Abstract
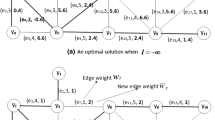
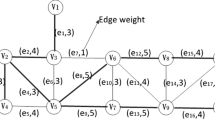
We consider some inverse min-max (or max-min) network problems. Such an inverse problem is to modify the weights with bound constraints so that a given feasible solution becomes an optimal solution of a min-max (or max-min) network problem, and the deviation of the weights, measured by the weighted l 1 norm or weighted l ∞ norm, is minimum. In this paper, we present strongly polynomial time algorithms to solve the inverse min-max spanning tree problem and the inverse maximum capacity path problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Guan YP (2005) The inverse optimal value problem. Math Program 102:91–110
Ahuja RK, Orlin JB (2001) Inverse optimization, part i: linear programming and general problem. Oper Res 35:771–783
Ahuja RK, Orlin JB (2000) A faster algorithm for the inverse spanning tree problem. J Algorithms 34:177–193
Burkard R, Pleschiutschnig C, Zhang JZ (2004) Inverse median problems. Discrete Optim 1:23–39
Burton D, Toint PhL (1992) On an instance of the inverse shortest paths problem. Math Program 53:45–61
Burton D, Toint PhL (1994) On the use of an inverse shortest paths algorithm for recovering linearly correlated costs. Math Program 63:1–22
Cai MC, Yang XG (1995) Inverse shortest path problems. Operations research and its applications. In: First international symposium ISORA’95 Beijing PR China
Cai MC, Yang XG, Zhang J (1999) The complexity analysis of the inverse center location problem. J Global Optim 15:213–218
Camerini PM (1978) The min-max spanning tree problem and some extensions. Inf Proc Lett 7:10–14
Hao J, Orlin JB (1994) A faster algorithm for finding the minimum cut in a directed graph. J Algorithms 17:424–446
Heuburger C (2004) Inverse optimization, a survey on problems, methods, and results. J Comb Optim 8:329–361
Hochbaum DS (2003) Efficient algorithms for the inverse spanning tree problem. Oper Res 51:785–797
He Y, Zhang B, Yao E (2005) Weighted inverse minimum spanning tree problems under Hamming distance. J Comb Optim 9:91–100
Iyengar G, Kang WM (2005) Inverse conic programming with applications. Oper Res Lett 33:319–330
Liu LC, He Y (2006) Inverse minimum spanning tree problem and reverse shortest-path problem with discrete values. Prog Nat Sci 16:649–655
Nagamochi H, Ibaraki T (1992) Computing edge-connectivity in multigraphs and capacitated graphs. SIAM J Discrete Math 5:54–66
Orlin JB (2003) Inverse optimization and partial inverse optimization. PPT presentation on Optimization Day Columbia University November 3
Schrijver A (2003) Combinatorial optimization: polyhedra and efficiency. Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg
Sokkalingam PT, Ahuja RK, Orlin JB (1999) Solving inverse spanning tree problems through network flow techniques. Oper Res 47:291–298
Xu S, Zhang J (1995) An inverse problem of the weighted shortest path problem. Japan J Ind Appl Math 12:47–59
Yang C, Zhang J (1998) Inverse maximum capacity problems. OR Spektrum 20:97–100
Yang C, Zhang J (1999) Two general methods for inverse optimization problems. Appl Math Lett 12:69–72
Zhang J, Liu Z (1999) A further study on inverse linear programming problems. J Comput Appl Math 106:345–359
Zhang J, Ma Z (1996) A network flow method for solving some inverse combinatorial optimization problems. Optimization 37:59–72
Zhang J, Xu S, Ma Z (1997) An algorithm for inverse minimum spanning tree problem. Optim Meth Soft 8:69–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhang, J. Some inverse min-max network problems under weighted l 1 and l ∞ norms with bound constraints on changes. J Comb Optim 13, 123–135 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-006-9016-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-006-9016-6