Abstract
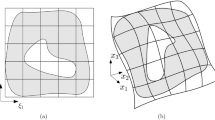
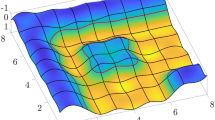
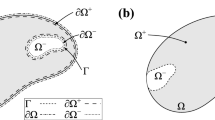
We propose a method which combines isogeometric analysis with the discontinuous Galerkin (DG) method for second and fourth order geometric flows to generate fairing surfaces, which are composed of multiple patches. This technique can be used to tackle a challenging problem in geometric modeling–gluing multi-patches together smoothly to create complex models. Non-uniform rational B-splines (NURBS), the most popular representations of geometric models developed in Computer Aided Design, are employed to describe the geometry and represent the numerical solution. Since NURBS basis functions over two different patches are independent, DG methods can be appropriately applied to glue the multiple patches together to obtain smooth solutions. We present semi-discrete DG schemes to solve the problem, and \(\mathcal {L}^{2}\)-stability is proved for the proposed schemes. Our method enjoys the following advantages. Firstly, the geometric flexibility of NURBS basis functions, especially the use of multiple patches, enable us to construct surface models with complex geometry and topology. Secondly, the constructed geometry is fair. Thirdly, since only the control points of the NURBS patches evolve in accordance with the geometric flows, and their number (degrees of freedom) is very small, our algorithm is very efficient. Finally, this method can be easily formulated and implemented. We apply the method in mean curvature flows and in quasi surface diffusion flows to solve various geometric modeling problems, such as minimal surface generation, surface blending and hole filling, etc. Examples are provided to illustrate the effectiveness of our method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolatos, A., Schmidt, R., Wuchner, R., Bletzinger, K.U.: A Nitsche-type formulation and comparison of the most common domain decomposition methods in isogeometric analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 97, 473–504 (2014)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Cockburn, B., Marini, L.D.: Unified analysis of discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39, 1749–1779 (2002)
Bazilevs, Y., Beirao de Veiga, L., Cottrell, J.A., Hughes, T.J.R., Sangalli, G.: Isogeometric analysis: approximation, stability and error estimates for h-refined meshes. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 16(07), 1031–1090 (2006)
Bazilevs, Y., Calo, V.M., Cottrell, J.A., Hughes, T.J.R., Reali, A., Scovazzi, G.: Variational multiscale residual-based turbulence modeling for large eddy simulation of incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 173–201 (2007)
Bazilevs, Y., Calo, V.M., Hughes, T.J.R., Zhang, Y.: Isogeometric fluid-structure interaction: theory, algorithms, and computations. Comput. Mech. 43, 3–37 (2008)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Generating blend surfaces using partial differential equations. Comput. Aided Des. 21(3), 165–171 (1989)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Generating N-sided patches with partial differential equations. In: Advances in Computer Graphics, pp. 129–145. Springer, Berlin, (1989)
Bloor, M.I.G., Wilson, M.J.: Using partial differential equations to generate free-form surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 22(4), 221–234 (1990)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer, Berlin (1991)
Brivadis, E., Buffa, A., Wohlmuth, B., Wunderlich, L.: Isogeometric mortar methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 284, 292–319 (2015)
Chen, C., Xu, G.: Construction of geometric partial differential equations for level sets. J. Comput. Math. 28(1), 105–121 (2010)
Ciarlet, P.G., Raviart, P.A.: A mixed finite element method for the biharmonic equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 24(4), 737–749 (1987)
Clarenz, U., Diewald, U., Dziuk, G., Rumpf, M., Rusu, R.: A finite element method for surface restoration with boundary conditions. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 21(5), 427–445 (2004)
Clarenz, U., Diewald, U., Rumpf, M.: Anisotropic geometric diffusion in surface processing. In: Proceedings of Viz2000, IEEE Visualization, Salt Lake City, Utah, pp. 397–405 (2000)
