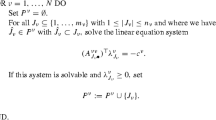Abstract
The generalized Nash equilibrium is a Nash game, where not only the players’ cost functions, but also the constraints of a player depend on the rival players decisions. We present a globally convergent algorithm that is suited for the computation of a normalized Nash equilibrium in the generalized Nash game with jointly convex constraints. The main tool is the regularized Nikaido–Isoda function as a basis for a locally convergent nonsmooth Newton method and, in another way, for the definition of a merit function for globalization. We conclude with some numerical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarke, F.H.: Optimization and Nonsmooth Analysis. Wiley, Amsterdam (reprinted by SIAM, 1990) (1983)
De Luca T., Facchinei F., Kanzow C.: A semismooth equation approach to the solution of nonlinear complementarity problems. Math. Program. 75, 407–439 (1996)
De Luca T., Facchinei F., Kanzow C.: A theoretical and numerical comparison of some semismooth algorithms for complementarity problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 16, 173–205 (2000)
Facchinei F., Kanzow C.: Generalized Nash equilibrium problems. 4OR—Q. J. Oper. Res. 5, 173–210 (2007)
Facchinei F., Kanzow C.: Penalty methods for the solution of generalized Nash equilibrium problems. SIAM J. Optim. 20, 2228–2253 (2010)
Facchinei H., Fischer A., Piccialli V.: On generalized Nash games and variational inequalities. Oper. Res. Lett. 35, 159–164 (2007)
Facchinei F., Soares J.: A new merit function for nonlinear complementarity problems and a related algorithm. SIAM J. Optim. 7, 225–247 (1997)
Flåm, S.D., Ruszczyński, R.: Noncooperative convex games: computing equilibrium by partial regularization. IIASA Working Paper 94–42, Laxenburg, Austria (1994)
Fukushima M.: Restricted generalized Nash equilibria and controlled penalty algorithm. Comput. Manage. Sci. 8, 201–218 (2011)
Janin R.: Directional derivative of the marginal function in nonlinear programming. Math. Program. Study 21, 110–126 (1984)
Kanzow C., Fukushima M.: Solving box constrained variational inequalities by using the natural residual with D-gap function globalization. Oper. Res. Lett. 23, 45–51 (1998)
Krawczyk J.B., Uryasev S.: Relaxation algorithms to find Nash equilibria with economic applications. Environ. Model. Assess. 5, 63–73 (2000)
Kubota K., Fukushima M.: Gap function approach to the generalized Nash equilibrium problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 144, 511–531 (2010)
Matioli, L.C., Sosa, W., Yuan, J.: A numerical algorithm for finding solutions of a generalized Nash equilibrium problem. Comput. Optim. Appl. (to appear). doi:10.1007/s10589-011-9407-1
Moré J.J., Sorensen D.C.: Computing a trust region step. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 4, 553–572 (1983)
Nabetani K., Tseng P., Fukushima M.: Parametrized variational inequality approaches to generalized Nash equilibrium problems with shared constraints. Comput. Optim. Appl. 48, 423–452 (2011)
Nikaido H., Isoda K.: Note on noncooperative convex games. Pac. J. Math. 5, 807–815 (1955)
Pang, J.-S., Fukushima, M.: Quasi-variational inequalities, generalized Nash equilibria, and multi-leader-follower games. Comput. Manage. Sci. 2, 21–56. [Erratum: ibid. 6, 373–375 (2009).] (2005)
Rosen J.B.: Existence and uniqueness of equilibrium points for concave N-person games. Econometrica 33, 520–534 (1965)
Uryasev S., Rubinstein R.Y.: On relaxation algorithms in computation of noncooperative equilibria. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 39, 1263–1267 (1994)
von Heusinger, A.: Numerical methods for the solution of the generalized Nash equilibrium problem, PhD Thesis, Institute of Mathematics, University of Würzburg (2009)
von Heusinger A., Kanzow C.: SC 1-optimization reformulations of the generalized Nash equilibrium problem. Optim. Methods. Softw. 23, 953–973 (2008)
von Heusinger A., Kanzow C.: Optimization reformulations of the generalized Nash equilibrium problem using Nikaido–Isoda-type functions. Comput. Optim. Appl. 43, 353–377 (2009)
von Heusinger A., Kanzow C.: Relaxation methods for generalized Nash equilibrium problems with inexact line search. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 143, 159–183 (2009)
von Heusinger, A., Kanzow, C., Fukushima, M.: Newton’s method for computing a normalized equilibrium in the generalized Nash game through fixed point formulation. Math. Program. (to appear). doi:10.1007/s10107-010-0386-2
Zhang J.Z., Qu B., Xiu N.H.: Some projection-like methods for the generalized Nash equilibria. Comput. Optim. Appl. 45, 89–109 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreves, A., von Heusinger, A., Kanzow, C. et al. A globalized Newton method for the computation of normalized Nash equilibria. J Glob Optim 56, 327–340 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-011-9824-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-011-9824-9