Abstract
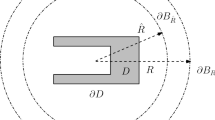
Consider the acoustic wave scattering by an impenetrable obstacle in two dimensions. The model is formulated as a boundary value problem for the Helmholtz equation with a transparent boundary condition. Based on a duality argument technique, an a posteriori error estimate is derived for the finite element method with the truncated Dirichlet-to-Neumann boundary operator. The a posteriori error estimate consists of the finite element approximation error and the truncation error of boundary operator which decays exponentially with respect to the truncation parameter. A new adaptive finite element algorithm is proposed for solving the acoustic obstacle scattering problem, where the truncation parameter is determined through the truncation error and the mesh elements for local refinements are marked through the finite element discretization error. Numerical experiments are presented to illustrate the competitive behavior of the proposed adaptive method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuška, I., Aziz, A.: Survey lectures on mathematical foundations of the finite element method. In: Aziz, A. (ed.) The Mathematical Foundations of the Finite Element Method with Application to the Partial Differential Equations, pp. 5–359. Academic Press, New York (1973)
Bayliss, A., Turkel, E.: Radiation boundary conditions for numerical simulation of waves. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 33, 707–725 (1980)
Bao, G.: Finite element approximation of time harmonic waves in periodic structures. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32, 1155–1169 (1995)
Bao, G., Chen, Z., Wu, H.: Adaptive finite element method for diffraction gratings. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 22, 1106–1114 (2005)
Bao, G., Li, P., Wu, H.: An adaptive edge element method with perfectly matched absorbing layers for wave scattering by periodic structures. Math. Comp. 79, 1–34 (2010)
Bao, G., Wu, H.: Convergence analysis of the perfectly matched layer problems for time-harmonic Maxwells equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43, 2121–2143 (2005)
Berenger, J.-P.: A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 114, 185–200 (1994)
Chen, Z., Wu, H.: An adaptive finite element method with perfectly matched absorbing layers for the wave scattering by periodic structures. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41, 799–826 (2003)
Chen, Z., Liu, X.: An adaptive perfectly matched layer technique for time-harmonic scattering problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43, 645–671 (2005)
Collino, F., Monk, P.: The perfectly matched layer in curvilinear coordinates. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19, 2061–2090 (1998)
Colton, D., Kress, R.: Integral Equation Methods in Scattering Theory. Wiley, New York (1983)
Colton, D., Kress, R.: Inverse Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering Theory, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Engquist, B., Majda, A.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves. Math. Comp. 31, 629–651 (1977)
Ernst, O.G.: A finite-element capacitance matrix method for exterior Helmholtz problems. Numer. Math. 75, 175–204 (1996)
Grote, M., Keller, J.: On nonreflecting boundary conditions. J. Comput. Phys. 122, 231–243 (1995)
Grote, M., Kirsch, C.: Dirichlet-to-Neumann boundary conditions for multiple scattering problems. J. Comput. Phys. 201, 630–650 (2004)
Hagstrom, T.: Radiation boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves. Acta Numer. 8, 47–106 (1999)
Hsiao, G.C., Nigam, N., Pasciak, J.E., Xu, L.: Error analysis of the DtN-FEM for the scattering problem in acoustics via Fourier analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235, 4949–4965 (2011)
Jiang, X., Li, P., Zheng, W.: Numerical solution of acoustic scattering by an adaptive DtN finite element method. Commun. Comput. Phys. 13, 1227–1244 (2013)
Jin, J.: The Finite Element Method in Electromagnetics. Wiley, New York (1993)
Monk, P.: Finite Element Methods for Maxwell’s Equations. Clarendon Press, Oxford (2003)
Schatz, A.H.: An observation concerning Ritz–Galerkin methods with indefinite bilinear forms. Math. Comp. 28, 959–962 (1974)
Teixeira, F.L., Chew, W.C.: Advances in the theory of perfectly matched layers. In: Chew, W.C., et al. (eds.) Fast and Efficient Algorithms in Computational Electromagnetics, pp. 283–346. Artech House, Boston (2001)
Turkel, E., Yefet, A.: Absorbing PML boundary layers for wave-like equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 27, 533–557 (1998)
Wang, Z., Bao, G., Li, J., Li, P., Wu, H.: An adaptive finite element method for the diffraction grating problem with transparent boundary condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53, 1585–1607 (2015)
Watson, G.N.: A Treatise on the Theory of Bessel Functions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1922)
Acknowledgements
The research of X.J. was supported in part by China NSF Grant 11401040 and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities 24820152015RC17. The research of P.L. was supported in part by the NSF Grant DMS-1151308. The research of J.L. was partially supported by the China NSF Grants 11126040 and 11301214. The author of W.Z. was supported in part by China NSF 91430215, by the Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (Grant 11321061), and by the National Magnetic Confinement Fusion Science Program (2015GB110003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Li, P., Lv, J. et al. An Adaptive Finite Element Method for the Wave Scattering with Transparent Boundary Condition. J Sci Comput 72, 936–956 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-017-0382-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-017-0382-2
Keywords
- Acoustic scattering problem
- Adaptive finite element method
- Transparent boundary condition
- A posteriori error estimate