Abstract
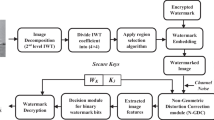
This study presents two types of data hiding methods based on coefficient alignment for electrocardiogram (ECG) signals, namely, lossy and reversible ECG steganographys. The lossy method is divided into high-quality and high-capacity ECG steganography, both of which are capable of hiding confidential patient data in ECG signals. The reversible data hiding method can not only hide secret messages but also completely restore the original ECG signal after bit extraction. Simulations confirmed that the perceived quality generated by the lossy ECG steganography methods was good, while hiding capacity was acceptable. In addition, these methods have a certain degree of robustness, which is rare in conventional ECG stegangraphy schemes. Moreover, the proposed reversible ECG steganography method can not only successfully extract hidden messages but also completely recover the original ECG data.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox, I. J., Miller, M. L., Bloom, J. A., Fridrich, J., and Kalker, T., Digital watermarking and steganography, 2nd edition. Morgan Kaufmann, MA, 2008.
Phadikar, A., Data hiding techniques and applications specific designs. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, Saarbrucken, 2012.
Eielinska, E., Mazurczyk, W., and Szczypiorski, K., Trends in steganography. Commun. ACM 57:86–95, 2014.
Su, P. C., Lu, M. T., and Wu, C. Y., A practical design of high-volume steganography in digital video files. Multimed. Tools Applic. 66:247–266, 2013.
Pan, J.S., Li, W., Yang, C.S., and Yan, L., “Image steganography based on subsampling and compressive sensing,”. Multimed. Tools Applic.. doi: 10.10071/s11042-014-2070-1.
Yang, C. Y., Robust watermarking scheme based on radius weight mean and feature-embedding technique. ETRI J. 35:512–522, 2013.
Wang, X. Y., Niu, P. P., Yang, H. Y., Wang, C. P., and Wang, A. L., A new robust color image watermarking using local quaternion exponent moments. Inf. Sci. 277:731–754, 2014.
Wang, S., Miyauchi, R., Unoki, M., and Kim, N. S., Tampering detection scheme for speech signals using formant enhancement based watermarking. J. Inform. Hiding Multimed. Sign. Process. 6:1264–1283, 2015.
Chen, Y. H., Huang, H. C., and Lin, C. C., “Block-based reversible data hiding with multi-round estimation and difference alteration”. Multimed. Tools Applic. 2015. doi:10.1007/s11042-015-2825-9).
Yan, B., Wang, Y. F., Song, L. Y., and Yang, H. M., Power spectrum compliant QIM watermarking for autoregressive host signals. J. Inform. Hiding Multimed. Sign. Process. 6:882–888, 2015.
Fang, W. C., Huang, H. C., and Tseng, S. Y., Design of heart rate variability processor for portable 3-lead ECG monitoring system-on-chip. Expert Syst. Applic. 40:1491–1504, 2013.
Ameen, M. A., Liu, J., and Kwak, K., Security and privacy issues in wireless sensor networks for healthcare applications. J. Med. Syst. 36:93–101, 2012.
Liu, J., Tang, G, and Sun, Y., “A secure steganography for privacy protection in healthcare system,” J. Med. Syst. 2013. doi:10.1007/s10916-012-9918-z.
Ibaida, A., Khalil, I. and Al-Shammary, D.,“Embedding patients confidential data in ECG signal for healthcare information systems,” 32nd Ann. Int. Conf. the IEEE EMBS Buenos Aires, Argentina, Aug. 31–Sept. 4, pp. 3897–3894, 2010.
Ibaida, A., Khalil, I., and Schynde, R. V., A low complexity high capacity ECG signal watermark for wearable sensor-net health monitoring system. Comput. Cardiol. 38:393–396, 2011.
Ibaida, A., and Khalil, I., Wavelet-based ECG steganography for protecting patient confidential information in point-of-care systems. IEEE T. Biomed. Eng. 60:3322–3330, 2013.
Shekhawat, A. S., Jain, A., and Patil, D., A study of ECG steganography for securing patient’s confidential data based on wavelet transformation. Int. J. Comput. App. 105:12–16, 2014.
Jero, S.E., Ramu, P. and Ramakrishnan, S.,“Discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition based ECG steganography for secured patient information transmission,” J. Med. Syst.38, doi: s10916-014-0132-z, 2014.
Kozat, S. S., Vlachos, M., and Lucchese, C., Embedding and retrieving private metadata in electrocardiograms. J. Med. Syst. 33:241–259, 2009.
Sufi, F., and Khalil, I., A new feature detection mechanism and its application in secured ECG transmission with noise masking. J. Med. Syst. 33:121–132, 2009.
Dogan, S., Tuncer, T., Avci, E., and Gulten, A., A new watermarking system based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) in color biometric images. J. Med. Syst. 36:2379–2385, 2011.
Tseng, K. K., He, X., Kung, W. M., Chen, S. T., Liao, M. H., and Huang, H. N., Wavelet-based watermarking and compression for ECG signals with verification evaluation. Sensors 14:3721–3736, 2014.
Chen, S.T., Guo, Y.J. and Huang, H.N., “Hiding patients confidential data in the ECG signal via a transform-domain quantization scheme,” J. Med. Syst. doi: s10916-014-0054-9, 2014.
Zheng, K.M. and Qian, X.,“Reversible data hiding for electrocardiogram signal based on wavelet transform,” Int. Conf. Comput. Intelli. Sec. 13–17 Dec. Suzhou, China, p. 295–299, 2008.
Nayak, J., Bhat, P. S., Achaya, U. R., and Kumar, M. S., Efficient storage and transmission of digital fundus images with patient information using reversible watermarking technique and error control codes. J. Med. Syst. 33:163–171, 2009.
Moody, G. B., and Mark, R. G., The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. 20:45–50, 2001.
PhysioNet, “The creighton university ventricular tachyarrhythmia database,” http://www.physionet.org/physiobank.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Mobile Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, CY., Wang, WF. Effective Electrocardiogram Steganography Based on Coefficient Alignment. J Med Syst 40, 66 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0426-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0426-9