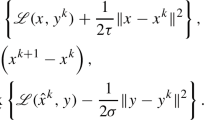Abstract
The primal–dual hybrid gradient method (PDHG) originates from the Arrow–Hurwicz method, and it has been widely used to solve saddle point problems, particularly in image processing areas. With the introduction of a combination parameter, Chambolle and Pock proposed a generalized PDHG scheme with both theoretical and numerical advantages. It has been analyzed that except for the special case where the combination parameter is 1, the PDHG cannot be casted to the proximal point algorithm framework due to the lack of symmetry in the matrix associated with the proximal regularization terms. The PDHG scheme is nonsymmetric also in the sense that one variable is updated twice while the other is only updated once at each iteration. These nonsymmetry features also explain why more theoretical issues remain challenging for generalized PDHG schemes; for example, the worst-case convergence rate of PDHG measured by the iteration complexity in a nonergodic sense is still missing. In this paper, we further consider how to generalize the PDHG and propose an algorithmic framework of generalized PDHG schemes for saddle point problems. This algorithmic framework allows the output of the PDHG subroutine to be further updated by correction steps with constant step sizes. We investigate the restriction onto these step sizes and conduct the convergence analysis for the algorithmic framework. The algorithmic framework turns out to include some existing PDHG schemes as special cases, and it immediately yields a class of new generalized PDHG schemes by choosing different step sizes for the correction steps. In particular, a completely symmetric PDHG scheme with the golden-ratio step sizes is included. Theoretically, an advantage of the algorithmic framework is that the worst-case convergence rate measured by the iteration complexity in both the ergodic and nonergodic senses can be established.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We analyzed the case \(\tau \in [-1,1]\) in [16]; but for simplicity we only focus on \(\tau \in [0,1]\) in this paper.
References
Arrow, K.J., Hurwicz, L., Uzawa, H.: Studies in linear and non-linear programming. In: Chenery, H.B., Johnson, S.M., Karlin, S., Marschak, T., Solow, R.M. (eds.) Stanford Mathematical Studies in the Social Science, vol. II. Stanford University Press, Stanford (1958)
Blum, E., Oettli, W.: Mathematische Optimierung Grundlagen und Verfahren. Springer, Berlin (1975)
Bonettini, S., Ruggiero, V.: On the convergence of primal–dual hybrid gradient algorithms for total variation image restoration. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 44, 236–253 (2012)
Chambolle, A.: An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 20, 89–97 (2004)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: A first-order primal–dual algorithms for convex problem with applications to imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 40, 120–145 (2011)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: On the ergodic convergence rates of a first-order primal–dual algorithm. Math. Program. 159, 253–287 (2016)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: A remark on accelerated block coordinate descent for computing the proximity operators of a sum of convex functions. SMAI J. Comput. Math. 1, 29–54 (2015)
Condat, L.: A primal–dual splitting method for convex optimization involving Lipschitzian, proximable and linear composite terms. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 158, 460–479 (2013)
Douglas, J., Rachford, H.H.: On the numerical solution of the heat conduction problem in 2 and 3 space variables. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 82, 421–439 (1956)
Esser, E., Zhang, X., Chan, T.F.: A general framework for a class of first order primal–dual algorithms for TV minimization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3, 1015–1046 (2010)
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.S.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems, Springer Series in Operations Research, vol. I. Springer, New York (2003)
Glowinski, R., Marrocco, A.: Approximation par éléments finis d’ordre un et résolution par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problèmes non linéaires. RAIRO R2, 41–76 (1975)
Goldstein, T., Li, M., Yuan, X.M.: Adaptive primal-dual splitting methods for statistical learning and image processing. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2089–2097 (2015)
Gol’shtein, E.G., Tret’yakov, N.V.: Modified Lagrangian in convex programming and their generalizations. Math. Program. Study 10, 86–97 (1979)
He, B.S., You, Y.F., Yuan, X.M.: On the convergence of primal–dual hybrid gradient algorithm. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 7, 2526–2537 (2014)
He, B.S., Yuan, X.M.: Convergence analysis of primal–dual algorithms for a saddle-point problem: from contraction perspective. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 5, 119–149 (2012)
He, B.S., Yuan, X.M.: On the \(O(1/n)\) convergence rate of Douglas–Rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 700–709 (2012)
He, B.S., Yuan, X.M.: On non-ergodic convergence rate of Douglas–Rachford alternating directions method of multipliers. Numer. Math. 130, 567–577 (2015)
Horn, R.A., Johnson, C.R.: Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Korpelevich, G.M.: The extragradient method for finding saddle points and other problems. Ekon. Mat. Metod. 12, 747–756 (1976)
Lions, P.L., Mercier, B.: Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 16, 964–979 (1979)
Martinet, B.: Regularization d’inequations variationelles par approximations successives. Rev. Fr. Inform. Rech. Oper. 4, 154–159 (1970)
Pock, T., Chambolle, A.: Diagonal preconditioning for first order primal–dual algorithms in convex optimization. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1762–1769 (2011)
Popov, L.D.: A modification of the Arrow–Hurwitz method of search for saddle points. Mat. Zamet. 28(5), 777–784 (1980)
Rudin, L., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D 60, 227–238 (1992)
Shefi, R.: Rate of convergence analysis for convex non-smooth optimization algorithms. PhD Thesis, Tel Aviv University, Israel (2015)
Weiss, P., Blanc-Feraud, L., Aubert, G.: Efficient schemes for total variation minimization under constraints in image processing. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(3), 2047–2080 (2009)
Zhang, X., Burger, M., Osher, S.: A unified primal–dual algorithm framework based on Bregman iteration. J. Sci. Comput. 46(1), 20–46 (2010)
Zhu, M., Chan, T.F.: An efficient primal–dual hybrid gradient algorithm for total variation image restoration. CAM Report 08–34,UCLA, Los Angeles, CA (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bingsheng He was supported by the NSFC Grants 11471156 and 91530115, Feng Ma was supported by the NSFC Grant 71401176 and Xiaoming Yuan was supported by the General Research Fund from Hong Kong Research Grants Council: HKBU12300515.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, B., Ma, F. & Yuan, X. An Algorithmic Framework of Generalized Primal–Dual Hybrid Gradient Methods for Saddle Point Problems. J Math Imaging Vis 58, 279–293 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-017-0709-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-017-0709-5