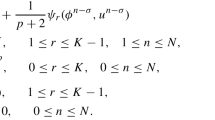Abstract
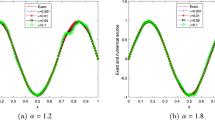
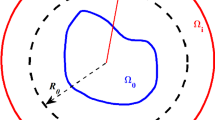
In this paper, we study the fictitious domain method with distributed Lagrange multiplier for the jump-coefficient parabolic problems with moving interfaces. The equivalence between the fictitious domain weak form and the standard weak form of a parabolic interface problem is proved, and the uniform well-posedness of the full discretization of fictitious domain finite element method with distributed Lagrange multiplier is demonstrated. We further analyze the convergence properties for the fully discrete finite element approximation in the norms of \(L^2\), \(H^1\) and a new energy norm. On the other hand, we introduce a subgrid integration technique in order to allow the fictitious domain finite element method to be performed on the triangular meshes without doing any interpolation between the authentic domain and the fictitious domain. Numerical experiments confirm the theoretical results, and show the good performances of the proposed schemes.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auricchio, F., Boffi, D., Gastaldi, L., Lefieux, A., Reali, A.: On a fictitious domain method with distributed Lagrange multiplier for interface problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 95, 36–50 (2015)
Bastian, P., Engwer, C.: An unfitted finite element method using discontinuous Galerkin. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 79(12), 1557–1576 (2009)
Bedrossian, J., Von Brecht, J.H., Zhu, S., Sifakis, E., Teran, J.M.: A second order virtual node method for elliptic problems with interfaces and irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 229(18), 6405–6426 (2010)
Boffi, D., Gastaldi, L., Ruggeri, M.: Mixed formulation for interface problems with distributed Lagrange multiplier. Comput. Math. Appl. 68(12, Part B), 2151–2166 (2014)
Chen, Z., Zou, J.: Finite element methods and their convergence for elliptic and parabolic interface problems. Numer. Math. 79(2), 175–202 (1998)
Ciarlet, P.G.: Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia (2002)
Cui, S.: Well-posedness of a multidimensional free boundary problem modelling the growth of nonnecrotic tumors. J. Funct. Anal. 245, 1–18 (2007)
Dillon, R.H., Fauci, L.J.: An integrative model of internal axoneme mechanics and external fluid dynamics in ciliary beating. J. Theor. Biol. 207, 415–430 (2000)
Donea, J., Giuliani, S., Halleux, J.P.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian finite element method for transient dynamic fluid-structure interactions. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 33(1), 689–723 (1982)
Escherb, J., Zhoua, F., Cui, S.: Well-posedness and stability of a free boundary problem modeling the growth of multi-layer tumors. J. Differ. Equ. 244, 2909–2933 (2008)
Gander, M., Japhet., C.: Algorithm 932: PANG: software for nonmatching grid projections in 2D and 3D with linear complexity. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS), 40(1):Article No. 6, (2013)
Gilmanov, A., Sotiropoulos, F.: A hybrid Cartesian/immersed boundary method for simulating flows with 3d, geometrically complex, moving bodies. J. Comput. Phys. 207(2), 457–492 (2005)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms, 1st edn. Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated (2011)
Glowinski, R., Kuznetsov, Y.: Distributed lagrange multipliers based on fictitious domain method for second order elliptic problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196(8), 1498–1506 (2007)
Glowinski, R., Pan, T.W., Hesla, T.I., Joseph, D.D.: A distributed Lagrange multiplier/fictitious domain method for particulate flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 25(5), 755–794 (1999)
Glowinski, R., Pan, T.W., Hesla, T.I., Joseph, D.D., Périaux, J.: A fictitious domain approach to the direct numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow past moving rigid bodies: application to particulate flow. J. Comput. Phys. 169(2), 363–426 (2001)
Gong, Y., Li, B., Li, Z.: Immersed-interface finite-element methods for elliptic interface problems with nonhomogeneous jump conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46, 472–495 (2008)
