Abstract
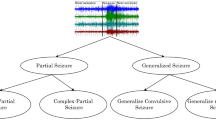
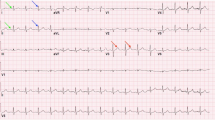
This paper presents the new automated detection method for electrocardiogram (ECG) arrhythmias. The detection system is implemented with integration of complex valued feature extraction and classification parts. In feature extraction phase of proposed method, the feature values for each arrhythmia are extracted using complex discrete wavelet transform (CWT). The aim of using CWT is to compress data and to reduce training time of network without decreasing accuracy rate. Obtained complex valued features are used as input to the complex valued artificial neural network (CVANN) for classification of ECG arrhythmias. Ten types of the ECG arrhythmias used in this study were selected from MIT-BIH ECG Arrhythmias Database. Two different classification tasks were performed by the proposed method. In first classification task (CT-1), whether CWT-CVANN can distinguish ECG arrhythmia from normal sinus rhythm was examined one by one. For this purpose, nine classifiers were improved and executed in CT-1. Second classification task (CT-2) was to recognize ten different ECG arrhythmias by one complex valued classifier with ten outputs. Training and test sets were formed by mixing the arrhythmias in a certain order. Accuracy rates were obtained as 99.8% (averaged) and 99.2% for the first and second classification tasks, respectively. All arrhythmias in training and test phases were classified correctly for both of the classification tasks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Özbay, Y., & Karlik, B., A recognition of ECG arrhythmias using artificial neural networks. Proceedings—23rd Annual Conference, IEEE/EMBS, Oct. 25–28, İstanbul, Turkey, 2001.
Yu, S. N., and Chou, K. T., Integration of independent component analysis and neural networks for ECG beat classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 34:2841–2846, 2008.
Tsipouros, M. G., and Fotiadis, D. I., Automatic arrhythmia detection based on time and time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 74:95–108, 2004. doi:10.1016/S0169-2607(03)00079-8.
Silipo, R., and Marchesi, C., Artificial neural networks for automatic ECG analysis. Signal Process. 46:1417–1425, 1998.
Dokur, Z., and Ölmez, T., ECG beat classification by a novel hybrid neural network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 66:167–181, 2001. doi:10.1016/S0169-2607(00)00133-4.
Özbay, Y., Ceylan, R., and Karlik, B., A fuzzy clustering neural network architecture for classification of ECG arrhythmias. Comput. Biol. Med. 36:376–388, 2006. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2005.01.006.
Gacek, A., and Pedrycz, W., A granular description of ECG signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53:101972–1982, 2006. doi:10.1109/TBME.2006.881782.
Engin, M., ECG beat classification using neuro-fuzzy network. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 25:1715–1722, 2004. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2004.06.014.
Acharya, U. R., Bhat, P. S., Iyengar, S. S., Rao, A., and Dua, S., Classification of heart rate data using artificial neural network and fuzzy equivalence relation. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 36:61–68, 2003. doi:10.1016/S0031-3203(02)00063-8.
Ceylan, R., and Özbay, Y., Comparison of FCM, PCA and WT techniques for classification ECG arrhythmias using artificial neural network. Exp. Syst. Appl. 33:286–295, 2007. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2006.05.014.
Froese, T., Hadjiloucas, S., Galvao, R. K. H., Becerra, V. M., and Coelho, C. J., Comparison of extrasystolic ECG signal classifiers using discrete wavelet transforms. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 27:393–407, 2006. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2005.09.002.
Chazal, P., and Reilly, R. B., A patient-adapting heartbeat classifier using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53:122535–2543, 2006. doi:10.1109/TBME.2006.883802.
Stridh, M., Sörnmo, L., Meurling, C. J., and Olsson, S. B., Sequential characterization of atrial tachyarrhythmias based on ECG time-frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51:1100–114, 2004. doi:10.1109/TBME.2003.820331.
