Abstract
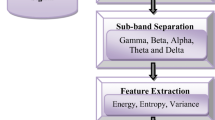
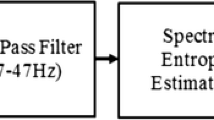
In the present study, both linear and nonlinear EEG synchronization methods so called Coherence Function (CF) and Mutual Information (MI) are performed to obtain high quality signal features in discriminating the Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) and Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) from controls. For this purpose, sleep EEG series recorded from patients and healthy volunteers are classified by using several Feed Forward Neural Network (FFNN) architectures with respect to synchronic activities between C3 and C4 recordings. Among the sleep stages, stage2 is considered in tests. The NN approaches are trained with several numbers of neurons and hidden layers. The results show that the degree of central EEG synchronization during night sleep is closely related to sleep disorders like CSA and OSA. The MI and CF give us cooperatively meaningful information to support clinical findings. Those three groups determined with an expert physician can be classified by addressing two hidden layers with very low absolute error where the average area of CF curves ranged form 0 to 10 Hz and the average MI values are assigned as two features. In a future work, these two features can be combined to create an integrated single feature for error free apnea classification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fogel, R. B., Malhotra, A., Dalagiorgou, G., Robinson, M. K., et al., Anatomic and physiologic predictors of apnea severity in morbidly obese subjects. Sleep 26:150–155, 2003.
Várady, P., Micsik, T., Benedek, S., Benyó, Z., A Novel method for the detection of apnea and hypopnea events in respiration signals. IEEE Trans. BME 49(9):936–942, 2002.
McNames, J. N., Fraser, A. M., Obstructive sleep apnea classification based on spectrogram patterns in the electrocardiogram. Comput. Cardiol. 27:749–752, 2000.
Shinar, Z., Baharav, A., Obstructive sleep apnea detection based on electrocardiogram analysis. Comput. Cardiol. 27:757–760, 2000.
Suhas, S. R., Behbehani, K., Vijendra, S., et al., Time domain analysis of R-wave attenuation envelope for sleep apnea detection. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2:3885–3888, 2004.
Álvarez, D., Hornero, R., et al., Improving diagnostic ability of blood oxygen saturation from overnight pulse oximetry in obstructive sleep apnea detection by means of central tendency measure. Artif. Intell. Med. 41(1):13–24, 2007.
Romero, O. F., Berdin, G., Betanzos, A. A., Bonillo, V. M., A new method for sleep apnea classification using wavelets and feed forward neural networks. Artif. Intell. Med. 34:65–76, 2005.
Tagluk, M. E., Akin, M., Sezgin, N., Classification of sleep apnea by using wavelet transform and artificial neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(2):1600–1607, 2010.
Tagluk, M. E., Sezgin, N., Classification of sleep apnea through sub-band energy of abdominal effort signal using wavelets + neural networks. J. Med. Syst., 2009, doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9330-5.
Bronzino, J. D., The biomedical engineering handbook. 2nd ed. CRC: Boca Raton, pp. 15, 2000.
Aydın, S., Comparison of power spectrum predictors in computing coherence functions for intracortical EEG signals. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37(1):192–200, 2009.
Koenig, T., Prichep, L., et al., Decreased EEG synchronization in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 26:165–171, 2005.
Aydın, S., Computer based synchronization analysis on sleep EEG in insomnia. J. Med. Syst., 2009. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9387-1, (published online on October 21, 2009).
Duman, F., Erdamar, A., Eroǧul, O., Telatar, Z., Yetkin, S., Efficient sleep spindle detection algorithm with decision tree. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(6):9980–9985, 2009.
Culebras, A., Clinical handbook of sleep disorders. Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, 1996.
Susmakova, K., Human sleep and sleep EEG. Meas. Sci. Rev. 4(2):59, 2004.
Boccaletti, S. et al., The synchronization of chaotic systems. Phys. Rep. 366:1–101, 2002.
Pereda, E., Quiroga, R. Q., Nonlinear multivariate analysis of neurophysiologic signals. Prog. Neurobiol. 77:1–37, 2005.
Koenig, T., Lehmann, D., et al., Decreased functional connectivity of EEG theta-frequency activity in first-episode, neuroleptic-native patients with schizophrenia: Preliminary results. Schizophr. Res. 50:55–60, 2001.
Ferria, R., Rundo, F., Bruni, O., Dynamics of the EEG slow-wave synchronization during sleep. Clin. Neurophysiol. 116:2783–2795, 2005.
Pizzagalli, D., Lehmann, D., Gianotti, L., et al., Brain electric correlates of strong belief in paranormal phenomena: Intracerebral EEG source and regional Omega complexity analyses. Neuroimaging 100:139–154, 2000.
Rappelsberger, P., Petsche, H., Probability mapping: Power and coherence analysis of cognitive processes. Brain Topogr. 1:46–54, 1988.
Proakis, J. G., Manolakis, D. G., Digital signal processing. 3rd ed., sec. 12. Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, pp. 925–956, 1996.
Aydın, S., Determination of autoregressive model orders for seizure detection. Turk. J. Elec. Eng. Comp. Sci. 18(1):1–22, 2010. doi:10.3906/elk-0906-83.
Neumaier, A., Shneider, T., Estimation of parameters and Eigen modes of multivariate autoregressive models. ACM Trans. Math. Soft. 27(1):27–57, 2001.
Wang, Q., Shen, Y., Zhang, J. Q., A nonlinear correlation measure for multivariate data set. Physica D 200:287–295, 2005.
Gray, R., Entropy and information theory. Springer: New York, 1990.
Hagan, M. T., Demuth, H. B., Beale, M. H., Neural network design. PWS: Boston, 1996.
Ali, A. N. (ed.), Advanced biosignal processing. 8, C, Springer: Berlin, 2009. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-89506-0.
Aydın, S., Saraoǧlu, H. M., Kara, S., Singular spectrum analysis of insomnia. J. Med. Syst., 2009. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9381-7.
Richard, P. B., Fast training algorithms for multi layer neural nets. IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 2:346–354, 1991.
Gulbag, A., Temurtas, F., A study on quantitative classification of binary gas mixture using neural networks and adaptive neuro fuzzy inference systems. Sens. Actuators 115:252–262, 2006.
Temurtas, F., Tasaltın, C., Temurtas, H., et al., Fuzzy logic and neural network applications on the gas sensor data: Concentration estimation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci., pp. 179–186, 2003.
Saraoǧlu, H. M., Edin, B., E-Nose system for anesthetic dose level detection using artificial neural network. J. Med. Syst. 6:475–482, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akṣahin, M., Aydın, S., Fırat, H. et al. Artificial Apnea Classification with Quantitative Sleep EEG Synchronization. J Med Syst 36, 139–144 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9453-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9453-8