). Framework based on number of basis functions complexity measure in investigation of the power characteristics of direct methanol fuel cell. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 155, 7–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2016.03.025.
Garg, A., Sarma, S., Panda, B., Zhang, J., & Gao, L. (2016b). Study of effect of nanofluid concentration on response characteristics of machining process for cleaner production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 135, 476–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.122.
Gobert, C., Reutzel, E. W., Petrich, J., Nassar, A. R., & Phoha, S. (2018). Application of supervised machine learning for defect detection during metallic powder bed fusion additive manufacturing using high resolution imaging. Additive Manufacturing, 21, 517–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.04.005.
Hajabdollahi, H., & Seifoori, S. (2016). Effect of flow maldistribution on the optimal design of a cross flow heat exchanger. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 109, 242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2016.06.014.
Han, X.-H., Cui, L.-Q., Chen, S.-J., Chen, G.-M., & Wang, Q. (2010). A numerical and experimental study of chevron, corrugated-plate heat exchangers. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 37(8), 1008–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2010.06.026.
Hudák, R., Šarik, M., Dadej, R., Živčák, J., & Harachová, D. (2013a). Material and thermal analysis of laser sinterted products. Acta Mechanica et Automatica, 7(1), 15–19.
Hussein, A., Hao, L., Yan, C., Everson, R., & Young, P. (2013). Advanced lattice support structures for metal additive manufacturing. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 213(7), 1019–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.01.020.
İpek, O., Kılıç, B., & Gürel, B. (2017). Experimental investigation of exergy loss analysis in newly designed compact heat exchangers. Energy, 124, 330–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.02.061.
Jiang, J., Xiong, Y., Zhang, Z., & Rosen, D. W. (2020). Machine learning integrated design for additive manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01715-6.
John, G. H., Kohavi, R., & Pfleger, K. (1994). Irrelevant features and the subset selection problem. In Machine Learning Proceedings 1994 (pp. 121–129). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Kan, M., Ipek, O., & Gurel, B. (2015). Plate heat exchangers as a compact design and optimization of different channel angles. Acta Physica Polonica A, 12, 49–52. https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.128.B-49.
Kays, W. M., & London, A. L. (1984). Compact heat exchangers. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Khudheyer, A. F., & Mahmoud, M. S. (2011). Numerical analysis of fin-tube plate heat exchanger by using CFD technique. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 6(7), 1–12.
Kim, P. (2017). Matlab deep learning: With machine learning, neural networks and artificial intelligence. Berkeley, CA: Apress.
Kwon, O., Kim, H. G., Ham, M. J., Kim, W., Kim, G.-H., Cho, J.-H., et al. (2020). A deep neural network for classification of melt-pool images in metal additive manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31(2), 375–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1451-6.
Lam, C., & Bremhorst, K. (1981). A modified form of the k–ε model for predicting wall turbulence. Asme Journal of Fluids Engineering, 103, 456–460.
Li, X., Jia, X., Yang, Q., & Lee, J. (2020). Quality analysis in metal additive manufacturing with deep learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31, 2003–2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01549-2.
Manfredi, D., Calignano, F., Ambrosio, E. P., Krishnan, M., Canali, R., Biamino, S., et al. (2013b). Direct Metal Laser Sintering: an additive manufacturing technology ready to produce lightweight structural parts for robotic applications. Metallurgia Italiana, 105(10), 15–24.
Narin, A., Isler, Y., & Ozer, M. (2014). Investigating the performance improvement of HRV Indices in CHF using feature selection methods based on backward elimination and statistical significance. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 45, 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.11.016.
Nicolet, G., Eckert, N., Morin, S., & Blanchet, J. (2017). A multi-criteria leave-two-out cross-validation procedure for max-stable process selection. Spatial Statistics, 22, 107–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spasta.2017.09.004.
Niu, X. D., Singh, S., Garg, A., Singh, H., Panda, B., Peng, X. B., et al. (2019). Review of materials used in laser-aided additive manufacturing processes to produce metallic products. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 14(3), 282–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-019-0526-1.
Özdamar, K. (2004). Paket programlar ile istatistiksel veri analizi (çok değişkenli analizler). Eskişehir: Kaan Kitabevi.
Patterson, J., & Gibson, A. (2017). Deep learning: A practitioner’s approach. Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media Inc.
Paul, A., Mozaffar, M., Yang, Z. J., Liao, W. K., Choudhary, A., Cao, J., et al. (2019). A real-time iterative machine learning approach for temperature profile prediction in additive manufacturing processes. In L. Singh, R. DeVeaux, G. Karypis, F. Bonchi, & J. Hill (Eds.), 2019 IEEE ınternational conference on data science and advanced analytics, Proceedings of the international conference on data science and advanced analytics (pp. 541–550).
