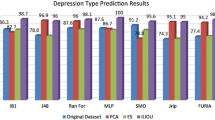
Abstract
Depression is a common but worrying psychological disorder that adversely affects one’s quality of life. It is more ominous to note that its incidence is increasing. On the other hand, screening and grading of depression is still a manual and time consuming process that might be biased. In addition, grades of depression are often determined in continuous ranges, e.g., ‘mild to moderate’ and ‘moderate to severe’ instead of making them more discrete as ‘mild’, ‘moderate’, and ‘severe’. Grading as a continuous range is confusing to the doctors and thus affecting the management plan at large. Given this practical issue, the present paper attempts to differentiate depression grades more accurately using two neural net learning approaches—‘supervised’, i.e., classification with Back propagation neural network (BPNN) and Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) classifiers, and ‘unsupervised’, i.e., ‘clustering’ technique with Self-organizing map (SOM), built in MATLAB 7. The reason for using the supervised and unsupervised learning approaches is that, supervised learning depends exclusively on domain knowledge. Supervision may induce biasness and subjectivities related to the decision-making. Finally, the performance of BPNN and ANFIS are compared and discussed. It was observed that ANFIS, being a hybrid system, performed much better compared to the BPNN classifier. On the other hand, SOM-based clustering technique is also found useful in constructing three distinct clusters. It also assists visualizing the multidimensional data clusters into 2-D.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gotlib, I. H., and Hammen, C. L., Psychological aspects of depression: Toward a cognitive-interpersonal integration, vol. xi. John Wiley & Sons, Oxford, England, pp. 330, 1992. The Wiley series in clinical psychology.
Keller, M. B., Depression: a long-term illness. Br. J. Psychiatry 26:9–15, 1994.
Kaplan, H. I., Saddock, B. J., and Greb, J. A., Synopsis of Psychiatry, Behavioural Science and Clinical Psychiatry. B I Waverly Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi India, pp. 803–823, 1994.
Hamilton, M., A Rating Scale for Depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 23:56–62, 1960.
Zung, W. W. K., The depression status inventory: An adjunct to the self-rating depression scale. J. Clin. Psychol. 28(4):539–543, 1972.
Beck, A. T., & Alford, B. A., Depression: Causes and Treatment, 2nd Edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, 2008.
Bagby, R. M., Andrew, G. R., Deborah, R. S., and Marshall, M. B., The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Am. J. Psychiatry 161:2163–177, 2004.
Chen, H., Fuller, S. S., Friedman, C., and Hersh, W., Knowledge management, Data mining, and Text mining in Medical informatics. In: Chen, H., Fuller, S. S., Friedman, C., and Hersh, W. (Eds.), Medical informatics Knowledge management and Data mining in Biomedicine. Springer’s Integrated Series in Information Systems, NY USA, pp. 4–30, 2005.
Kohonen, T., Self organizing maps. Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1995.
Astion, M. L., and Wilding, P., The application of backpropagation neural networks to problems in pathology and laboratory medicine. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 116(10):995–1001, 1992.
Wilding, P., Morgan, M. A., Grygotis, A. E., Shoffner, M. A., and Rosato, E. F., Application of backpropagation neural networks to diagnosis of breast and ovarian cancer. US National Library of Medicine 77(2–3):145–53, 1994.
Cho, J. M., Chromosome classification using backpropagation neural networks. IEEE 19(1):28–33, 2000.
Guler, I., and Ubeyli, E. D., Detection of ophthalmic artery stenosis by least-mean squares backpropagation neural network. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 18(4):413–422, 2003.
Aruna, P., Puviarasan, N., and Palaniappan, B., An investigation of neurofuzzy system in psychosomatic disorders. Exp. Syst. Appl. 28(4):673–679, 2005.
Aruna, P., Puviarasan, N., and Palaniappan, B., Neuro-Fuzzy model for diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders, in proc. of 5th International Conference on Neural Networks & Expert Systems in Medicine & Healthcare & 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Medicine & Healthcare, Sheffield Hallam University, England, 2003.
Tu, J. V., Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 49:1225–1231, 1996.
Bhatikar, S. R., DeGroff, C., and Mahajan, R. L., A classifier based on the artificial neural networks for cardiologic auscultation in pediatrics. Artif. Intell. Med. 33(3):251–60, 2004.
Li, Y., Liu, L., Chiu, W., and Jian, W., Neural Network modeling for surgical decisions on traumatic brain injury patients. Int. J. Med. Inform. 57(1):1–9, 2000.
