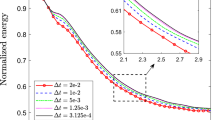
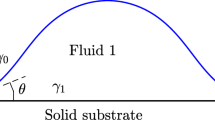
Abstract
In this paper, the binary fluid-surfactant phase field model on evolving surfaces is presented and numerically studied for interfacial sciences. Based on the evolving surface finite element method, the first-order and second-order standard semi-implicit schemes are shown and analyzed to be conditionally stable. The energy dissipation law of the binary fluid-surfactant phase field model does not hold for evolving surfaces with arbitrary surface velocities which can be viewed as an action of external force. Therefore, this paper is dedicated to addressing the difficulties of conditional stability and numerical stiffness caused by the small interfacial parameters instead of energy stability. The first-order and second-order stabilizing approaches are employed to improve the stabilities of semi-implicit schemes. For the efficiency of long time simulation, an adaptive time-stepping technique considering energy evolution and surface velocity is developed. The effectiveness of the proposed stabilizing and adaptive time-stepping approaches is verified by numerical experiments. Various numerical simulations are performed to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method, and numerically investigate the behavior of the binary fluid-surfactant on evolving surfaces.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article. The codes generated during the study are all available on request from the corresponding author Xufeng Xiao.
References
Barreira, R., Elliott, C.M., Madzvamuse, A.: The surface finite element method for pattern formation on evolving biological surfaces. J. Math. Biol. 63(6), 1095–1119 (2011)
Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: A fully discrete evolving surface finite element method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(5), 2677–2694 (2012)
Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: Finite element methods for surface PDEs. Acta Numer. 22, 289–396 (2013)
Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: Finite elements on evolving surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 27(2), 262–292 (2007)
Dziuk, G., Lubich, C., Mansour, D.: Runge–Kutta time discretization of parabolic differential equations on evolving surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 32(2), 394–416 (2012)
Elliott, C.M., Ranner, T.: Evolving surface finite element method for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Numer. Math. 129(3), 483–534 (2015)
Eggleton, C.D., Tsai, T.M., Stebe, K.J.: Tip streaming from a drop in the presence of surfactants. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(4), 048302 (2001)
Fonseca, I., Morini, M., Slastikov, V.: Surfactants in foam stability: a phase-field model. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 183(3), 411–456 (2007)
Feng, X., Tang, T., Yang, J.: Stabilized Crank–Nicolson/Adams–Bashforth schemes for phase field models. East Asian J. Appl. Math. 3(1), 59–80 (2013)
Gompper, G.: Self-assembling amphiphilic systems. Phase Transit Crit Phenomena 16 (1994)
Gu, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z.: An energy-stable finite-difference scheme for the binary fluid-surfactant system. J. Comput. Phys. 270, 416–431 (2014)
Huang, S., Xiao, X., Feng, X.: An adaptive time-stepping method for the phase-field molecular beam epitaxial growth model on evolving surfaces. Appl. Math. Comput. 439, 127622 (2023)
Hu, Y.T., Pine, D.J., Leal, L.G.: Drop deformation, breakup, and coalescence with compatibilizer. Phys. Fluids 12(3), 484–489 (2000)
Hou, D., Qiao, Z.: A linear adaptive BDF2 scheme for phase field crystal equation. ArXiv Preprint arXiv:2206.07625 (2022)
Hansbo, P., Larson, M.G., Zahedi, S.: Characteristic cut finite element methods for convection-diffusion problems on time dependent surfaces. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 293, 431–461 (2015)
Hartmann, E.: A marching method for the triangulation of surfaces. Vis. Comput. 14(3), 95–108 (1998)
He, Y.: A fully discrete stabilized finite-element method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes problem. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 23(4), 665–691 (2003)
Komura, S., Kodama, H.: Two-order-parameter model for an oil-water-surfactant system. Phys. Rev. E 55(2), 1722 (1997)
Liao, H.L., Ji, B., Zhang, L.: An adaptive BDF2 implicit time-stepping method for the phase field crystal model. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 42(1), 649–679 (2022)
Liao, H.L., Ji, B., Wang, L., Zhang, Z.: Mesh-robustness of an energy stable BDF2 scheme with variable steps for the Cahn–Hilliard model. J. Sci. Comput. 92(2), 1–26 (2022)
Lehrenfeld, C., Olshanskii, M.A., Xu, X.: A stabilized trace finite element method for partial differential equations on evolving surfaces. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56(3), 1643–1672 (2018)
Lehto, E., Shankar, V., Wright, G.B.: A radial basis function (RBF) compact finite difference (FD) scheme for reaction-diffusion equations on surfaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39(5), A2129–A2151 (2017)
