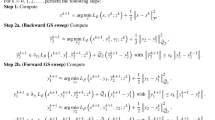In this paper we apply Meyer’s G-norm for image processing problems. We use a definition of the G-norm as norm of linear functionals on BV, which seems to be more feasible for numerical computation. We establish the equivalence between Meyer’s original definition and ours and show that computing the norm can be expressed as an interface problem. This allows us to define an algorithm based on the level set method for its solution. Alternatively we propose a fixed point method based on mean curvature type equations. A computation of the G-norm according to our definition additionally gives functions which can be used for denoising of simple structures in images under a high level of noise. We present some numerical computations of this denoising method which support this claim.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams R.A. (1975). Sobolev Spaces. Academic Press, New York San Francisco, London
Ambrosio L., Fusco N., Pallara D. (2000). Functions of Bounded Variation and Free Discontinuity Problems. Oxford University Press, New York
Aubert G., Aujol J.-F. (2005). Modeling very oscillating signals. application to image processing. Appl. Math. Optim. 51, 163–182
Aujol F., Aubert G., Blanc-Féraud L., Chambolle A. (2005). Image decomposition into a bounded variation component and an oscillating component. J. Math. Imag. Vis. 22, 71–88
Chan T., Esedo \(\bar{g}\)lu S., Nikolova, M. (2004). Algorithms for finding global minimizers of image segmentation and denoising models, preprint, CAM-report, UCLA, 2004.
Chan T.F., Vese L.A. (2001). Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 10, 266–277
Crandall M.G., Lions P.-L. (1984). Two approximations of solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi equations. Math. Comp. 43, 1–19
Ekeland I., Témam R. (1999). Convex analysis and variational problems, vol. 28, SIAM, Philadelphia, PA
Engl H.W., Hanke M., Neubauer A. (1996). Regularization of Inverse Problems. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Enquist B., Tornberg A.-K., Tsai R. (2005). Discretization of dirac delta functions in level set methods. J. Comp. Phys. 207, 28–51
Esedo \(\bar{g}\)lu S., Osher S.J. (2004). Decomposition of mages by the anisotropic Rudin-Osher-Fatemi model. Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 57, 1609–1626
Esedo \(\bar{g}\)lu S., Tsai R. (2006). Threshold dynamics for he piecewise constant mumford-shah functional. J. Comput. Phys. 211, 367–384
Gilbarg D., Trudinger N.S. (1997). Elliptic Partial ifferential Equation of Second-Order. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Giusti E.(1984). Minimal Surfaces and Functions of Bounded Variation, vol. 80 of Monographs in Mathematics, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel
Haddard, A., and Meyer, Y. (2004). Variational methods in image processing, preprint, CAM-report, UCLA, 2004.
Jiang G.-S., Peng D. (2000). Weighted ENO schemes for Hamilton-Jacobi equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 21, 2126–2143
Jiang G.-S., Shu C.-W. (1996). Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 126, 202–228
Kindermann S., Osher S. (2005). Saddle point formulation for a cartoon-texture decomposition, preprint, CAM-report, UCLA, 2005.
Le T.M., Vese L. (2005). Image decomposition using total variation and div(BMO). Multisc. Model. and Simul. 4, 390–423
Liu X.-D., Osher S., Chan T. (1994). Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 115, 200–212
Meyer Y. (2001). Oscillating Patterns in Image Processing and Nonlinear Evolution Equations, vol. 22 of University Lecture Series, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI
Mumford D., Shah J. (1989). Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems. Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 42, 577–685
Osher S., Burger M., Goldfarb D., Xu J., Yin W. (2005). An iterative regularization method for total variation based image restauration. Multisc. Model. Simul. 4, 460–489
Osher S., Fedkiw R. (2003). Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces, vol. 153 of Applied Mathematical Sciences, Springer-Verlag, New York
Osher S., Scherzer O. (2004). G-norm properties of bounded variation regularization. Commun. Math. Sci. 2, 237–254
Osher S., Sethian J.A. (1988). Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79, 12–49
Rudin L.I., Osher S., Fatemi E. (1992). Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D 60, 259–268
Shu C.-W., Osher S. (1988). Efficient implementation of essentially nonoscillatory shock-capturing schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 77, 439–471
Shu C.-W., Osher S. (1989). Efficient implementation of essentially nonoscillatory shock-capturing schemes. II. J. Comput. Phys. 83, 32–78
Strang, G. (1983). L1 and L∞ approximation of vector fields in the plane. In Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations in Applied Science (Tokyo, 1982), vol. 81 of North-Holland Math. Stud., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1983, pp. 273–288.
Sussman M., Smereka P., Osher S. (1994). A level set approach for computing solutions to incompressible two-phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 114, 146–159
Vese L.A., Osher S.J. (2004). Image denoising and decomposition with total variation minimization and oscillatory functions. J. Math. Imaging Vision. 20, 7–18
Zeidler E. (1985). Nonlinear Functional Analysis and its Applications III. Springer-Verlag, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to David Gottlieb on his 60th birthday.
Stefan Kindermann on leave from University Linz, Austria.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kindermann, S., Osher, S. & Xu, J. Denoising by BV-duality. J Sci Comput 28, 411–444 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-006-9074-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-006-9074-z