Magnotta, V. A., Andreasen, N. C., Heckel, D., Cizadlo, T., Corson, P. W., Ehrhardt, J. C., and Yuh, W. T. C., Measurement of Brain Structures with Artificial Neural Networks: Two and three dimensional applications. Radiology 211:781–90, 1999.
Pradhan, N., Sadasivan, P. K., and Arunodaya, G. R., Detection of seizure activity in EEG by an Artificial Neural Network: A preliminary study. Comput. Biomed. Res. 29(4):303–13, 1999.
Zou, Y., Shen, Y., Shu, L., Wang, Y., Feng, F., Xu, K., Ou, Y., Song, Y., Zhong, Y., Wang, M., and Liu, W., Artificial Neural Network to assist psychiatric diagnosis. Br J Psych 169:64–67, 1996.
Davis, G. E., Lowell, W. E., and Davis, G. L., A Neural Network that predicts psychiatric length of stay. MD Comput 10(2):87–92, 1993.
Chattopadhyay, S., Kaur, P., Rabhi, F., Acharya, U. R., An Automated System to Diagnose the Severity of Adult Depression. In Jana D, Pal P (Eds.), the proceedings of 2nd International conference on Emerging Areas of IT, pp. 121–124, 2011.
Chattopadhyay, S., Kaur, P., Rabhi, F., Acharya, U. R., Automatic Grading of Adult Depression using a Back Propagation Neural Net Classifier. In Advances in Data mining in Biomedical signalling, Imaging, and Systems by Dua S. and Acharya U.R (Eds.). CRC Press, USA. (Accepted 2010; in press).
Jang, J. S. R., ANFIS—Adaptive—Network—based Fuzzy Inference System. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(3):665–685, 1993.
Vieira, J., Dias, F. M., Mota, A., Neuro—Fuzzy Systems: A Survey, 5th WSEAS NNA International Conference, 2004.
Zadeh, L. A., Fuzzy Sets. Inform. Control 8:338–353, 1965.
Phuong, N. H., and Kreinovich, V., Fuzzy Logic and Its Applications in Medicine. I. J. Med. Informatics 62(2):165–173, 2001.
Arzi, M., and Magnin, M., A fuzzy set theoretical approach to automatic analysis of nystagmic eye movements. IEEE Trans Biomed. Eng. 36(9):954–963, 1989.
Grant, P., A New Approach to Diabetic Control: Fuzzy logic and Insulin Pump Technology. Med Eng Phys 29(7):824–827, 2007.
Watanabe, H., Yakowenko, W. J., Kim, Y.-M., Anbe, J., and Tobi, T., Application of a fuzzy discrimination analysis for diagnosis of valvular heart disease. IEEE T. Fuzzy Syst. 2(4):267–276, 1994.
Kovalerchuk, B., Triantaphyllou, E., Ruiz, J. F., and Clayton, J., Fuzzy Logic in Computer-Aided Breast Cancer Diagnosis: Analysis of Lobulation. Artif. Intell. Med. 11(1):75–885, 1997.
Schineider, J., Bitterlich, N., and Schulze, G., Improved Sensitivity in the Diagnosis of Gastro-Intestinal Tumors by Fuzzy Logic based Tumor Marker Profiles including the Tumor M2-PK. International Journal of Cancer Research and Treatment 25(3):1507–1515, 2005.
Presedo, J., Vila, J., Delgado, M., Barro, S., Palacios, F., and Ruiz, R., A Proposal for the Fuzzy Evaluation of Ischaemic Episodes. Comput Cardio, 709–712, 1995.
McBurnie, K, Kwiatkowska, M., Matthews, L., and D’Anguiulli, A., A Multi-Factor Model for the Assessment of Depression Associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Fuzzy Logic Approach. Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society, pp. 301–306, 2007.
Yu, S.-C., and Lin, Y.-H., Applications of Fuzzy Theory on Health Care: An Example of Depression Disorder Classification Based on FCM. WSEAS Transactions on Information Science & Applications 5(1):31–36, 2008.
Chattopadhyay, S., Pratihar, D. K., and De Sarkar, S. C., Statistical Modelling of Psychoses Data. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 100(3):222–236, 2010.
Chattopadhyay, S., Pratihar, D. K., and De Sarkar, S. C., Fuzzy Logic-based Screening and Prediction of Adult Psychoses: A Novel Approach. IEEE T. Syst. Man Cy A 39(2):381–387, 2009.