Laradji, M., Guo, H., Grant, M., Zuckermann, M.J.: The effect of surfactants on the dynamics of phase separation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 4(32), 6715 (1992)
Li, Y., Choi, Y., Kim, J.: Computationally efficient adaptive time step method for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 73(8), 1855–1864 (2017)
Macdonald, C.B., Ruuth, S.J.: Level set equations on surfaces via the closest point method. J. Sci. Comput. 35(2), 219–240 (2008)
Macdonald, C.B., Ruuth, S.J.: The implicit closest point method for the numerical solution of partial differential equations on surfaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(6), 4330–4350 (2010)
O’Connor, D.: Phase field models on evolving surfaces. University of Warwick (2016)
Olshanskii, M.A., Reusken, A.: Trace finite element methods for PDEs on surfaces. Geometrically Unfitted Finite Element Methods and Applications, pp. 211–258 (2017)
Olshanskii, M.A., Xu, X.: A trace finite element method for PDEs on evolving surfaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39(4), A1301–A1319 (2017)
Persson, P.O., Strang, G.: A simple mesh generator in MATLAB. SIAM Rev. 46(2), 329–345 (2004)
Petras, A., Ling, L., Piret, C., Ruuth, S.J.: A least-squares implicit RBF-FD closest point method and applications to PDEs on moving surfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 381, 146–161 (2019)
Petras, A., Ling, L., Ruuth, S.J.: An RBF-FD closest point method for solving PDEs on surfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 370, 43–57 (2018)
Petras, A., Ruuth, S.J.: PDEs on moving surfaces via the closest point method and a modified grid based particle method. J. Comput. Phys. 312, 139–156 (2016)
Ruuth, S.J., Merriman, B.: A simple embedding method for solving partial differential equations on surfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 227(3), 1943–1961 (2008)
Shankar, V., Wright, G.B., Kirby, R.M., Fogelson, A.L.: A radial basis function (RBF)-finite difference (FD) method for diffusion and reaction-diffusion equations on surfaces. J. Sci. Comput. 63(3), 745–768 (2015)
Shen, J.: Long time stability and convergence for fully discrete nonlinear Galerkin methods. Appl. Anal. 38(4), 201–229 (1990)
Sun, M., Feng, X., Wang, K.: Numerical simulation of binary fluid-surfactant phase field model coupled with geometric curvature on the curved surface. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 367, 113123 (2020)
Sun, H., Zhao, X., Cao, H., Yang, R., Zhang, M.: Stability and convergence analysis of adaptive BDF2 scheme for the Swift-Hohenberg equation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 111, 106412 (2022)
Teng, C.H., Chern, I.L., Lai, M.C.: Simulating binary fluid-surfactant dynamics by a phase field model. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst.-B 17(4), 1289 (2012)
Teramoto, T., Yonezawa, F.: Droplet growth dynamics in a water/oil/surfactant system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 235, 329–333 (2001)
Van der Sman, R.G.M., Van der Graaf, S.: Diffuse interface model of surfactant adsorption onto flat and droplet interfaces. Rheol. Acta 46, 3–11 (2006)
Yang, X., Ju, L.: Linear and unconditionally energy stable schemes for the binary fluid-surfactant phase field model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 318, 1005–1029 (2017)
Yang, X.: Numerical approximations for the Cahn–Hilliard phase field model of the binary fluid-surfactant system. J. Sci. Comput. 74(3), 1533–1553 (2018)
Yang, X.: On a novel fully decoupled, second-order accurate energy stable numerical scheme for a binary fluid-surfactant phase-field model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43(2), B479–B507 (2021)
Zhu, G., Kou, J., Sun, S., Yao, J., Li, A.: Decoupled, energy stable schemes for a phase-field surfactant model. Comput. Phys. Commun. 233, 67–77 (2018)
Zhang, J., Yang, X.: Non-iterative, unconditionally energy stable and large time-stepping method for the Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model with Flory-Huggins-de Gennes free energy. Adv. Comput. Math. 46(3), 1–27 (2020)
Zhang, Z., Qiao, Z.: An adaptive time-stepping strategy for the Cahn–Hilliard equation. Commun. Comput. Phys. 11(4), 1261–1278 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and referees for their valuable comments and suggestions which helped us to improve the results of this paper.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is supported by the NSF of China (No. 12001466, No. U19A2079 and No. 11671345), the scientific research plan of universities in Xinjiang (No. XJEDU2020Y001 and No. XJEDU2020I001), and the Research Fund from Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Province (No. 2020D04002).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Xiao, X. & Feng, X. An Adaptive Time-Stepping Method for the Binary Fluid-Surfactant Phase Field Model on Evolving Surfaces. J Sci Comput 95, 29 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02150-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-023-02150-4