Abstract
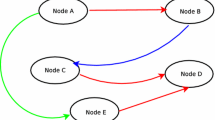
Link Prediction Problem (LPP) is defined as the likelihood of a future connection between two nodes on a network that does not currently have a link between them. Usually, the description of LPP in online social networks is done in a single-layer, while this can lead to incorrect modeling of real-world details. Hence, LPP is described as multi-layer networks that involve performing predictions on a target layer taking into account the information of other layers. Multiplex networks are a common type of multi-layer network with the same nodes and different links in each layer. Because the topological structure is correlated between different layers in MSN, the LPP solution can be improved by combining information from different layers. This paper introduces a method for LPP on Multiplex Social Networks (MSN) based on discovering dependable pathways. Dependable pathways are defined by considering the importance of each link in the communication paths between nodes, where we present the importance of links by network mapping as a weighted network. The weight of the links is calculated based on the topological structures between the different layers in MSN by formulating the interlayer and intralayer links. Finally, we propose a new similarity measure with the development of the Local Random Walk measure based on dependable pathways and weighted network. This measure records network structure using pure random walk to calculate similarities and discovery of unknown links. Experimental studies have been performed on seven MSN real-world datasets. The results show the superiority of the proposed method compared to some state-of-the-art methods such as MLRW and LPIS.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Barabâsi AL, Jeong H, Néda Z, Ravasz E, Schubert A, Vicsek T (2002) Evolution of the social network of scientific collaborations. Phys A 311(3–4):590–614
Bianconi G (2019) Multilayer networks: structure and dynamics. APS March Meet Abstr 2019:S53-002
Bobadilla J, Ortega F, Hernando A, Gutiérrez A (2013) Recommender systems survey. Knowl Based Syst 46:109–132
Ghobaei-Arani M, Shahidinejad A (2021) An efficient resource provisioning approach for analyzing cloud workloads: a metaheuristic-based clustering approach. J Supercomput 77(1):711–750
Ghobaei-Arani M, Shamsi M, Rahmanian AA (2017) An efficient approach for improving virtual machine placement in cloud computing environment. J Exp Theor Artif Intell 29(6):1149–1171
Gupta N, Singh A (2014) A novel strategy for link prediction in social networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 CoNEXT on student workshop, pp 12–14
Hmimida M, Kanawati R (2015) Community detection in multiplex networks: a seed-centric approach. Netw Heterog Media 10(1):71
Jalili M, Orouskhani Y, Asgari M, Alipourfard N, Perc M (2017) Link prediction in multiplex online social networks. Royal Soc Open Sci 4(2):160863
Katz L (1953) A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika 18(1):39–43
Kuhnle A, Alim MA, Li X, Zhang H, Thai MT (2018) Multiplex influence maximization in online social networks with heterogeneous diffusion models. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 5(2):418–429
Kuncheva Z, Montana G (2015) Community detection in multiplex networks using locally adaptive random walks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining 2015, pp 1308–1315
Kuo TT, Yan R, Huang YY, Kung PH, Lin SD (2013) Unsupervised link prediction using aggregative statistics on heterogeneous social networks. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 775–783
Lei C, Ruan J (2013) A novel link prediction algorithm for reconstructing protein–protein interaction networks by topological similarity. Bioinformatics 29(3):355–364
Lorrain F, White HC (1971) Structural equivalence of individuals in social networks. J Math Soc 1(1):49–80
Lü L, Jin CH, Zhou T (2009) Similarity index based on local paths for link prediction of complex networks. Phys Rev E 80(4):046122
Malik D, Singh A (2020) Link prediction in multilayer networks. Int J Bus Intell Data Min 16(4):490–505
Maruyama WT, Digiampietri LA (2016) Co-authorship prediction in academic social network. In: Anais do V Brazilian workshop on social network analysis and mining, pp 61–72. SBC.
Mishra S, Singh SS, Kumar A, Biswas B (2022) MNERLP-MUL: merged node and edge relevance based link prediction in multiplex networks. J Comput Sci 60:101606
Nasiri E, Berahmand K, Li Y (2021) A new link prediction in multiplex networks using topologically biased random walks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 151:111230
Nasiri E, Berahmand K, Samei Z, Li Y (2022) Impact of centrality measures on the common neighbors in link prediction for multiplex networks. Big Data 10(2):138–150
Ou Q, Jin YD, Zhou T, Wang BH, Yin BQ (2007) Power-law strength-degree correlation from resource-allocation dynamics on weighted networks. Phys Rev E 75(2):021102
Pan L, Zhou T, Lü L, Hu CK (2016) Predicting missing links and identifying spurious links via likelihood analysis. Sci Rep 6(1):1–10
Papadimitriou A, Symeonidis P, Manolopoulos Y (2012) Fast and accurate link prediction in social networking systems. J Syst Softw 85(9):2119–2132
Pujari M, Kanawati R (2015) Link prediction in multiplex networks. Netw Heterog Media 10(1):17
Rezaeipanah A, Ahmadi G, Sechin Matoori S (2020) A classification approach to link prediction in multiplex online ego-social networks. Soc Netw Anal Min 10(1):1–16
Rezaeipanah A, Amiri P, Jafari S (2021) Performing the kick during walking for robocup 3d soccer simulation league using reinforcement learning algorithm. Int J Soc Robot 13(6):1235–1252
Rubin FRANK (1978) Enumerating all simple paths in a graph. IEEE Trans Circ Syst 25(8):641–642
Samei Z, Jalili M (2019) Application of hyperbolic geometry in link prediction of multiplex networks. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Tang J, Cui Y, Li Q, Ren K, Liu J, Buyya R (2016) Ensuring security and privacy preservation for cloud data services. ACM Comput Surv CSUR 49(1):1–39
Tang R, Chen X, Wei C, Li Q, Wang W, Wang H, Wang W (2022) Interlayer link prediction based on multiple network structural attributes. Comput Netw 203:108651
Wang P, Xu B, Wu Y, Zhou X (2015) Link prediction in social networks: the state-of-the-art. Sci China Inf Sci 58(1):1–38
Wang G, Wang Y, Li J, Liu K (2021) A multidimensional network link prediction algorithm and its application for predicting social relationships. J Comput Sci 53:101358
Yang R, Yang C, Peng X, Rezaeipanah A (2022) A novel similarity measure of link prediction in multi-layer social networks based on reliable paths. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 34(10):e6829
Zhou T, Lü L, Zhang YC (2009) Predicting missing links via local information. Eur Phys J B 71(4):623–630
Acknowledgements
Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20180209. Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China under Grant 18KJD520004. Research Funds of Suzhou Vocational Institute of Industrial Technology 2019kyqd018. Innovative Research Team Project of Suzhou Institute of Industrial Technology (2021KYTD003).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Li, T. & Berahmand, K. An effective link prediction method in multiplex social networks using local random walk towards dependable pathways. J Comb Optim 45, 31 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-022-00961-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-022-00961-z