Inan, O. T., Giovangrandi, L., and Kovacs, G. T. A., Robust neural-network-based classification of premature ventricular contractions using wavelet transform and timing interval features. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53:122507–2515, 2006. doi:10.1109/TBME.2006.880879.
Hirose, A., and Hiramatsu, K., Proposal of complex-valued region-based-coupling segmentation neural Networks and the application to radar imaging systems. Proceedings of the IEEE-INNS-ENNS international joint conference on neural networks, IJCNN 2000, vol. 1, pp. 146–151.
Ceylan, M., Ceylan, R., Dirgenali, F., Kara, S., and Özbay, Y., Classification of carotid artery Doppler signals in the early phase of atherosclerosis using complex-valued artificial neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 37:128–36, 2007. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2005.08.005.
Özbay, Y., Kara, S., Latifoğlu, F., Ceylan, R., and Ceylan, M., Complex-valued wavelet artificial neural network for Doppler signals classifying. Artif. Intell. Med. 40:2143–156, 2007.
Beylkin, G., Coifman, R., and Rokhlin, V., Fast wavelet transforms and numerical algorithms. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 44:141–183, 1991. doi:10.1002/cpa.3160440202
Unser, M., Texture classification and segmentation using wavelet frames. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 4:1549–1560, 1995. doi:10.1109/83.469936.
Neumann, J., and Steidl, G., Dual-tree complex wavelet transform in the frequency domain and an application to signal classification. Technical Report, University of Mannheim, 2003.
Donoho, D. L., De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 41:613–627, 1995. doi:10.1109/18.382009.
Fernandes, F. C. A., Directional, shift-insensitive, complex wavelet transforms with controllable redundancy. PhD Thesis, Rice University, 2002.
Oppenheim, A. V., and Lim, J. S., The importance of phase in signals. Proc. IEEE. 69:529–541, 1981. doi:10.1109/PROC.1981.12022.
Lorenzetto, G. P., and Kovesi, P., A phase based image comparison technique. DICTA99, University of Western Australia, 1999.
Driesen, J., and Belmasn, R., Time-frequency analysis in power measurement using complex wavelets. IEEE Int. Symp. Circuits Syst. ISCAS2002:681–684, 2002.
Lina, J. M., Image processing with complex Daubechies wavelets. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 7:211–223, 1997. doi:10.1023/A:1008274210946.
Bulow, T., and Sommer, G., Hypercomplex signals—A novel extension of the analytic signal to the multidimensional case. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49:2844–2852, 2001. doi:10.1109/78.960432.
Selesnick, I. W., Baraniuk, R. G., and Kingsbury, N. G., The dual-tree complex wavelet transform. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 22:123–151, 2005. doi:10.1109/MSP.2005.1550194.
Georgin, N., and Koutsougeras, C., Complex domain backpropagation. IEEE Trans. CAS. 39:330–334, 1992.
Nitta, T., An extension of the back-propagation algorithm to complex numbers. Neural Netw. 10:1391–1415, 1997. doi:10.1016/S0893-6080(97)00036-1.
Nitta, T., An analysis of the fundamental structure of complex-valued neurons. Neural Process. Lett. 12:239–246, 2000. doi:10.1023/A:1026582217675.
Haykin, S., Adaptive filter theory. NJ: Prentice Hall, 2002.
Physiobank Archieve Index, M.: IT-BIH Arrhythmia Database: http://www.physionet.org/physiobank/database (Access time: 16.01.2004).
Özbay, Y., and Ceylan, M., Effects of window types on classification of carotid artery Doppler signals in the early phase of atherosclerosis using complex-valued artificial neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 37:287–295, 2007. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2006.01.008.
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the Coordinatorship of Selcuk University’s Scientific Research Projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özbay, Y. A New Approach to Detection of ECG Arrhythmias: Complex Discrete Wavelet Transform Based Complex Valued Artificial Neural Network. J Med Syst 33, 435–445 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9205-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-008-9205-1