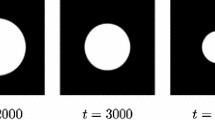
Abstract
We consider in this paper numerical approximations of two-phase incompressible flows with different densities and viscosities. We present a variational derivation for a thermodynamically consistent phase-field model that admits an energy law. Two decoupled time discretization schemes for the coupled nonlinear phase-field model are constructed and shown to be energy stable. Numerical experiments are carried out to validate the model and the schemes for problems with large density and viscosity ratios.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
After we derived the model independently, we learned that the identical model was already derived in [2].
References
Abels, H.: Existence of weak solutions for a diffuse interface model for viscous, incompressible fluids with general densities. Commun. Math. Phys. 289(1), 45–73 (2009)
Abels, H., Garcke, H., Grün, G.: Thermodynamically consistent diffuse interface models for incompressible two-phase flows with different densities. arXiv preprint arXiv:1011.0528 (2010)
Abels, H., Garcke, H., Grün, G.: Thermodynamically consistent, frame indifferent diffuse interface models for incompressible two-phase flows with different densities. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 22, 1150013 (2012)
Abraham, R., Marsden, J.E.: Foundations of Mechanics. Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co., Inc., Advanced Book Program, Reading, MA (1978). Second edition, revised and enlarged, With the assistance of Tudor Ratiu and Richard Cushman
Anderson, D.M., McFadden, G.B., Wheeler, A.A.: Diffuse-interface methods in fluid mechanics. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 139–165 (1998)
Arnold, V.I.: Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics. Springer, New York (1989). Translated from the 1974 Russian original by K. Vogtmann and A. Weinstein, Corrected reprint of the second (1989) edition
Arnold, V.I.: Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (1997)
Becker, R., Feng, X., Prohl, A.: Finite element approximations of the Ericksen–Leslie model for nematic liquid crystal flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46(4), 1704–1731 (2008)
Boyer, F. Nonhomogeneous Cahn–Hilliard fluids. Ann. Inst. H. Poincaré Anal. Non Linéaire 18(2), 225–259 (2001)
Cahn, J.W., Hilliard, J.E.: Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial free energy. J. Chem. Phys. 28, 258–267 (1958)
Chaikin, P.M., Lubensky, T.C.: Principles of Condensed Matter Physics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1995)
Chen, F., Shen, J.: Efficient spectral-Galerkin methods for systems of coupled second-order equations and their applications. J. Comput. Phys. 231(15), 5016–5028 (2012)
Chen, W., Conde, S., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.: A linear energy stable scheme for a thin film model without slope selection. Preprint (2011)
Ding, H., Spelt, P.D.M., Shu, C.: Calculation of two-phase Navier–Stokes flows using phase-field modeling. J. Comput. Phys. 226(2), 2078–2095 (2007)
Weinan, E., Liu, J.-G.: Gauge method for viscous incompressible flows. Commun. Math. Sci. 1(2), 317–332 (2003)
Egorov, Y.V., Shubin, M.A.: Foundations of the Classical Theory of Partial Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (1998). Translated from the 1988 Russian original by R. Cooke, Reprint of the original English edition from the series Encyclopaedia of Mathematical Sciences [ıt Partial differential equations. I, Encyclopaedia Math. Sci., 30, Springer, Berlin, 1992; MR1141630 (93a:35004b)]
Eyre, D.J.: Unconditionally gradient stable time marching the Cahn–Hilliard equation. In: Computational and Mathematical Models of Microstructural Evolution (San Francisco, CA, 1998), Mater. Res. Soc. Sympos. Proc., Warrendale, PA, vol. 529, pp. 39–46, (1998)
Feng, X., He, Y., Liu, C.: Analysis of finite element approximations of a phase field model for two-phase fluids. Math. Comput. 76(258), 539–571 (2007). (electronic)
Fjordholm, U.S., Mishra, S., Tadmor, E.: Well-balanced and energy stable schemes for the shallow water equations with discontinuous topography. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5587–5609 (2011)
Gilbarg, D., Trudinger, N.S.: Elliptic Partial Differential Equations of Second Order. Classics in Mathematics. Springer, Berlin (2001). Reprint of the 1998 edition
Guermond, J.L., Minev, P., Shen, J.: An overview of projection methods for incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 6011–6045 (2006)
Guermond, J.-L., Quartapelle, L.: A projection FEM for variable density incompressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 165(1), 167–188 (2000)
Guermond, J.-L., Salgado, A.: A splitting method for incompressible flows with variable density based on a pressure Poisson equation. J. Comput. Phys. 228(8), 2834–2846 (2009)
Gurtin, M.E., Polignone, D., Vinals, J.: Two-phase binary fluids and immiscible fluids described by an order parameter. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 6(6), 815–831 (1996)
Hirsch, F., Lacombe, G.: Elements of functional analysis, volume 192 of Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Springer, New York (1999). Translated from the 1997 French original by Silvio Levy
Jacqmin, D.: Diffuse interface model for incompressible two-phase flows with large density ratios. J. Comput. Phys. 155(1), 96–127 (2007)
