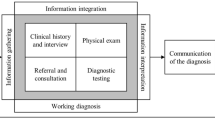
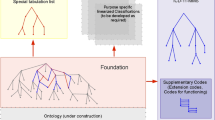
Abstract
In this paper we describe a novel model for differential diagnosis designed to make recommendations by utilizing semantic web technologies. The model is a response to a number of requirements, ranging from incorporating essential clinical diagnostic semantics to the integration of data mining for the process of identifying candidate diseases that best explain a set of clinical features. We introduce two major components, which we find essential to the construction of an integral differential diagnosis recommendation model: the evidence-based recommender component and the proximity-based recommender component. Both approaches are driven by disease diagnosis ontologies designed specifically to enable the process of generating diagnostic recommendations. These ontologies are the disease symptom ontology and the patient ontology. The evidence-based diagnosis process develops dynamic rules based on standardized clinical pathways. The proximity–based component employs data mining to provide clinicians with diagnosis predictions, as well as generates new diagnosis rules from provided training datasets. This article describes the integration between these two components along with the developed diagnosis ontologies to form a novel medical differential diagnosis recommendation model. This article also provides test cases from the implementation of the overall model, which shows quite promising diagnostic recommendation results.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Rodriguez, A., Mencke, M., Alor-Hernandez, G., Posada-Gomez, R., Gomez, J.M., Aguilar-Lasserre, A.A.: MEDBOLI: Medical Diagnosis Based on Ontologies and Logical Inference. In: IEEE International Conference on eHealth, Telemedicine, and Social Medicine, 2009, eTELEMED '09, Cancun, Mexico, Feb.1-7 (2009)
Köhler, S., Schulz, MH., Krawitz, P., Bauer, S., Dölken, S., Ott, C.E., Mundlos, C., Horn, D., Mundlos, S., Robinson, P.N.: Clinical diagnostics in human genetics with semantic similarity searches in ontologies. In: Am J Hum Genet., 85 (4), pp. 457–464. October 9 (2009), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2756558/?tool=pubmed
Weiner, M., Pifer, E., Williams, V.: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. In: Encyclopedia of Biostatics, Published Online by John Wiley & Sons, 15 JUL (2005)
Diamond, H., Clinical Reminder System: A Relational Database Application for Evidence-Based Medicine Practice, 2004.
Yeh, Y.C., Kuo, Y.H., Hsu, D.S.: Building expert systems by embedding analogical reasoning into deductive reasoning mechanism. In: Ninth Annual International Phoenix Conference on Computers and Communications, pp. 822 - 826. Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 21-23 March (1990)
Wim, B.K., Wiegerinck, W., Akay, E., Neijt, J., Van Beek, A.: Promedas: A clinical diagnostic decision support system. In: Proceedings of the 15th Belgian-Dutch Conference on Artificial Intelligence (BNAIC), Netherlands (2003), http://www.kiranreddys.com/articles/clinicaldiagnosissupportsystems.pdf
Matsumoto, T., Shimada, Y., Kawaji, S.: Clinical diagnosis support system based on symptoms and remarks by neural networks. In: 2004 I.E. Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems, pp. 1304 - 1307. Singapore (2004)
Alexandrou, D. and Pardalis, K. V.: SEMantic PATHways: Modeling, Executing, and Monitoring Intra-Organizational Healthcare Business Processes towards Personalized Treatment”, In: e-Health Technologies and Improving Patient Safety: Exploring Organizational Factors, by Moumtzoglou A. and Kastania, A. N. edition, IGI Global Publisher, pp. 98-123, (2013).
Hu, Z. Li, J.S., Zhou, T.S., Yu, H.Y.: Ontology-Based Clinical Pathways with Semantic Rules, In: Journal of Medical Systems , 36:4, pp.2203–2212, DOI: 10.1007/s10916-011-9687-0, (2012).
Alexandrou, D., Xenikoudakis, F., Mentzas, G., SEMPATH: Semantic Adaptive and Personalized Clinical Pathways. In: eTELEMED '09, International Conference on eHealth, Telemedicine, and Social Medicine, pp. 36 – 41. Cancun, Mexico 1-7 Feb. (2009)
Alexandrou, D., Xenikoudakis, F., and Mentzas, G., Adaptive Clinical Pathways with Semantic Web Rules. In: IEEE International Conference on Health Informatics, Madeira, Portugal 28–31(January), 2008.
Chabalier, J., Dameron, O., Burgun, A.: Integrating and querying disease and pathway ontologies: building an OWL model and using RDFS queries. In: The 10th Annual Bio-Ontologies Meeting, Co-Located with ISMB/ECCB 2007, Austria, July (2007), http://www.ea3888.univ-rennes1.fr/lim/doc_184.pdf
13. Ye, Y., Jiang, Z., Yang, D., Du, G.: A semantics-based clinical pathway workflow and variance management framework. In: IEEE Intl. Conf. on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics, pp. 758-763. Beijing, China, IEEE Press (2008)
Chen, H., Colaert, D., De Roo, J.: Towards Adaptable Clinical Pathway Using Semantic Web Technology. In: W3C Workshop Semantic Web for Life Science, Position Paper, July (2004), http://www.w3.org/2004/07/swls-cfp.html
Chen, H.: Semantic Web in Adaptable Health Care Protocols and Pathways Group Charter - A proposal. February (2006), http://www.w3.org/2001/sw/hcls/task_forces/AHPP_Task_Force.doc
Popescu, M., Khalilia, M.: Improving disease prediction using ICD-9 ontological features. In: 2011 I.E. International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp.1805-1809. Taipei, Taiwan, 27-30 June (2011)
Ye, Y., Jiang, Z., Diao, X., Yang, D., and Du, G., An ontology-based hierarchical semantic modeling approach to clinical pathway workflows. In: Computers in Biology and Medicine 39(8):722–732, 2009.
