Abstract
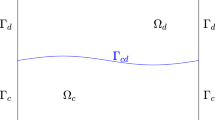
In this paper, we propose and analyze the parallel Robin–Robin domain decomposition method based on the modified characteristic finite element method for the time-dependent dual-porosity-Navier–Stokes model with the Beavers–Joseph interface condition. For the coupling terms, we treat them in an explicit manner which takes advantage of information obtained in previous time steps to construct a non-iteration domain decomposition method. By this means, two single dual-porosity equations and a single Navier–Stokes equation are needed to solve at each time. In particular, we solve the Navier–Stokes equation by the modified characteristic finite element method, which avoids the computational inefficiency caused by the nonlinear convection term. Furthermore, we prove the error convergence of solutions by mathematical induction, whose proof implies the uniform \(L^{\infty }\)-boundedness of the fully discrete velocity solution in conduit flow. Finally, some numerical examples are presented to show the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Discacciati, M.: Domain decomposition methods for the coupling of surface and groundwater flows. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Sausanne, Sausanne, Switzerland (2004)
Cesmelioǧlu, A., Riviere, B.: Primal discontinuous Galerkin methods for time-dependent coupled surface and subsurface flow. J. Sci. Comput. 40(1), 115–140 (2009)
Layton, W., Tran, H., Trenchea, C.: Analysis of long time stability and errors of two partitioned methods for uncoupling evolutionary groundwater-surface water flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(1), 248–272 (2013)
Nassehi, V.: Modelling of combined Navier–Stokes and Darcy flows in crossflow membrane filtration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 53(6), 1253–1265 (1998)
Hanspal, N., Waghode, A., Nassehi, V., Wakeman, R.: Numerical analysis of coupled Stokes/Darcy flows in industrial filtrations. Transp. Porous Media 64(1), 73–101 (2006)
Arbogast, T., Brunson, D.: A computational method for approximating a Darcy–Stokes system governing a vuggy porous medium. Comput. Geosci. 11(3), 207–218 (2007)
Chen, J., Sun, S., Wang, X.: A numerical method for a model of two-phase flow in a coupled free flow and porous media system. J. Comput. Phys. 268, 1–16 (2014)
D’Angelo, C., Zunino, P.: Robust numerical approximation of coupled Stokes’ and Darcy’s flows applied to vascular hemodynamics and biochemical transport. ESAIM Math. Modell. Numer. Anal. 45(3), 447–476 (2011)
Chen, N., Gunzburger, M., Wang, X.: Asymptotic analysis of the differences between the Stokes–Darcy system with different interface conditions and the Stokes–Brinkman system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 368(2), 658–676 (2010)
Mu, M., Xu, J.: A two-grid method of a mixed Stokes–Darcy model for coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(5), 1801–1813 (2007)
Gatica, N., Meddahi, S., Oyarzúa, R.: A conforming mixed finite-element method for the coupling of fluid flow with porous media flow. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 29(1), 86–108 (2008)
Badea, L., Discacciati, M., Quarteroni, A.: Numerical analysis of the Navier–Stokes/Darcy coupling. Numer. Math. 115(2), 195–227 (2010)
Rui, H., Zhang, R.: A unified stabilized mixed finite element method for coupling Stokes and Darcy flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(33–36), 2692–2699 (2009)
Shan, L., Zheng, H.: Partitioned time stepping method for fully evolutionary Stokes–Darcy flow with Beavers–Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(2), 813–839 (2013)
Cao, Y., Chu, Y., He, X., Wei, M.: Decoupling the stationary Navier–Stokes–Darcy system with the Beavers–Joseph–Saffman interface condition. Abstract Appl. Anal. 2013, 1–10 (2013)
Mu, M., Zhu, X.: Decoupled schemes for a non-stationary mixed Stokes–Darcy model. Math. Comput. 79(270), 707–731 (2010)
Chen, W., Gunzburger, M., Dong, S., Wang, X.: Efficient and long-time accurate second-order methods for Stokes–Darcy system. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51(5), 2563–2584 (2013)
Girault, V., Rivière, B.: DG approximation of coupled Navier–Stokes and Darcy equations by Beaver–Joseph–Saffman interface condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(3), 2052–2089 (2009)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X., Wang, X.: Robin–Robin domain decomposition methods for the steady-state Stokes–Darcy system with the Beavers–Joseph interface condition. Numer. Math. 117(4), 601–629 (2011)
Cai, M., Mu, M., Xu, J.: Numerical solution to a mixed Navier–Stokes/Darcy model by the two-grid approach. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(5), 3325–3338 (2009)
He, X., Jiang, N., Qiu, C.: An artificial compressibility ensemble algorithm for a stochastic Stokes–Darcy model with random hydraulic conductivity and interface conditions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 121(4), 712–739 (2020)
Cao, L., He, Y., Li, J., Yang, D.: Decoupled modified characteristic FEMs for fully evolutionary Navier–Stokes–Darcy model with the Beavers–Joseph interface condition. J. Comput. Appl. Math. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2020.113128
Sun, Y., Sun, W., Zheng, H.: Domain decomposition method for the fully-mixed Stokes–Darcy coupled problem. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2020.113578
Discacciati, M., Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Robin–Robin domain decomposition methods for the Stokes–Darcy coupling. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(3), 1246–1268 (2007)
Chen, W., Gunzburger, M., Hua, F., Wang, X.: A parallel Robin–Robin domain decomposition method for the Stokes–Darcy system. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(3), 1064–1084 (2011)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X., Wang, X.: Parallel, non-iterative, multi-physics domain decomposition methods for time-dependent Stokes–Darcy systems. Math. Comput. 83(288), 1617–1644 (2014)