Kim, J.: Phase-field models for multi-component fluid flows. Commun. Comput. Phys. 12(3), 613–661 (2012)
Kubo, R.: The fluctuation-dissipation theorem. Reports on Progress in Physics (1966)
Lin, P., Liu, C., Zhang, H.: An energy law preserving \(C^0\) finite element scheme for simulating the kinematic effects in liquid crystal dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 227(2), 1411–1427 (2007)
Liu, C., Shen, J.: A phase field model for the mixture of two incompressible fluids and its approximation by a Fourier-spectral method. Physica D 179(3–4), 211–228 (2003)
Lowengrub, J., Truskinovsky, L.: Quasi-incompressible Cahn–Hilliard fluids and topological transitions. R. Soc. Lond. Proc. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(1978), 2617–2654 (1998)
Nochetto, R., Pyo, J.-H.: The gauge-Uzawa finite element method part i: the Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43, 1043–1068 (2005)
Onsager, L.: Reciprocal relations in irreversible processes. I. Phys. Rev. 37, 405 (1931)
Onsager, L.: Reciprocal relations in irreversible processes. II. Phys. Rev. 38, 2265 (1931)
Prohl, A.: Projection and quasi-compressibility methods for solving the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. In: Advances in Numerical Mathematics. B. G. Teubner, Stuttgart (1997)
Pyo, J., Shen, J.: Gauge-Uzawa methods for incompressible flows with variable density. J. Comput. Phys. 221, 181–197 (2007)
Rannacher, R.: On Chorin’s projection method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. In: Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 1530 (1991)
Rayleigh, L.: Some general theorems relating to vibrations. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 4, 357–368 (1873)
Rayleigh, L.: On the theory of surface forces II. Philols. Mag. 33, 209 (1892)
Shen, J.: Efficient spectral-Galerkin method I. Direct solvers for second- and fourth-order equations by using Legendre polynomials. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 15, 1489–1505 (1994)
Shen, J.: On error estimates of projection methods for the Navier–Stokes equations: second-order schemes. Math. Comput. 65, 1039–1065 (1996)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: An efficient moving mesh spectral method for the phase-field model of two-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 2978–2992 (2009)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Energy stable schemes for Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model of two-phase incompressible flows. Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 31, 743–758 (2010)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: A phase-field model and its numerical approximation for two-phase incompressible flows with different densities and viscositites. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32, 1159–1179 (2010)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Decoupled, energy stable schemes for phase-field models of two-phase incompressible flows. Submitted (2013)
Shen, J. Modeling and numerical approximation of two-phase incompressible ows by a phase-eld approach. In: Bao, W., Du, Q. (eds.) Multiscale Modeling and Analysis for Materials Simulation, Lecture Note Series, vol. 9. IMS, National University of Singapore, pp. 147–196 (2011)
Shen, J., Yang, X., Wang, Q.: On mass conservation in phase field models for binary fluids. Commun. Comput. Phys. 13, 1045–1065 (2013)
Tadmor, E., Zhong, W.: Energy-preserving and stable approximations for the two-dimensional shallow water equations. “Mathematics and Computation—A Contemporary View”, Proceedings of the Third Abel Symposium, vol. 3. Springer, pp. 67–94 (2008)
van der Waals, J.: The thermodynamic theory of capillarity under the hypothesis of a continuous density variation. J. Stat. Phys. 20, 197–244 (1893)
Wang, C., Liu, J.-G.: Convergence of gauge method for incompressible flow. Math. Comput. 69, 1385–1407 (2000)
Wang, C., Wise, S.M.: An energy stable and convergent finite-difference scheme for the modified phase field crystal equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49, 945–969 (2011)
Yamaleev, N.K., Carpenter, M.H.: A systematic methodology for constructing high-order energy stable weno schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 228(11), 4248–4272 (2009)
Yang, X., Feng, J.J., Liu, C., Shen, J.: Numerical simulations of jet pinching-off and drop formation using an energetic variational phase-field method. J. Comput. Phys. 218, 417–428 (2006)
Yue, P., Feng, J.J., Liu, C., Shen, J.: A diffuse-interface method for simulating two-phase flows of complex fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 515, 293–317 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The research of C. Liu is partially supported by NSF DMS-1109107 and DMS-1216938. The research of J. Shen is partially supported in part by NSF DMS-1217066 and AFOSR FA9550-11-1-0328. The work of X. Yang is partially supported by SC EPSCOR GEAR program, AFOSR FA9550-12-1-0178 and NSF DMS-1200487.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Shen, J. & Yang, X. Decoupled Energy Stable Schemes for a Phase-Field Model of Two-Phase Incompressible Flows with Variable Density. J Sci Comput 62, 601–622 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9867-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9867-4