Abstract
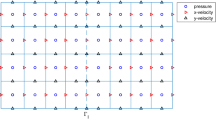
For decades, the widely used finite difference method on staggered grids, also known as the marker and cell (MAC) method, has been one of the simplest and most effective numerical schemes for solving the Stokes equations and Navier–Stokes equations. Its superconvergence on uniform meshes has been observed by Nicolaides (SIAM J Numer Anal 29(6):1579–1591, 1992), but the rigorous proof is never given. Its behavior on non-uniform grids is not well studied, since most publications only consider uniform grids. In this work, we develop the MAC scheme on non-uniform rectangular meshes, and for the first time we theoretically prove that the superconvergence phenomenon (i.e., second order convergence in the \(L^2\) norm for both velocity and pressure) holds true for the MAC method on non-uniform rectangular meshes. With a careful and accurate analysis of various sources of errors, we observe that even though the local truncation errors are only first order in terms of mesh size, the global errors after summation are second order due to the amazing cancellation of local errors. This observation leads to the elegant superconvergence analysis even with non-uniform meshes. Numerical results are given to verify our theoretical analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner, S., Scott, L.R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Cockburn, B., Kanschat, G., Schötzau, D.: A locally conservative LDG method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comp. 74, 1067–1095 (2005)
Daly, B.J., Harlow, F.H., Shannon, J.P., Welch, J.E.: The MAC Method, Tech. report LA-3425, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, University of California (1965)
Girault, V., Lopez, H.: Finite-element error estimates for the MAC scheme. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 16, 347–379 (1996)
Gustafsson, B., Nilsson, J.: Boundary conditions and estimates for the steady Stokes equations on staggered grids. J. Sci. Comput. 15, 29–59 (2000)
Han, H., Wu, X.: A new mixed finite element formulation and the MAC method for the Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35(2), 560–571 (1998)
Huang, Y., Li, J., Wu, C., Yang, W.: Superconvergence analysis for linear tetrahedral edge elements. J. Sci. Comput. doi:10.1007/s10915-014-9848-7
Huang, Y., Li, J., Yang, W., Sun, S.: Superconvergence of mixed finite element approximations to 3-D Maxwell’s equations in metamaterials. J. Comp. Phys. 230, 8275–8289 (2011)
Huang, Y., Zhang, S.: Supercloseness of the divergence-free finite element solutions on rectangular grids. Commun. Math. Stat. 1, 143–162 (2013)
Ito, K., Qiao, Z.: A high order compact MAC finite difference scheme for the Stokes equations: augmented variable approach. J. Comp. Phys. 227, 8177–8190 (2008)
Kanschat, G.: Divergence-free discontinuous Galerkin schemes for the Stokes equations and the MAC scheme. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 56, 941–950 (2008)
Lebedev, V.L.: Difference analogues of orthogonal decompositions, fundamental differential operators and certain boundary-value problems of mathematical physics. Z. Vycisl. Mat. i Mat. Fiz. 4, 449–465 (1964)
Li, J., Huang, Y.: Time-Domain Finite Element Methods for Maxwell’s Equations in Metamaterials, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 43. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Li, M., Tang, T., Fornberg, B.: A compact fourth-order finite difference scheme for the steady incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 20, 1137–1151 (1995)
Minev, P.D.: Remarks on the links between low-order DG methods and some finite-difference schemes for the Stokes problem. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 58, 307–317 (2008)
Monk, P., Süli, E.: A convergence analysis of Yee’s scheme on nonuniform grids. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32(2), 393–412 (1994)
Nicolaides, R.A.: Analysis and convergence of the MAC scheme I. The linear problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(6), 1579–1591 (1992)
Nicolaides, R.A., Wu, X.: Analysis and convergence of the MAC scheme. II. Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 65, 29–44 (1996)
Qiao, Z., Yao, C., Jia, S.: Superconvergence and extrapolation analysis of a nonconforming mixed finite element approximation for time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations. J. Sci. Comput. 46, 1–19 (2011)
Rannacher, R., Turek, S.: Simple nonconforming quadrilateral Stokes element. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 8, 97–111 (1992)
Samelson, R., Temam, R., Wang, C., Wang, S.: Surface pressure Poisson equation formulation of the primitive equations: numerical schemes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41, 1163–1194 (2003)
Samelson, R., Temam, R., Wang, C., Wang, S.: A fourth-order numerical method for the planetary geostrophic equations with inviscid geostrophic balance. Numer. Math. 107, 669–705 (2007)
Süli, E.: Convergence of finite volume schemes for Poisson’s equation on nonuniform meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28(5), 1419–1430 (1991)
Weiser, A., Wheeler, M.F.: On convergence of block-centered finite differences for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 25(2), 351–375 (1988)
Yang, Y., Shu, C.-W.: Analysis of optimal superconvergence of discontinuous Galerkin method for linear hyperbolic equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 3110–3133 (2012)
Zhang, Z. (ed.): Special issues of “Superconvergence and a Posteriori Error Estimates in Finite Element Methods”. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model 2(1), 1–126 (2005) and 3(3), 255–376 (2006)
Acknowledgments
J. Li would like to thank UNLV for granting his sabbatical leave during spring 2014 so that he could enjoy his time working on this during his stay at KAUST. S. Sun would like to acknowledge that research reported in this publication was supported in part by KAUST. Finally, the authors like to thank two anonymous referees for their insightful comments that improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Sun, S. The Superconvergence Phenomenon and Proof of the MAC Scheme for the Stokes Equations on Non-uniform Rectangular Meshes. J Sci Comput 65, 341–362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9963-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9963-5