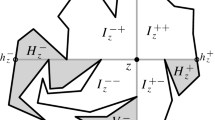
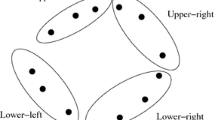
Abstract
This paper gives optimal algorithms for the construction of the Nearest Neighbor Embracing Graph (NNE-graph) of a given point set V of size n in the k-dimensional space (k-D) for k = 2,3. The NNE-graph provides another way of connecting points in a communication network, which has lower expected degree at each point and shorter total length of connections with respect to those using Delaunay triangulation. In fact, the NNE-graph can also be used as a tool to test whether a point set is randomly generated or has some particular properties.
We show that in 2-D the NNE-graph can be constructed in optimal \(\Theta(n^2)\) time in the worst case. We also present an \(O(n \log n + nd)\) time algorithm, where d is the \(\Omega(\log n)\)-th largest degree in the utput NNE-graph. The algorithm is optimal when \(d=O(\log n)\). The algorithm is also sensitive to the structure of the NNE-graph, for instance when \(d=g \cdot(\log n)\), the number of edges in NNE-graph is bounded by \(O(gn \log n)\) for any value g with \(1 \leq g \leq \frac{n}{\log n}\). We finally propose an \(O(n \log n + nd \log d^*)\) time algorithm for the problem in 3-D, where d and \(d^*\) are the \(\Omega(\frac{\log n}{\log \log n})\)-th largest vertex degree and the largest vertex degree in the NNE-graph, respectively. The algorithm is optimal when the largest vertex degree of the NNE-graph \(d^*\) is \(O(\frac{\log n}{\log \log n})\).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baddeley AJ, Silverman BW (1984) A cautionary example on the use of second-order methods for analyzing point patterns. Biometrics 40:1089–1093
Callahan PB, Kosaraju SR (1995) A decomposition of multidimensional point sets with applications to k-nearest-neighbors and n-body potential fields. Journal of the ACM 42(1):67–90
Chin F, Wang CA (1998) Finding the constrained delaunay triangulation and constrained Voronoi diagram of a simple polygon in linear time. SIAM Journal of Computing 28(2):471–486
Chiu SN, Molchanov IS (2003) A new graph related to the directions of nearest neighbours in a point process. Advances in Applied Probability 35(1)
Cormen TH, Leiserson CE, Rivest RL, Stein C (2001) Introduction to algorithms, 2nd edition. McGraw-Hill, New York
Harary F (1971) Graph theory. Addison-Wesley
Preparata FP, Shamos MI (1985) Computational geometry: An introduction. Springer-Verlag
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, M.Y., Chen, D.Z., Chin, F.Y.L. et al. Construction of the nearest neighbor embracing graph of a point set. J Comb Optim 11, 435–443 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-006-8459-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-006-8459-0