Lin, Y. C.: Development of an Ontology-based Flexible Clinical Pathway System. In: WSEAS Transactions on Information Science and Applications, 6 (12), (2009), http://www.wseas.us/e-library/transactions/information/2009/32-900.pdf
Hu, Z., Li, J. S., Zhou, T. S., Yu, H. Y., Suzuki, M., and Araki, K., Ontology-Based Clinical Pathways with Semantic Rules. J Med Syst, Springe, 2011.
Huang, Z., Lu, X., Duang, H.: Using Recommendation to Support Adaptive Clinical Pathways, In: Journal of Medical Systems, 36:3, pp.1849–1860, DOI: 10.1007/s10916-010-9644-3, (2012)
Martínez-Pérez, B., and Torre-Díez, I., Mobile Clinical Decision Support Systems and Applications: A Literature and Commercial Review. In: Journal of Medical Systems 38:4, 2014. doi:10.1007/s10916-013-0004-y.
Hurley, K.F., Abidi, S.S.R.: Ontology Engineering to Model Clinical Pathways: Towards the Computerization and Execution of Clinical Pathways, In: Proc of the 20th IEEE Int. Symposium on Computer-based Medical Systems, pp. 536-541, 20-22 June 2007, Maribor, Slovenia, (2007)
Shen, C.P., Jigjidsuren, C., Dorjgochoo, S: A Data-Mining Framework for Transnational Healthcare System, In: Journal of Medical Systems, 36:4, pp.2565–2575, DOI 10.1007/s10916-011-9729-7, (2012)
Jalali,V., Borujerdi, M.R.M.: A Unified Architecture for Biomedical Search Engines Based on Semantic Web Technologies, In: Journal of Medical Systems, 35:2, pp.237–249, DOI: 10.1007/s10916-009-9360-z, (2011)
Scheuermann, R. H., Werner, C., Smith, B.: Toward an Ontological Treatment of Disease and Diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 2009 AMIA Summit on Translational Bioinformatics, pp. 116-120. San Francisco, CA, (2009), http://ontology.buffalo.edu/medo/Disease_and_Diagnosis.pdf
Hamm, R., Knoop, S.E., Schwarz, P., Block, A.D., Davis, W.L.: Harmonizing clinical terminologies: driving interoperability in healthcare. In: Loinic Stud Health Technol Inform Report No. 129:660-3, (2007), http://loinc.org/articles/Hamm2007a
Liu, R. L., Tung, S. Y., and Lu, Y. L., Identifying Disease Diagnosis Factors by Proximity-Based Mining of Medical Texts, In Intelligent Information and Database Systems. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS) 6592:171–180, 2011.
Mohammed, O., and Benlamri, R., Building a Diseases Symptoms Ontology for Medical Diagnosis. In: An Integrative Approach, IEEE International Conference on Future Generation Communication Technology, British Computer Society, London, 2012.
Mohammed, O.: “Semantic Web System for Differential Diagnosis Recommendations”. MSc Thesis, Supervised By: Prof. Dr. Rachid Benlamri, Lakehead University, (2012)
Hughes, T.C., Ashpole, B.C.: The Semantics of Ontology Alignment. In: I3CO Information Interpretation and Integration Conference, (2004), http://www.atl.lmco.com/projects/ontology/papers/SOA.pdf
Zhang, S., Bodenreider, O.: Alignment of multiple ontologies of anatomy: deriving indirect mappings from direct mappings to a reference. In: Proceedings for AMIA Annual Symposium, Washington, DC (2005), http://www.lhncbc.nlm.nih.gov/lhc/docs/published/2005/pub2005039.pdf
Doan, A.H. et al: Learning to match ontologies on the Semantic Web. In: The VLDB Journal — The International Journal on Very Large Data Bases archive, vol. 12, issue 4. November (2003)
Homola, M., Serafini, L.: Towards Formal Comparison of Ontology Linking, Mapping and Importing. In: Proceeding of 23rd Int. Workshop on Description Logics (DL2010), CEUR-WS 573, Waterloo, Canada (2010), http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/conferences/dl2010/papers/paper_26.pdf
Victoria Dept. of Health: Pathways for Prediabetes, Type 1, Type 2 and Gestational Diabetes. Department of Health - Loddon Mallee Region, Victoria, Australia (2009)
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NHS): Hypertension: management of hypertension in adults in primary care, August (2004)
Goodnough et al: Detection, Evaluation, and Management of Anemia in the Elective Surgical Patient. In: The International Anesthesia Research Society, (2005)
Famili, A., Ouyang, J.: Data Mining: Understanding Data and Disease Modeling. In: Proceedings of IASTED-AI-03 Conference. Innsbruck, Austria, February 10-13 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, O., Benlamri, R. Developing a Semantic Web Model for Medical Differential Diagnosis Recommendation. J Med Syst 38, 79 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0079-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0079-0