Abstract
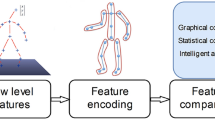
This paper presents a novel approach to screening children with ADHD, one of the most prevalent childhood disorders. We have designed the robot-assisted, game-like test that directly reflects children’s behavior on measuring ADHD symptoms. Using the sensors in the robot system, most of the children’s behavior is automatically measured during the entire course of the test. We collected real data by carrying out tests to 326 children from 3rd to 4th grades in the field. A unified frame that classifies multiple categories of ADHD, ADHD-at-Risk and normal has been set up to investigate a wide spectrum of classifiers and their optimal hyper-parameters. The results of the data analysis show highly confident ADHD classification, up to 97% (F1 score). It could be a practical tool for clinicians and special teachers to use in the diagnosis of childhood ADHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T.M., McConaughy, S.H., Howell, C.T.: Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychol. Bullet. 101(2), 213 (1987)
Baddeley, A.: Working memory: theories, models, and controversies. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 63, 1–29 (2012)
Barkley, R.A.: Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. Guilford Publications, New York (2014)
Bergstra, J., Bengio, Y.: Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(1), 281–305 (2012)
Bishop, C.: Pattern Recognition and Machine learning, 2nd edn, Information Science and Statistics (2007)
Breiman, L.: Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Castle, L., Aubert, R.E., Verbrugge, R.R., Khalid, M., Epstein, R.S.: Trends in medication treatment for adhd. J. Atten. Disord. 10(4), 335–342 (2007)
Clarke, A.R., Barry, R.J., McCarthy, R., Selikowitz, M.: EEG analysis in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: a comparative study of two subtypes. Psychiatry Res. 81(1), 19–29 (1998)
Dulcan, M. et al.: Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children, adolescents, and adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Amer. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 36(10), 85S–121S (1997)
DuPaul, G.J., Stoner, G.: ADHD in the schools: Assessment and intervention strategies. Guilford Publications, New York (2014)
Feil-Seifer, D., Mataric, M.J.: Defining Socially Assistive Robotics. In: 2005. ICORR 2005. 9Th International Conference On Rehabilitation Robotics, pp. 465–468. IEEE (2005)
Fridin, M., Yaakobi, Y.: Educational Robot for Children with Adhd/Add. In: Architectural Design, In. Conferenc on Computational Vision and Robotics. Citeseer (2011)
Friedman, J.H.: Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics 29(5), 1189–1232 (2001)
Greenberg, L.M., Waldmant, I.D.: Developmental normative data on the test of variables of attention (tova™). J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 34(6), 1019–1030 (1993)
Gualtieri, C.T., Johnson, L.G.: Reliability and validity of a computerized neurocognitive test battery, cns vital signs. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 21(7), 623–643 (2006)
Hart, H., Chantiluke, K., Cubillo, A.I., Smith, A.B., Simmons, A., Brammer, M.J., Marquand, A.F., Rubia, K.: Pattern classification of response inhibition in adhd: toward the development of neurobiological markers for adhd. Human Brain Mapp. 35(7), 3083–3094 (2014)
Kane, R.L., Kay, G.G.: Computerized assessment in neuropsychology: a review of tests and test batteries. Neuropsychol. Rev. 3(1), 1–117 (1992)
Kim, J.W., Sharma, V., Ryan, N.D.: Predicting methylphenidate response in adhd using machine learning approaches. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 18(11), 1–7 (2015)
Klingberg, T., Fernell, E., Olesen, P.J., Johnson, M.: Computerized training of working memory in children with ADHD-a randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 44(2), 177–186 (2005)
Kohavi, R.: A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. IJCAI 14 (2), 1137–1145 (1995)
