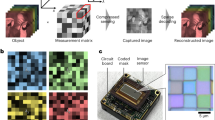
Abstract
The use of a custom filter mosaic overlaying a CMOS/CCD sensor represents a novel idea to multispectral imaging. The innovation provides simple, miniaturized, low cost instrumentation that has many potential biological applications which require a hand-held detector. This makes it extremely adaptable and can serve as an integrated component to distributed diagnosis and home healthcare (D2H2). A mosaicked sensor is a monolithic array of many sensors, arranged in a geometric pattern with each sensor covered by an optical filter sensitive to a specified wavelength. In this way, only one spectral component is sensed at each pixel and the other spectral components must be estimated from neighbors. Although with great potential, one challenge faced by this device, however, is the reconstruction of the high-resolution full-spectral image from the low-resolution input. Due to the physical limitations in fabrication and the usage of the multispectral filter mosaic, two types of degradations exist, including filter misalignment and the missing spectral components, that must be corrected using intelligent algorithms to take full advantage of the hardware capability of the device. In this paper, we first describe a custom geometric correction method to restore the image from the misalignment distortion. We then present a binary tree-based generic demosaicking algorithm to efficiently estimate the missing special components and reconstruct a high-resolution full-spectral image. We choose early detection of pressure ulcer as a targeting area as early stage pressure ulcers and other subcutaneous lesions are nearly invisible in clinical settings, particularly so for dark pigmented skin. We show how the geometric correction and demosaicking algorithms successfully reconstruct a full-spectral image from which apparent contrast enhancement between damaged skin and the normal skin is observed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karacali, B., and Snyder, W., Automatic target detection using multispectral imaging. In: 31st Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop. p. 55. Washington, DC, 2002.
Chen, Y. R., Chao, K., and Kim, M. S., Machine vision technology for agriculture applications. Comput. Electron. Agric. 36(2–3):173–191, 2002.
Blackman, G., Surface inspection—scanning the surface. In: Imaging and Machine Vision Europe, 2009.
Lu, R., and Park, B., Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging for food quality and safety. Sensing and Instrumentation for Food Quality and Safety 2(3):131–132, 2008.
Lu, R., Multispectral imaging for predicting firmness and soluble solids content of apple fruit. Elsevier Journal on Postharvest Biology and Technology 31:147–157, 2004.
Miao, L., Qi, H., and Szu, H., A maximum entropy approach to unsupervised mixed pixel decomposition. IEEE Trans. Image Process 16(4):1008–1021, 2007.
Silva, D. M., and Abileah, R., System and method for multispectral image processing of ocean imagery. United State Patent 6304664, 2010.
Wu, Q., Zeng, L., Ke, H., Zheng, H., Gao, X., and Wang, D., A multispectral imaging analysis system for early detection of cervical cancer. In: Medical Imaging: Physics of Medical Imaging. Vol. 5745, pp. 801–809. SPIE, 2005.
Levenson, R. M., Lynch, D. T., Kobayashi, H., Backer, J. M., and Backer, M. V., Multiplexing with multispectral imaging: from mice to microscopy. ILAR J. (Institute for Laboratory Animal Research). 49(1):78–88, 2008.
Levenson, R. M., and Mansfield, J. R., Multispectral imaging in biology and medicine: Slices of life. Cytometry: Part A. 69A(8):748–758, 2006.
Scribner, D. A., Schuler, J., and Kruer, M. R., Infrared multispectral sensors: re-considering typical design assumptions. Naval Research Lab., Code 5636, 1998.
Barrie, J. D., Aitchison, K. A., Rossano, G. S., and Abraham, M. H., Patterning of multilayer dielectric optical coating for multispectral CCDs. Thin Solid Films 270(1–2):6–9, 1995.
Kong, L., Sprigle, S., Duckworth, M., Yi, D., Caspall, J., Wang, J., and Zhao, F., Handheld erythema and bruise detector. In: Proceedings of SPIE—Medical Imaging: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. Vol. 6915, 2008.
Kong, L., Yi, D., Sprigle, S., Wang, F., Wang, C., Liu, F., Adibi, A., and Tummala, R., Single sensor that outputs narrowband multispectral images. J. Biomed. Opt. 15:010502, 2010.
Themelis, G., Yoo, J. S., and Ntziachristos, V., Multispectral imaging using multiple-band pass filters. Opt. Lett. 33(9):1023, 2008.
Vila, J., Calpe, J., Pla, F., Gomez, L., Connell, J., Marchant, J., Calleja, J., Mulqueen, M., Munoz, J., and Klaren, A., SmartSpectra: Applying multispectral imaging to industrial environments. Real-Time Imaging 11:85–98, 2005.
Bayer, E. B., Color imaging array. United States Patent 3,971,065, 1976.
Packer, O., and Williams, D. R., Light, the retinal image, and photoreceptors. In: Shevell, S. K. (Ed.), The Science of Color. pp. 41–102. Optical Society of America, 2003.
Ramanath, R., Snyder, W. E., and Bilbro, G., Demosaicking methods for bayer color arrays. J. Electron. Imaging 11(3):306–315, 2002.
Lukac, R., Martin, K., and Plataniotis, K. N., Demosaikced image postprocessing using local color ratios. EEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 14(6):914–920, 2004.
Chang, L., and Tan, Y. P., Effective use of spatial and spectral correlations for color filter array demosaicking. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 50(1):355–365, 2004.
Gunturk, B. K., Altunbasak, Y., and Mersereau, R. M., Color plane interpolation using alternating projections. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 11(9):997–1013, 2002.
Li, X., and Orchard, M. T.: New edge-directed interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(10):1521–1527, 2001.
Miao, L., Qi, H., Ramanath, R., and Snyder, W. E., Binary tree-based generic demosaicking algorithm for multispectral filter arrays. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(11):3550–3558, 2006.
Ramanath, R., Snyder, W. E., and Qi, H., Mosaic multispectral focal plane array cameras. In: SPIE Defense and Security Symposium, Orlando (Kissimmee), FL, 12–16 April 2004.
Sprigle, S., Zhang, L., and Duckworth, M., Detection of skin erythema in darkly pigmented skin using multispectral images. Skin & Wound Care 22(4):172–179, 2009.
Mersereau, R., The processing of hexagonally samples two-dimensional signals. Proc. IEEE 67(6):930–949, 1979.
Middleton, L., and Sivaswamy, J., Edge detection in a hexagonal-image processing framework. Image Vis. Comput. 19(14):1071–1081, 2001.
Miao, L., and Qi, H., The design and evaluation of a generic method for generating mosaicked multispectral filter arrays. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(9):2780–2791, 2006.
Lu, W., and Tan, Y. P., Color filter array demosaicking: new method and performance measures. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 12(10):1194–1210, 2003.
Kimmel, R., Demosaicing: Image reconstruction from color ccd samples. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 8(9):1221–1228, 1999.
Mosby’s Medical Dictionary, 8th edn. Elsevier, 2009. http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/pressure+ulcer.
Mcgraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2002. http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/pressure+ulcer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Qi and L. Kong contributed equally in the presented work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, H., Kong, L., Wang, C. et al. A Hand-held Mosaicked Multispectral Imaging Device for Early Stage Pressure Ulcer Detection. J Med Syst 35, 895–904 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9508-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9508-x