Gupta, S.C.: The Classical Stefan Problem: Basic Concepts. Modelling and Analysis. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2003)
Hansbo, A., Hansbo, P.: An unfitted finite element method, based on Nitsches method, for elliptic interface problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 191(47C48), 5537–5552 (2002)
He, X., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: Interior penalty bilinear IFE discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficient. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 23(3), 467–483 (2010)
Hirth, C., Amsden, A.A., Cook, J.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian computing method for all flow speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 14(3), 227–253 (1974)
Huang, J.G., Zou, J.: Some new a priori estimates for second-order elliptic and parabolic interface problems. J. Differ. Equ. 184(2), 570–586 (2002)
Li, Z.L.: The immersed interface method using a finite element formulation. Appl. Numer. Math. 27(3), 253–267 (1998)
Liu, C., Shen, J.: A phase field model for the mixture of two incompressible fluids and its approximation by a Fourier-spectral method. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 179(34), 211–228 (2003)
Muntean, A.: Well-posedness of a moving-boundary problem with two moving reaction strips. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10, 2541–2557 (2009)
Nicaise, S.: Polygonal Interface Problems. Methoden und Verfahren der Mathematischen Physik (Methods and Procedures in Mathematical Physics), vol. 39. Verlag Peter D. Lang, Frankfurt am Main (1993)
Parvizian, J., Düster, A., Rank, E.: Finite cell method. Comput. Mech. 41(1), 121–133 (2007)
Peskin, C.S., McQueen, D.M.: A three-dimensional computational method for blood flow in the heart. 1. immersed elastic fibers in a viscous incompressible fluid. J. Comput. Phys. 81(2), 372–405 (1989)
Peskin, C.S.: Flow patterns around heart valves: a numerical method. J. Comput. Phys. 10(2), 252–271 (1972)
Peskin, C.S.: The immersed boundary method. Acta Numer. 11, 479–517 (2002)
Portegies, J.W., Peletier, M.A.: Well-posedness of a parabolic moving-boundary problem in the setting of Wasserstein gradient flows. Interfaces Free Bound. 12, 121–150 (2010)
Prüss, J., Simonett, G.: Moving Interfaces and Quasilinear Parabolic Evolution Equations. Monographs in Mathematics, vol. 105, 1st edn. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel (2016)
Sapiro, G., Fedkiw, R.P., Shu, C.W.: Shock capturing, level sets, and PDE based methods in computer vision and image processing: a review of Osher’s contributions. J. Comput. Phys. 185(2), 309–341 (2003)
Shi, X., Thien, N.P.: Distributed Lagrange multiplier/fictitious domain method in the framework of lattice Boltzmann method for fluid-structure interactions. J. Comput. Phys. 206(1), 81–94 (2005)
Sinha, R.K., Deka, B.: On the convergence of finite element method for second order elliptic interface problems. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 27(1), 99–115 (2006)
Wachs, A.: Numerical simulation of steady bingham flow through an eccentric annular cross-section by distributed Lagrange multiplier/fictitious domain and augmented Lagrangian methods. J. Non-Newton Fluid Mech. 142, 183–198 (2007)
Yu, Z.: A DLM/FD method for fluid/flexible-body interactions. J. Comput. Phys. 207(1), 1–27 (2005)
Zhou, Y.C., Zhao, S., Feig, M., Wei, G.W.: High order matched interface and boundary method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. J. Comput. Phys. 213(1), 1–30 (2006)
Zhu, L.D., Peskin, C.S.: Simulation of a flapping flexible filament in a flowing soap film by the immersed boundary method. J. Comput. Phys. 179(2), 452–468 (2002)
Acknowledgments
P. Sun was partially supported by NSF Grant DMS-1418806 and UNLV Faculty Opportunity Award (2013–2015); C. Wang was supported by UNLV Faculty Opportunity Award during his visit at UNLV in 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Sun, P. A Fictitious Domain Method with Distributed Lagrange Multiplier for Parabolic Problems With Moving Interfaces. J Sci Comput 70, 686–716 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0262-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0262-1
Keywords
- Fictitious domain method
- Distributed Lagrange multiplier
- Fully discrete finite element scheme
- Subgrid integration
- Immersed moving interface