Kokkalia, G., Drigas, A.: Working memory and adhd in preschool education. the role of ict’s as a diagnostic and intervention tool: an overview. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 10(5), 4–9 (2015)
Lim, K., Cho, B.: The prevalence of adhd in elementary school children. J. Elem. Educ. 17, 235–260 (2004)
Martín-Martínez, D., Casaseca-De-La-Higuera, P., Alberola-López, S., Andrés-de Llano, J., López-Villalobos, J., Ardura-Fernández, J., Alberola-López, C.: Nonlinear analysis of actigraphic signals for the assessment of the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd). Med. Eng. Phys. 34(9), 1317–1329 (2012)
Mayes, R., Bagwell, C., Erkulwater, J.: Adhd and the rise in stimulant use among children. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 16(3), 151–166 (2008)
Milgram, J., Cheriet, M., Sabourin, R.: “One against One” Or “One against All”: Which One is Better for Handwriting Recognition with Svms?. In: Tenth International Workshop on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition. Suvisoft (2006)
Nakamura, B.J., Ebesutani, C., Bernstein, A., Chorpita, B.F.: A psychometric analysis of the child behavior checklist dsm-oriented scales. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 31(3), 178–189 (2009)
Nunnally, J.C.: Psychometric theory—25 years ago and now. Educ. Res. 4(10), 7–21 (1975)
Nylund, D.: Treating Huckleberry Finn: A new narrative approach to working with kids diagnosed ADD/ADHD. Jossey-Bass (2000)
O’Mahony, N., Florentino-Liano, B., Carballo, J.J., Baca-garcía, E., Rodríguez, A.A.: Objective diagnosis of adhd using imus. Med. Eng. Phys. 36(7), 922–926 (2014)
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., et al.: Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12(Oct), 2825–2830 (2011)
Peng, X., Lin, P., Zhang, T., Wang, J.: extreme learning Machine-Based classification of ADHD using brain structural MRI data. PloS one 8(11), e79,476 (2013)
Robins, B., Dautenhahn, K., Dickerson, P.: From Isolation to Communication: a Case Study Evaluation of Robot Assisted Play for Children with Autism with a Minimally Expressive Humanoid Robot. In: 2009. ACHI’09. Second International Conferences On Advances in Computer-Human Interactions, pp. 205–211. IEEE (2009)
Robocare Co.: Silbot. http://www.robocare.co.kr/
Rusu, R.B., Cousins, S.: 3D is Here: Point Cloud Library (Pcl). In: 2011 IEEE International Conference On Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2011)
Sammut, C., Webb, G.I.: Encyclopedia of machine learning. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2011)
Shin, Y.: The study on parents perception according to diagnostic and educational history of children with attention deficits and hyperactivity problems (in Korean). J. Spec. Educ. Rehabil. Sci. 51, 21–44 (2012)
Sokolova, M., Lapalme, G.: A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 45(4), 427–437 (2009)
Song, Y.J.: Estimated prevalence of adhd symptoms and relationships among adhd symptoms, environmental variables, and peer relationships in elementary school students. Asian J. Educ. 15, 189–217 (2014)
Wolraich, M.L., Lambert, E.W., Bickman, L., Simmons, T., Doffing, M.A., Worley, K.A.: Assessing the impact of parent and teacher agreement on diagnosing attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 25(1), 41–47 (2004)
Yu, H.F., Huang, F.L., Lin, C.J.: Dual Coordinate Descent Methods for Logistic Regression and Maximum Entropy Models. Mach. Learn. 85(1-2), 41–75 (2011)
Zuckerman, O., Hoffman, G., Kopelman-Rubin, D., Klomek, A.B., Shitrit, N., Amsalem, Y., Shlomi, Y.: Kip3: Robotic companion as an external cue to students with adhd. In: Proceedings of the TEI’16: Tenth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, pp. 621–626. ACM (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Program (10048451), funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, MT., Yeom, J., Shin, Y. et al. Robot-Assisted ADHD Screening in Diagnostic Process. J Intell Robot Syst 95, 351–363 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-018-0890-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-018-0890-9