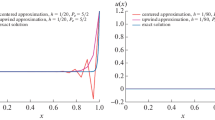
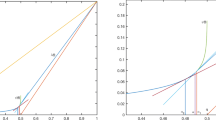
Abstract
In this paper, we study the stability and accuracy of adaptive finite element methods for the convection-dominated convection-diffusion-reaction problem in the two-dimension space. Through various numerical examples on a type of layer-adapted grids (Shishkin grids), we show that the mesh adaptivity driven by accuracy alone cannot stabilize the scheme in all cases. Furthermore the numerical approximation is sensitive to the symmetry of the grid in the region where the solution is smooth. On the basis of these two observations, we develop a multilevel-homotopic-adaptive finite element method (MHAFEM) by combining streamline diffusion finite element method, anisotropic mesh adaptation, and the homotopy of the diffusion coefficient. We use numerical experiments to demonstrate that MHAFEM can efficiently capture boundary or interior layers and produce accurate solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bank, R., Bürger, J., Fichtner, W., Smith, R.: Some upwinding techniques for finite element approximations of convection diffusion equations. Numer. Math. 58, 185–202 (1990)
Bank, R.E., Smith, R.K.: Mesh smoothing using a posteriori error estimates. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 34, 979–997 (1997)
Bank, R.E., Xu, J.: Asymptotically exact a posteriori error estimators, Part I: Grids with superconvergence. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(6), 2294–2312 (2003)
Bank, R.E., Xu, J.: Asymptotically exact a posteriori error estimators, Part II: General unstructured grids. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(6), 2313–2332 (2003)
Bänsch, E., Morin, P., Nochetto, R.H.: An adaptive Uzawa FEM for the Stokes problem: convergence without the inf-sup condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(4), 1207–1229 (2002)
Baumann, C.E., Oden, J.T.: A discontinuous hp finite element method for convection-diffusion problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 175, 311–341 (1999)
Brezzi, F., Franca, L., Russo, A.: Further considerations on residual free bubbles for advection-diffusive equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 166, 25–33 (1998)
Brezzi, F., Franca, L.P., Hughes, T.J.R., Russo, A.: b=∫ g. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 145, 329–339 (1997)
Brezzi, F., Hughes, T.J.R., Marini, L.D., Russo, A., Süli, E.: A priori error analysis of residual-free bubbles for advection-diffusion problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36(4), 1933–1948 (1999)
Brezzi, F., Marini, D., Süli, E.: Residual-free bubbles for advection-diffusion problems: the general error analysis. Numer. Math. 85, 31–47 (2000)
Brezzi, F., Marini, L.D., Pietra, P.: Two-dimensional exponential fitting and applications to drift-diffusion models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 26(6), 1342–1355 (1989)
Brooks, A., Hughes, T.: Streamline upwind/Petrov-Galerkin formulations for convection dominated flows with particular emphasis on the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 32, 199–259 (1982)
Chen, L.: Mesh smoothing schemes based on optimal Delaunay triangulations. In: 13th International Meshing Roundtable, Williamsburg, VA, 2004, pp. 109–120. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque (2004)
Chen, L.: Robust and accurate algorithms for solving anisotropic singularities. PhD thesis, Department of Mathematics, The Pennsylvania State University (2005)
Chen, L., Sun, P., Xu, J.: Multilevel homotopic adaptive finite element methods for convection dominated problems. In: The Proceedings for 15th Conferences for Domain Decomposition Methods. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol. 40, pp. 459–468. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Chen, L., Sun, P., Xu, J.: Optimal anisotropic simplicial meshes for minimizing interpolation errors in L p-norm. Math. Comput. 76(257), 179–204 (2007)
Chen, L., Xu, J.: Stability and accuracy of adapted finite element methods for singularly perturbed problems. Numer. Math. 109(2), 167–191 (2008)
Heinrich, J.C., Huyakorn, P.S., Zienkiewicz, O.C., Mitchell, A.R.: An ‘upwind’ finite element scheme for two-dimensional convective transport equation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 11, 131–143 (1977)
Hemker, P.W.: A singularly perturbed model problem for numerical computation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 76(1–2), 277–285 (1996)
Holmes, M.H.: Introduction to Perturbation Methods. Texts in Applied Mathematics, vol. 20. Springer, New York (1995)
Houston, P., Schwab, C., Suli, E.: Discontinuous hp-finite element methods for advection-diffusion-reaction problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39(6), 2133–2163 (2002)