Cockburn, B., Karniadakis, G., Shu, C.W.: The development of discontinuous Galerkin methods. In: Cockburn, B., Karniadakis, G., Shu, C.W. (eds.) Discontinuous Galerkin Methods: Theory, Computation and Applications. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering. Part I: Overview, vol. 11, pp. 3–50. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Cottrell, J.A., Hughes, T.J.R., Bazilevs, Y.: Isogeometric Analysis: Toward Integration of CAD and FEA. Wiley, Chichester (2009)
Cottrell, J.A., Hughes, T.J.R., Reali, A.: Studies of refinement and continuity in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196, 4160–4183 (2007)
Cottrell, J.A., Reali, A., Bazilevs, Y., Hughes, T.J.R.: Isogeometric analysis of structural vibrations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 5257–5296 (2006)
Deckelnick, K., Dziuk, G.: A fully descrite numerical scheme for weighted mean curvature flow. Numer. Math. 91, 423–452 (2002)
Deckelnick, K., Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: Computation of geometric partial differential equations and mean curvature flow. Acta Numer. 14, 139–232 (2005)
Dedner, A., Madhavan, P., Stinner, B.: Analysis of the discontinuous Galerkin method for elliptic problems on surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 33(3), 952–973 (2012)
Desbrun, M., Meyer, M., Schröder, P., Barr, A.H.: Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow. In: SIGGRAPH99, Los Angeles, USA, pp. 317C324 (2002)
Di Pietro, D.A., Ern, A.: Mathematical Aspects of Discontinuous Galerkin Methods. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Farin, G.: Curves and Surfaces for CAGD, 5th edn. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Burlington (2002)
Gudi, T., Nataraj, N., Pani, A.K.: Mixed discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for the biharmonic equation. J. Sci. Comput. 37(2), 139–161 (2008)
Hughes, T.J.R., Cottrell, J.A., Bazilevs, Y.: Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry, and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 194, 4135–4195 (2005)
Langer, U., Moore, S.E.: Discontinuous Galerkin Isogeometric Analysis of Elliptic PDEs on Surfaces, arXiv:1402.1185 (2014)
Li, M., Xu, G.: \(G^{1}\) B-spline surface construction by geometric partial differential equations. J. Comput. Aided Des. Comput. Graphics 22(7), 1087–1093 (2010)
Ohtake, Y., Belyaev, A.G., Bogaevski, I.A.: Polyhedral surface smoothing with simultaneous mesh regularization. In: Geometric Modeling and Processing Proceedings, pp. 229–237 (2000)
Riviere, B.: Discontinuous Galerkin methods for Solving Elliptic and Parabolic Equations. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, SIAM, Philadelphia (2008)
Schneider, R., Kobbelt, L.: Generating fair meshes with \(G^{1}\) boundary conditions. In: Geometric Modeling and Processing, Hong Kong, China, pp. 251–261 (2000)
Schneider, R., Kobbelt, L.: Geometric fairing of irregular meshes for free-form surface design. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 18(4), 359–379 (2001)
Xu, G., Zhang, Q.: A general framework for surface modeling using geometric partial differential equations. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 18(4), 359–379 (2001)
Xu, G., Zhang, Q.: Geometric Partial Differential Equation Methods in Computational Geometry. Science Press, Beijing (2013)
Yoshizawa, S., Belyaev, A.G.: Fair triangle mesh generation with discrete elastica. In: Geometric Modeling and Processing, Saitama, Japan, pp. 119–123 (2002)
Zhang, F., Xu, Y., Chen, F.: Discontinuous Galerkin methods for isogeometric analysis for elliptic equations on surfaces. Commun. Math. Stat. 2, 431–461 (2014)
Zhao, H., Osher, S., Merriman, B., Kang, M.: Implicit and nonparametric shape reconstruction from unorganized data using a variational level set method. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 80, 295–314 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Research of Yan Xu is supported by NSFC Grant Nos. 11371342 and 11526212. The Research of Falai Chen is supported by NSFC Grant No.11571138.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Xu, Y. & Chen, F. Discontinuous Galerkin Based Isogeometric Analysis for Geometric Flows and Applications in Geometric Modeling. J Sci Comput 71, 525–546 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0307-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0307-5