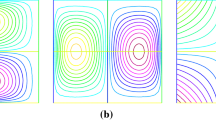
Abstract
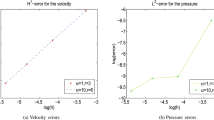
Based on domain decomposition and two-grid discretization, a parallel subgrid stabilized finite element method for simulation of 2D/3D steady convection dominated incompressible flows is proposed and analyzed. In this method, a subgrid stabilized nonlinear Navier–Stokes problem is first solved on a coarse grid where the stabilization term is based on an elliptic projection defined on the same coarse grid, and then corrections are calculated in overlapped fine grid subdomains by solving a linearized problem. By the technical tool of local a priori estimate for finite element solution, error bounds of the approximate solution are estimated. Algorithmic parameter scalings of the method are derived. Numerical results are also given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the method.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behara, S., Mittal, S.: Parallel finite element computation of incompressible flows. Parallel Comput. 35, 195–212 (2009)
Elman, H., Howle, V.E., Shadid, J., et al.: A taxonomy and comparison of parallel block multi-level preconditioners for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 1790–1808 (2008)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: Parallel iterative finite element algorithms based on full domain partition for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60(7), 719–737 (2010)
Henniger, R., Obrist, D., Kleiser, L.: High-order accurate solution of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations on massively parallel computers. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 3543–3572 (2010)
Xu, C.J., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations. Math. Comput. 69, 881–909 (2000)
Xu, C.J., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for nonlinear problems. Adv. Comput. Math. 14, 293–327 (2001)
He, Y.N., Xu, C.J., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Navier–Stokes problem. J. Comput. Math. 24(3), 227–238 (2006)
He, Y.N., Mei, L.Q., Shang, Y.Q.: Newton iterative parallel finite element algorithm for the steady Navier–Stokes equations. J. Sci. Comput. 44(1), 92–106 (2010)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel two-level linearization method for incompressible flow problems. Appl. Math. Lett. 24, 364–369 (2011)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N., Luo, Z.D.: A comparison of three kinds of local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Fluids 40, 249–257 (2011)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: A parallel Oseen-linearized algorithm for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 209–212, 172–183 (2012)
Ma, Y.C., Zhang, Z.M., Ren, C.F.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretization for the stream function form of Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 175, 786–813 (2006)
Ma, F.Y., Ma, C.Y., Wo, W.F.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretization for steady Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Mech. 28(1), 27–35 (2007)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N., Kim, D.W., Zhou, X.J.: A new parallel finite element algorithm for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 47, 1262–1279 (2011)
Erturk, E., Corke, T., Gokcol, C.: Numerical solutions of 2-D steady incompressible driven cavity flow at high Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 48, 747–774 (2005)
Layton, W., Lee, H., Peterson, J.: A defect-correction method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 129, 1–19 (2002)
Zhang, Y., He, Y.N.: Assessment of subgrid-scale models for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 234, 593–604 (2010)
Shang, Y.Q.: A two-level subgrid stabilized Oseen iterative method for the steady Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 233, 210–226 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel subgrid stabilized finite element method based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the Navier–Stokes equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 403, 667–679 (2013)
Adams, R.: Sobolev Spaces. Academic Press, New York (1975)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem I: regularity of solutions and second-order error estimates for spatial discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19(2), 275–311 (1982)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Approximation of the Navier–Stokes Equations. Springer, Berlin (1979)
Nitsche, J., Schatz, A.H.: Interior estimates for Ritz–Galerkin methods. Math. Comput. 28, 937–955 (1974)
Schatz, A.H., Wahlbin, L.B.: Interior maximum-norm estimates for finite element methods. Math. Comput. 31, 414–442 (1977)
Schatz, A.H., Wahlbin, L.B.: Interior maximum-norm estimates for finite element methods, part II. Math. Comput. 64, 907–928 (1995)
Arnold, D.N., Liu, X.: Local error estimates for finite element discretizations of the Stokes equations. RAIRO M2AN 29, 367–389 (1995)
Fortin, M.: Calcul numérique des ecoulements fluides de Bingham et des fluides Newtoniens incompressible par des méthodes d’eléments finis. Doctoral thesis, Université de Paris VI (1972)
Hood, P., Taylor, C.: A numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations using the finite element technique. Comput. Fluids 1, 73–100 (1973)
Crouzeix, M., Raviart, P.A.: Conforming and nonconforming finite element methods for solving the stationary Stokes equations. RAIRO Anal. Numer. 7(R–3), 33–76 (1973)
Mansfield, L.: Finite element subspaces with optimal rates of convergence for stationary Stokes problem. RAIRO Anal. Numer. 16, 49–66 (1982)
Layton, W.: A connection between subgrid-scale eddy viscosity and mixed methods. Appl. Math. Comput. 133(1), 147–157 (2002)
Kaya, S., Layton, W., Riviere, B.: Subgrid stabilized defect correction methods for the Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 1639–1654 (2006)
Guermond, J.L., Marra, A., Quartapelle, L.: Subgrid stabilized projection method for 2D unsteady flows at high Reynolds numbers. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 5857–5876 (2006)
Hughes, T., Mazzei, L., Jansen, K.: Large eddy simulation and the variational multiscale method. Comput. Vis. Sci. 3, 47–59 (2000)
John, V., Kaya, S.: A finite element variational multiscale method for the Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26, 1485–1503 (2005)
Kaya, S., Rivire, B.: A two-grid stabilization method for solving the steady-state Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 22, 728–743 (2005)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel two-level finite element variational multiscale method for the Navier–Stokes equations. Nonlinear Anal. 84, 103–116 (2013)
John, V., Kindl, A.: Numerical studies of finite element variational multiscale methods for turbulent flow simulations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 841–852 (2010)
Hecht, F., Pironneau, O., Ohtsuka, K.: FreeFem++, Version 3.9-2. http://www.freefem.org. Accessed 08 Dec 2010
He, Y.N., Li, J.: Convergence of three iterative methods based on finite element discretization for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1351–1359 (2009)
Layton, W.: A two level discretization method for the Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 5(26), 33–38 (1993)
Ghia, U., Ghia, K., Shin, C.: High-Re solutions for incompressible flow using the Navier–Stokes equations and a multigrid method. J. Comput. Phys. 48, 387–411 (1982)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11361016), the Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry, the Scientific Research Foundation of Southwest University, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. SWU113095), and the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province, China (No. [2013]2212). The authors appreciate the valuable comments and suggestions made by the reviewer which led to an improvement of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Y., Huang, S. A Parallel Subgrid Stabilized Finite Element Method Based on Two-Grid Discretization for Simulation of 2D/3D Steady Incompressible Flows. J Sci Comput 60, 564–583 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9806-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9806-9