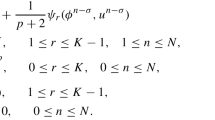Abstract
In this paper, an explicit numerical method and its fast implementation are proposed and discussed for the solution of a wide class of semilinear parabolic equations including the Allen–Cahn equation as a special case. The method combines decompositions of compact spatial difference operators on a regular mesh with stable and accurate exponential time integrators and efficient discrete FFT-based algorithms. It can deal with stiff nonlinearity and both homogeneous and inhomogeneous boundary conditions of different types based on multistep approximations and analytic evaluations of time integrals. Numerical experiments demonstrate effectiveness of the new method for both linear and nonlinear model problems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, S., Cahn, J.W.: A microscopic theory for antiphase boundary motion and its application to antiphase domain coarsening. Acta Metall. 27, 1084–1095 (1979)
Chen, L.-Q., Shen, J.: Applications of semi-implicit Fourier-spectral method to phase field equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 108, 147–158 (1998)
Cox, S., Matthews, P.: Exponential time differencing for stiff systems. J. Comput. Phys. 176, 430–455 (2002)
Du, Q., Liu, C., Wang, X.: A phase field approach in the numerical study of the elastic bending energy for vesicle membranes. J. Comput. Phys. 198, 450–468 (2004)
Du, Q., Zhu, W.-X.: Stability analysis and applications of the exponential time differencing schemes and their contour integration modifications. J. Comput. Math. 22, 200–209 (2004)
Du, Q., Zhu, W.-X.: Analysis and applications of the exponential time differencing schemes. BIT Numer. Math. 45, 307–328 (2005)
Evans, L.C., Spruck, J.: Motion of level sets by mean curvature. I. J. Differ. Geom. 33, 635–681 (1991)
Feng, X., Prohl, A.: Numerical analysis of the Allen-Cahn equation and approximation for mean curvature flows. Numer. Math. 94, 33–65 (2003)
Gustafsson, B., Kreiss, H.-O., Oliger, J.: Time Dependent Problems and Difference Methods. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1996)
Hochbruck, M., Lubich, C., Selhofer, H.: Exponential integrators for large systems of differential equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19, 1552–1574 (1998)
Hochbruck, M., Ostermann, A.: Exponential integrators. Acta Numer. 19, 209–286 (2010)
Kessler, D., Nochetto, R.H., Schmidt, A.: A posteriori error control for the Allen–Cahn problem: circumventing Gronwall’s inequality. Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 38, 129–142 (2004)
Krogstad, S.: Generalized integrating factor methods for stiff PDEs. J. Comput. Phys. 203, 72–88 (2005)
Loan, C.V.: Computational Frameworks for the Fast Fourier Transform. SIAM, Philadelphia (1992)
Li, Y., Lee, H.-G., Jeong, D., Kim, J.: An unconditionally stable hybrid numerical method for solving the Allen–Cahn equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 60, 1591–1606 (2010)
de Mottoni, P., Schatzman, M.: Geometrical evolution of developed interfaces. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 347, 1533–1589 (1989)
Nie, Q., Wan, F., Zhang, Y.-T., Liu, X.-F.: Compact integration factor methods in high spatial dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 5238–5255 (2008)
Nie, Q., Zhang, Y.-T., Zhao, R.: Efficient semi-implicit schemes for stiff systems. J. Comput. Phys. 214, 521–537 (2006)
Wang, D., Zhang, L., Nie, Q.: Array-representation integration factor method for high-dimensional systems. J. Comput. Phys. 258, 585–600 (2014)
Wiegmann, A.: Fast Poisson, Fast Helmholtz and fast linear elastrostatic solvers on rectangular parallelepipeds, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Paper #LBNL-43565, (1999)
Xu, C., Tang, T.: Stability analysis of large time-stepping methods for epitaxial growth models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 1759–1779 (2006)
Yang, X., Feng, J., Liu, C., Shen, J.: Numerical simulations of jet pinching-off and drop formation using an energetic variational phase-field method. J. Comput. Phys. 218, 417–428 (2007)
Zhang, L.-B.: Un schéma de semi-discrétisation en temps pour des systèmes différentiels discretises en espace par la méthode de Fourier résolution numérique des équations de Navier-Stokes stationnaires par la méthode multigrille, Ph.D. Dissertation, Universit Paris-Sud XI (1987)
Zhang, J., Du, Q.: Numerical studies of discrete approximations to the Allen–Cahn equation in the sharp interface limit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31, 3042–3063 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Ju’s research is partially supported by the US National Science Foundation under Grant Number DMS-1215659 and the U.S. Department of Energy under Grant Number DE-SC0008087-ER65393. J. Zhang’s research is partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Numbers 11271350 and 91130019. L. Zhu’s research is partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Number 91130019, ISTCP of China under Grant Number 2010DFR00700, China Fundamental Research of Civil Aircraft under Grant Number MJ-F-2012-04, and the State Key Laboratory of Software Development Environment under Grant Number SKLSDE-2014ZX-03. Q. Du’s research is partially supported by the US National Science Foundation under Grant Number DMS-1318586.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, L., Zhang, J., Zhu, L. et al. Fast Explicit Integration Factor Methods for Semilinear Parabolic Equations. J Sci Comput 62, 431–455 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9862-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9862-9
Keywords
- Integration factor method
- Explicit scheme
- Multistep approximation
- Discrete fast transforms
- Diffusion–reaction equation
- Allen–Cahn equation