Chattopadhyay, S., Pratihar, D. K., and De Sarkar, S. C., Developing Fuzzy Classifiers to Predict the Chance of Occurrence of Adult Psychoses. Knowledge-based Systems 20:479–497, 2008.
Chattopadhyay, S., Pratihar, D. K., and De Sarkar, S. C., Some Studies on Fuzzy clustering of psychosis data. International Journal of Business Intelligence and Data Mining 2(2):143–159, 2007.
Takagi, T., and Sugeno, M., Fuzzy identifiation of systems and its application to modeling and control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics—Part C (SMC-15): 116–132, 1985.
Manish, K., Hakan, N., Aarup, L R, Nottrup, T. J., Olsen, D. R., Respiratory Motion Prediction by Using the ANFIS. Phys. Med. Biol. 50(19), 2005.
Magenes, G., Signorini, M. G., and Sassi, R., Automatic Diagnosis of Fetal Heart Rate: Comparison of Different Methodological Approaches. Proceedings of the 23 rd Annual International Conference of Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society IEEE, 2:1604–1607, 2001.
Forouzanfar, M., Dajani, H. R., Groza, V. Z., Bolic, M., Rajan, S., ANFIS for Oscillometric Blood Pressure Estimation. IEEE International Workshop on Medical Measurements and Applications Proceedings, pp. 125–129, 2010.
Vosoulipour, A, Teshnehlab M, and Moghadam, H. A., Classification on Diabetes Mellitus Data-set Based on ANN and ANFIS. Proceedings of 4th Kala Lumpur International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, pp. 27–30, 2008.
Ozkan, A. O., Sadik, K., Salli, A., Sakarya, M. E., and Gunes, S., Medical Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease from Right and Left Hand Ulnar Artery Doppler Signals using ANFIS and MUSIC Methods. Adv Eng Softw 41(12):1295–1301, 2010.
Kannathal, N., Lim, C. M., Acharya, U. R., and Sadasivan, P. K., Cardiac state diagnosis using adaptive neuro fuzzy technique. Med Eng Phys 28:809–815, 2006.
Vatankhah, M., and Yaghubi, M., ANFIS for Classification of EEG Signals using Fractal Dimension, 3rd UKSIM European Symposium on Computer Modeling and Simulation: pp. 214–218, 2009.
Noor, N. M., Khalid, N. E. A., Hassan, R., Ibrahim, S., Yassin, I. M., ANFIS for Brain Abnormality Segmentation, Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium IEEE: pp. 68–70, 2010.
Kannathal, N., Lim, C. M., Acharya, U. R., and Sadasivan, P. K., Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 80:187–194, 2005.
Kohonen, T., Self Organizing Maps. Proc IEEE 78(9):1464–80, 1990.
Ball, H. A., McGuffin, P., and Farmer, A. E., Attributional style and depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 192:275–278, 2008.
Austin, M. P., Mitchell, P., and Goodwin, G. M., Cognitive deficits in depression: Possible implications for functional neuropathology. Br. J. Psychiatry 178:200–206, 2001.
Forsell, Y., Jorm, A. F., and Winblad, B., Association of age, sex, cognitive dysfunction, and disability with major depressive symptoms in an elderly sample. Am. J. Psychiatry 151:1600–1604, 1994.
Cronbach, L. J., Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 16:297–334, 1951.
Fisher, R. A. The use of multiple measurements in axonomic problems. Annals of Eugenics 7:179–188, 1936.
Han, J., and Kamber, M., Data Mining Concepts and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco, California USA, pp. 327–36, 2006.
Chiu, S., Fuzzy Model Identification Based on Cluster Estimation. J. Int. Fuzzy Syst. 2(3):267–268, 1994.
Shing, J., and Jang, R., ANFIS: Adaptive-Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(3):665–85, 1993.
Jolliffe, I. T., Principal Component Analysis. Springer-Verlag Heidelberg, Germany, 1986.
Nunnaly, J., Psychometric theory. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1978.
Gliem, J. A., Gliem, R. R., Calculating, Interpreting and Reporting Cronbac’s Alpha Reliability Coefficient for Likert-Type Scales. In the proceedings of Midwest Research-to-Practice Conference in Adult, Continuing and Community Education, pp. 45–48, 2003.
Acknowledgement
Authors gratefully acknowledge the psychologists and psychiatrist colleagues who had helped in collecting depression data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chattopadhyay, S., Kaur, P., Rabhi, F. et al. Neural Network Approaches to Grade Adult Depression. J Med Syst 36, 2803–2815 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9759-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9759-1