Huang, W.: Mathematical principles of anisotropic mesh adaptation. Commun. Comput. Phys. 1, 276–310 (2006)
Huang, W., Sun, W.: Variational mesh adaptation II: error estimates and monitor functions. J. Comput. Phys. 184, 619–648 (2003)
Hughes, T.J.R., Brooks, A.: A multidimensional upwind scheme with no crosswind diffusion. In: Hughes, T.J.R. (ed.) Finite Element Methods for Convection Dominated Flows. AMD, vol. 34, pp. 19–35. ASME, New York (1979)
John, V.: A numerical study of a posteriori error estimators for convection-diffusion equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190(5–7), 757–781 (2000)
John, V., Knobloch, P.: On spurious oscillations at layers diminishing (SOLD) methods for convection-diffusion equations: part I—a review. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196(17–20), 2197–2215 (2007)
John, V., Knobloch, P.: On spurious oscillations at layers diminishing (SOLD) methods for convection-diffusion equations: part II—analysis for P1 and Q1 finite elements. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 1997–2014 (2008)
Kang, T., Yu, D.: Some a posteriori error estimates of the finite-difference streamline-diffusion method for convection-dominated diffusion equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 15, 193–218 (2001)
Li, R., Tang, T., Zhang, P.: Moving mesh methods in multiple dimensions based on harmonic maps. J. Comput. Phys. 170(2), 562–588 (2001)
Li, R., Tang, T., Zhang, P.: A moving mesh finite element algorithm for singular problems in two and three space dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 177(2), 365–393 (2002)
Linß, T.: Analysis of a Galerkin finite element method on a Bakhvalov-Shishkin mesh for a linear convection-diffusion problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 20, 621–632 (2000)
Linß, T.: The necessity of Shishkin-decompositions. Appl. Math. Lett. 14, 891–896 (2001)
Linß, T.: Layer-adapted meshes for convection-diffusion problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192, 1061–1105 (2003)
Linß, T., Stynes, M.: Numerical methods on Shishkin meshes for linear convection-diffusion problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190(28), 3527–3542 (2001)
Linß, T., Stynes, M.: The SDFEM on Shishkin meshes for linear convection-diffusion problems. Numer. Math. 87, 457–484 (2001)
Miller, J.J.H., O’Riordan, E., Shishkin, G.I.: On piecewise-uniform meshes for upwind- and central-difference operators for solving singularly perturbed problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 15, 89–99 (1995)
Miller, J.J.H., O’Riordan, E., Shishkin, G.I.: Fitted Numerical Methods for Singular Perturbation Problems. World Scientific, Singapore (1996)
Morton, K.W.: Numerical Solution of Convection-Diffusion Problems. Applied Mathematics and Mathematical Computation, vol. 12. Chapman & Hall, London (1996)
Nooyen, R.R.P.V.: A Petrov-Galerkin mixed finite element method with exponential fitting. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 11(5), 501–524 (1995)
Roos, H.G., Stynes, M., Tobiska, L.: Numerical Methods for Singularly Perturbed Differential Equations. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 24. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Roos, H.G.R.G.: A note on the conditioning of upwind schemes on Shishkin meshes. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 16, 529 (1996)
Shishkin, G.I.: Grid approximation of singularly perturbed elliptic and parabolic equations. PhD thesis, Second doctoral thesis, Keldysh Institute, Moscow (1990) (in Russian)
Stynes, M.: Steady-state convection-diffusion problems. Acta Numer. 14, 445–508 (2005)
Sun, P., Russell, R.D., Xu, J.: A new adaptive local mesh refinement algorithm and its application on fourth order thin film flow problem. J. Comput. Phys. 224(2), 1021–1048 (2007)
Tobiska, L.: Analysis of a new stabilized higher order finite element method for advection-diffusion equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196, 538–550 (2006)
Xu, J., Zikatanov, L.: A monotone finite element scheme for convection diffusion equations. Math. Comput. 68, 1429–1446 (1999)
Zhang, Z., Tang, T.: An adaptive mesh redistribution algorithm for convection-dominated problems. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 1(3), 341–357 (2002)
Zhang, Z.M.: Finite element superconvergence on Shishkin mesh for 2-D convection-diffusion problems. Math. Comput. 72(243), 1147–1177 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, P., Chen, L. & Xu, J. Numerical Studies of Adaptive Finite Element Methods for Two Dimensional Convection-Dominated Problems. J Sci Comput 43, 24–43 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-009-9337-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-009-9337-6