Penumuru, D. P., Muthuswamy, S., & Karumbu, P. (2020). Identification and classification of materials using machine vision and machine learning in the context of industry 4.0. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31(5), 1229–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01508-6.
Peyre, P., Rouchausse, Y., Defauchy, D., & Regnier, G. (2015). Experimental and numerical analysis of the selective laser sintering (SLS) of PA12 and PEKK semi-crystalline polymers. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 225, 326–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.04.030.
Priddy, K. L., & Keller, P. E. (2005). Artificial neural networks: An introduction (Vol. 68). Bellingham: SPIE Press.
Qi, Z. X., Wang, H. Z., Li, J. Z., & Gao, H. (2018). FROG: Inference from knowledge base for missing value imputation. Knowledge-Based Systems, 145, 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.01.005.
Ranganayakulu, C., Luo, X., & Kabelac, S. (2017). The single-blow transient testing technique for offset and wavy fins of compact plate-fin heat exchangers. Applied Thermal Engineering, 111, 1588–1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.05.118.
Roberts, I. A., Wang, C. J., Esterlein, R., Stanford, M., & Mynors, D. J. (2009). A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the temperature field during laser melting of metal powders in additive layer manufacturing. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 49(12–13), 916–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.07.004.
Ross, S. M. (2014). Introduction to probability and statistics for engineers and scientists. Canada: Academic Press.
Sarafraz, M. M., & Hormozi, F. (2016). Heat transfer, pressure drop and fouling studies of multi-walled carbon nanotube nano-fluids inside a plate heat exchanger. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 72, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2015.11.004.
Sheikholeslami, M., Gorji-Bandpy, M., & Ganji, D. D. (2016). Experimental study on turbulent flow and heat transfer in an air to water heat exchanger using perforated circular-ring. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 70, 185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2015.09.002.
Silbernagel, C., Aremu, A., & Ashcroft, I. (2019). Using machine learning to aid in the parameter optimisation process for metal-based additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 26(4), 625–637. https://doi.org/10.1108/rpj-08-2019-0213.
Stathatos, E., & Vosniakos, G. C. (2019). Real-time simulation for long paths in laser-based additive manufacturing: A machine learning approach. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 104(5–8), 1967–1984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04004-6.
Stone, M. (1974). Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 36(2), 111–133.
Tan, C. K., Ward, J., Wilcox, S. J., & Payne, R. (2009). Artificial neural network modelling of the thermal performance of a compact heat exchanger. Applied Thermal Engineering, 29(17–18), 3609–3617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2009.06.017.
Tiryaki, S., & Aydin, A. (2014). An artificial neural network model for predicting compression strength of heat treated woods and comparison with a multiple linear regression model. Construction and Building Materials, 62, 102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.03.041.
Tsopanos, S., Sutcliffe, C., & Owen, I. The manufacture of micro cross-flow heat exchangers by selective laser melting. In Fifth International Conference on Enhanced, Compact and Ultra-Compact Heat Exchangers: Science, Engineering and Technology, Hoboken, NJ, United State, September 11–16 2005
Uğuz, S. (2020). Makine öğrenmesi teorik yönleri ve Python uygulamaları ile bir yapay zeka ekolü. Isparta: Nobel academic publish.
Usta, Y., & Köylü, A. (2012). Yakıt hücrelerinde kullanılacak gözenekli paslanmaz çelik toz metal parçaların üretim parametrelerinin araştırılması. Journal of the Faculty of Engineering & Architecture of Gazi University, 27(2), 265–274.
Ventola, L., Robotti, F., Dialameh, M., Calignano, F., Manfredi, D., Chiavazzo, E., et al. (2014). Rough surfaces with enhanced heat transfer for electronics cooling by direct metal laser sintering. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 75, 58–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.03.037.
Wang, C., Tan, X., Tor, S., & Lim, C. (2020). Machine learning in additive manufacturing: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Additive Manufacturing, 36, 101538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101538.
Yang, Y., He, M., & Li, L. (2020). Power consumption estimation for mask image projection stereolithography additive manufacturing using machine learning based approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 251, 119710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119710.
Zhao, D., & Guo, W. (2019). Mixed-layer adaptive slicing for robotic Additive Manufacturing (AM) based on decomposing and regrouping. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31, 985–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01490-z.
Zheng, A. (2015). Evaluating machine learning models: A beginner’s guide to key concepts and pitfalls. Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Scientific and Technology Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK), under project name: TUBITAK 1001, 214M070. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the TUBITAK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uguz, S., Ipek, O. Prediction of the parameters affecting the performance of compact heat exchangers with an innovative design using machine learning techniques. J Intell Manuf 33, 1393–1417 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01729-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01729-0