Abstract
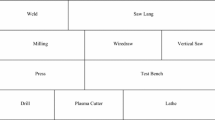
In this paper, the healthcare facility layout problem with area constraints is considered, a proper departments arrangement is selected such that the operating cost and system efficiency are guaranteed. We propose an integrated method to consider both quantitative and qualitative criteria to get a synthesize rank of the feasible alternatives. On quantitative aspects, several feasible layout solutions are generated with the ranking of operation cost; On qualitative aspects, the layout alternatives are evaluated by experts on their multiple attributes, the evaluation scores given by experts are in the form of intuitionistic fuzzy sets. We assume that the weights of attributes and experts are partially known or unknown in advance, and the weights of each expert on different attributes are different. An illustrative example is shown to demonstrate the application of the proposed methodology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnolds I, Nickel S, Shashaani S, Wernz C (2012) Using simulation in hospital layout planning. In: Proceedings of the winter simulation conference, winter simulation conference, p 395
Assem M, Ouda BK, Wahed MA (2012) Improving operating theatre design using facilities layout planning. In: Biomedical engineering conference (CIBEC), Cairo International. IEEE, pp 109–113
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Cabrerizo FJ, Moreno JM, Pérez IJ, Herrera-Viedma E (2010) Analyzing consensus approaches in fuzzy group decision making: advantages and drawbacks. Soft Comput 14(5):451–463
Cabrerizo FJ, Ureña R, Pedrycz W, Herrera-Viedma E (2014) Building consensus in group decision making with an allocation of information granularity. Fuzzy Sets Syst 255:115–127
Castillo I, Westerlund J, Emet S, Westerlund T (2005) Optimization of block 315 layout design problems with unequal areas: a comparison of milp and minlp optimization methods. Comput Chem Eng 30(1):54–69
Chen S-J, Hwang C-L (1992) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making methods. In: Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Springer, pp 289–486
Chraibi A, Kharraja S, Osman IH, Elbeqqali O (2016) A particle swarm algorithm for solving the multi-objective operating theater layout problem. IFAC-PapersOnLine 49(12):1169–1174
Chraibi A, Kharraja S, Osman IH, Elbeqqali O, et al (2014) A multi-objective mixed-integer programming model for a multi-section operating theatre facility layout. ICORES, pp 196–204
Elshafei AN (1977) Hospital layout as a quadratic assignment problem. J Oper Res Soc 28(1):167–179
Fan J, Lu XW (2015) Supply chain scheduling problem in the hospital with periodic working time on a single machine. J Comb Optim 30(4):892C905
Gu YH, Fan J, Tang GC, Zhong JF (2013) Maximum latency scheduling problem on two-person cooperative games. J Comb Optim 1–11
Gu YH, Goh M, Chen QL, Souza RD, Tang GC (2013) A new two-party bargaining mechanism. J Comb Optim 25(1):135C163
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E et al (1996) A model of consensus in group decision making under linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78(1):73–87
Hwang C-L, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attributes decision making methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Kim SH, Ahn BS (1999) Interactive group decision making procedure under incomplete information. Eur J Oper Res 116(3):498–507
Konak A, Kulturel-Konak S, Norman BA, Smith AE (2006) A new mixed integer programming formulation for facility layout design using flexible bays. Oper Res Lett 34(6):660–672
Lin Q-L, Liu H-C, Wang D-J, Liu L (2015) Integrating systematic layout planning with fuzzy constraint theory to design and optimize the facility layout for operating theatre in hospitals. J Intell Manuf 26(1):87–95
Montreuil B (1991) A modelling framework for integrating layout design and ownetwork design. In: Material handling. Springer, pp 95–115
Opricovic S (1998) Multicriteria optimization of civil engineering systems. Fac Civ Eng Belgrade 2(1):5–21
Sherali HD, Fraticelli BM, Meller RD (2003) Enhanced model formulations for optimal facility layout. Oper Res 51(4):629–644
Tompkins JA, White JA, Bozer YA, Tanchoco JMA (2010) Facilities planning. Wiley, Hoboken
Wan S-P, Dong J-Y (2014) Possibility linear programming with trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Appl Math Model 38(5):1660–1672
Wang S, Su HQ, Wan GH (2015) Resource-constrained machine scheduling with machine eligibility restriction and its applications to surgical operations scheduling. J Comb Optim 30(4):982C995
Wu J, Chiclana F (2014) Visual information feedback mechanism and attitudinal prioritisation method for group decision making with triangular fuzzy complementary preference relations. Inf Sci 279:716–734
Xu Y, Da Q (2008) A method for multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information under uncertain linguistic environment. Knowl Based Syst 21(8):837–841
Xu Z (2004) A method based on linguistic aggregation operators for group decision making with linguistic preference relations. Inf Sci 166(1):19–30
Xu Z (2007) Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(6):1179–1187
Xu Z (2007) A method for multiple attribute decision making with incomplete weight information in linguistic setting. Knowl Based Syst 20(8):719–725
Xu Z (2008) Group decision making based on multiple types of linguistic preference relations. Inf Sci 178(2):452–467
Xu Z, Yager RR (2006) Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Gen Syst 35(4):417–433
Xu Z, Yager RR (2008) Dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making. Int J Approx Reason 48(1):246–262
Ye J (2009) Multicriteria fuzzy decision-making method based on a novel accuracy function under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):6899–6902
Yu G-F, Li D-F, Qiu J-M, Ye Y-F (2017) Application of satisfactory degree to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(1):1019–1028
Yue Z (2011) Deriving decision makers weights based on distance measure for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 38(9):11665–11670
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang F, Ignatius J, Lim CP, Zhao Y (2014) A new method for deriving priority weights by extracting consistent numerical-valued matrices from interval-valued fuzzy judgement matrix. Inf Sci 279:280–300
Zhang X, Xu Z (2015) Soft computing based on maximizing consensus and fuzzy topsis approach to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making. Appl Soft Comput 26:42–56
Zhao X, Lin R, Wei G (2013) Fuzzy prioritized operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making. Appl Math Model 37(7):4759–4770
Zhong LW, Luo SC, Wu LD, Xu L, Yang JH, Tang GC (2014) A two-stage approach for surgery scheduling. J Comb Optim 27(3):545C556
Zhong LW, Tang GC (2017) Preface, special issue on combinatorial optimization in health care. J Comb Optim 24(1–2):3C5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research supported by NSFC (11201333).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gai, L., Ji, J. An integrated method to solve the healthcare facility layout problem under area constraints. J Comb Optim 37, 95–113 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-017-0212-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-017-0212-3