Qiu, C., He, X., Li, J., Lin, Y.: A domain decomposition method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes–Darcy model with Beavers–Joseph interface condition and defective boundary condition. J. Comput. Phys. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109400
Warren, J., Root, P.: The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 3(03), 245–255 (1963)
Aguilera, R.: Naturally Fractured Reservoirs, 1st edn. Pennwell Corp (1980)
Serra, K., Reynolds, A., Raghavan, R.: New pressure transient analysis methods for naturally fractured reservoirs. J. Pet. Technol. 35(12), 2271–2283 (1983)
Hou, J., Qiu, M., He, X., Guo, C., Wei, M., Bai, B.: A dual-porosity-Stokes model and finite element method for coupling dual-porosity flow and free flow. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 38(5), B710–B739 (2016)
Shan, L., Hou, J., Yan, W., Chen, J.: Partitioned time stepping method for a dual-porosity-Stokes model. J. Sci. Comput. 79(1), 389–413 (2019)
Mahbub, M., He, X., Nasu, N., Qiu, C., Zheng, H.: Coupled and decoupled stabilized mixed finite element methods for nonstationary dual-porosity-Stokes fluid flow model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 120(6), 803–833 (2019)
Mahbub, M., Shi, F., Nasu, N., Wang, Y., Zheng, H.: Mixed stabilized finite element method for the stationary Stokes-dual-permeability fluid flow model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2019.112616
Hou, J., Yan, W., Hu, D., He, Z.: Robin–Robin domain decomposition methods for the dual-porosity-conduit system. Adv. Comput. Math. 47(1), 1–33 (2021)
Cao, L., He, Y., Li, J., Mahbub, M.: Decoupled modified characteristic finite element method with different subdomain time steps for nonstationary dual-porosity-Navier–Stokes model. Appl. Numer. Math. 166, 238–271 (2021)
Benque, J., Labadie, G., Ronat, J.: A new finite element method for Navier–Stokes equations coupled with a temperature equation. In: Fourth International Symposium on Finite Elements in Flow Problems, NorthHolland, Amsterdam, pp. 295–302 (1982)
Douglas, J., Russell, T.: Numerical methods for convection-dominated diffusion problems based on combining the method of characteristics with finite element or finite difference procedures. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19(5), 871–885 (1982)
Pironneau, O.: On the transport-diffusion algorithm and its applications to the Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 38(3), 309–332 (1982)
Allievi, A., Bermejo, R.: Finite element modified method of characteristics for the Navier–Stokes equations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 32(4), 439–463 (2000)
Chen, Z., Ewing, R., Jiang, Q., Spagnuolo, A.: Error analysis for characteristics-based methods for degenerate parabolic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(4), 1491–1515 (2002)
Si, Z., Wang, J., Sun, W.: Unconditional stability and error estimates of modified characteristics FEMs for the Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 134(1), 139–161 (2016)
Wang, J., Si, Z., Sun, W.: A new error analysis of characteristics-mixed FEMs for miscible displacement in porous media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52(6), 3000–3020 (2014)
Evans, L.: Partial Differential Equations, 2nd edn. American Mathematical Society (2010)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hua, F., Wang, X.: Coupled Stokes–Darcy model with Beavers–Joseph interface boundary condition. Commun. Math. Sci. 8(1), 1–25 (2010)
Brenner, S., Scott, R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods, 3rd edn. Springer (2008)
Achdou, Y., Guermond, J.: Convergence analysis of a finite element projection/Lagrange–Galerkin method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 37(3), 799–826 (2000)
Heywood, J., Rannacher, R.: Finite-element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem. Part iv: error analysis for second-order time discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27(2), 353–384 (1990)
Süli, E.: Convergence and nonlinear stability of the Lagrange–Galerkin method for the Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 53(4), 459–483 (1988)
Russell, T.: Time stepping along characteristics with incomplete iteration for a Galerkin approximation of miscible displacement in porous media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 22(5), 970–1013 (1985)
Hecht, F., Pironneau, O., Ohtsuka, K.: Freefem++. http://www.freefem.org/
Taber, J., Seright, R.: Horizontal injection and production wells for EOR or waterflooding. In: Permian Basin Oil and Gas Recovery Conference, Midland, Texas, March (1992). https://doi.org/10.2118/23952-MS
Li, J., Yao, M., Mahbub, M., Zheng, H.: The efficient rotational pressure-correction schemes for the coupling Stokes/Darcy problem. Comput. Math. Appl. 79(2), 337–353 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11771348 and No. 11771259 and the Major Research and Development Program of China under Grant No. 2016YFB0200901. It is also supported by the China Scholarship Council Grant 202006280440 and the special support program to develop innovative talents in the region of Shaanxi province, innovation team on computationally efficient numerical methods based on new energy problems in Shaanxi province, and innovation team project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (No. 21JP013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, L., He, Y. & Li, J. A Parallel Robin–Robin Domain Decomposition Method based on Modified Characteristic FEMs for the Time-Dependent Dual-porosity-Navier–Stokes Model with the Beavers–Joseph Interface Condition. J Sci Comput 90, 16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01674-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01674-x