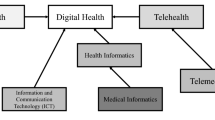
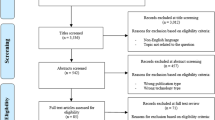
Abstract
Wellness is a term often used to talk about optimal health as “dynamic balance of physical, emotional, social, spiritual, and intellectual health.” While healthcare is a term about care offered to patients for improving their health. We use both terms, as well as the Business Model Canvas (BMC) methodology, to design a digital ecosystem model for healthcare and wellness called DE4HW; the model considers economic, technological, and legal asymmetries, which are present on e-services beyond geographical regions. BMC methodology was embedded into the global project strategy called: IBOT (Initiate, Build, Operate and Transfer); it is a methodology to establish a functional, integrated national telemedicine network and virtual education network; of which we took its phases rationale. The results in this work illustrate the design of DE4HW model, into the first phase of IBOT, enriched with the BMC, which enables us to define actors, their interactions, rules and protocols, in order to build DE4HW, while IBOT strategy manages the project goal, up to the transfer phase, where an integral service platform of healthcare and wellness is turned over to stakeholders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuller, G., Shulyak, L., Rodman, S., The innovation algorithm: TRIZ, systematic innovation and technical creativity: Technical Innovation Center, Inc., 1999.
Christensen, H. B, Hansen, K. M, Kyng, M., Manikas, K., Analysis and design of software ecosystem architectures towards the 4s telemedicine ecosystem. Inf. Softw. Technol. 56(11):1476–1492, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2014.05.002. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950584914001050. Special issue on Software Ecosystems.
College of American Pathologists (CAP): Snomed ct. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/Snomed/snomed_main.html (2015)
Erl, T.: SOA Design patterns pearson education. https://books.google.es/books?id=Kgng8I2gVH4C (2008)
International Electrotechnical Commission: Iec 60086-4:2014. https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/671 (2015)
International Electrotechnical Commission: Iec 60601-1-2:2007. http://www.iec.ch/emc/basic_emc/basic_emc_immunity.htm (2015)
International Electrotechnical Commission: Iec 61000-4-3. http://www.iec.ch/emc/basic_emc/basic_emc_immunity.htm (2015)
International Electrotechnical Commission: Iec 62133:2012. https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/6515 (2015)
International Electrotechnical Commission: International standards and conformity assessment for all electrical electronic and related technologies. http://www.iec.ch/ (2015)
Kwak, Y. H, and Anbari, F. T, Benefits, obstacles, and future of six sigma approach. Technovation 26 (5–6):708–715, 2006. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2004.10.003.
Latifi, R., initiate-build-operate-transfer-a strategy for establishing sustainable telemedicine programs not only in the developing countries. Studies in health technology and informatics 165:3–10, 2010.
Latifi, R., Dasho, E., Lecaj, I., Latifi, K., Bekteshi, F., Hadeed, M., Doarn, C. R, Merrell, R. C, Beyond initiate-build-operate-transfer strategy for creating sustainable telemedicine programs: Lesson from the first decade. TELEMEDICINE and e-HEALTH 18(5):388–390, 2012.
Latifi, R., Dasho, E., Merrell, R. C, Lopes, M., Azevedo, V., Bekteshi, F., Osmani, K. L, Qesteri, O., Kucani, J., Lecaj, I., Cabo verde telemedicine program: Initial results of nationwide implementation. Telemedicine and e-Health 20(11):1027–1034, 2014.
Latifi, R., Merrell, R. C, Doarn, C. R, Hadeed, G. J, Bekteshi, F., Lecaj, I., Boucha, K., Hajdari, F., Hoxha, A., Koshi, D., de Leonni Stanonik, M., Berisha, B., Novoberdaliu, K., Imeri, A., Weinstein, R. S, Initiate build operate transfer a strategy for establishing sustainable telemedicine programs in developing countries: Initial lessons from the balkans. Telemedicine and e-Health 15(10):956–969, 2009. doi:10.1089/tmj.2009.0084.
Latifi, R., Merrell, R. C, Doarn, C. R, Hadeed, G. J, Bekteshi, F., Lecaj, I., Boucha, K., Hajdari, F., Hoxha, A., Koshi, D., et al., Initiate–build–operate–transfer, a strategy for establishing sustainable telemedicine programs in developing countries: Initial lessons from the balkans. Telemedicine and e-Health 15(10): 956–969, 2009.
Lee, B. Y, Wong, K. F, Bartsch, S. M, Yilmaz, S. L, Avery, T. R, Brown, S. T, Song, Y., Singh, A., Kim, D. S, Huang, S. S, The regional healthcare ecosystem analyst (rhea): a simulation modeling tool to assist infectious disease control in a health system. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 20(e1):e139–e146, 2013.
Lee, E., Grooms, R., Mamidala, S., Nagy, P., Six easy steps on how to create a lean sigma value stream map for a multidisciplinary clinical operation. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 11(12, Part A):1144–1149, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2014.08.031. Special Issue: Quality Improvement in Radiology.
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G, Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gøtzsche, P. C, Ioannidis, J. P, Clarke, M., Devereaux, P., Kleijnen, J., Moher, D.: The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration, Vol. 151 (2009)
Lin, C., Song, Z., Song, H., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, G., Differential privacy preserving in big data analytics for connected health. J. Med. Syst. 40(4):1–9, 2016.
Liyanage, H., Liaw, S. T, De Lusignan, S., Accelerating the development of an information ecosystem in health care, by stimulating the growth of safe intermediate processing of health information (iphi). Informatics in primary care 20(2):81–86 , 2012.
Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad: Ecie 10es edición electrónica de la clasificación internacional de enfermedades-10-es diagnósticos. https://eciemaps.mspsi.es/ecieMaps/browser/index_10_mc.html (2015)
Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo: Real decreto 1591/2009. http://www.boe.es/diario_boe/txt.php?id=BOE-A-2009-17606 (2015)
Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo: Real decreto 437/2002. http://www.boe.es/diario_boe/txt.php?id=BOE-A-2002-10228 (2015)
Nachira, F., et al.: Towards a network of digital business ecosystems fostering the localdevelopment (2002). Retrieved on 16 (2007)
National Center for Biotechnology Information: National center for biotechnology information. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (2015)
Osterwalder, A., and Pigneur, Y.: Business model canvas. Self published. Last retrieval May 5, 2011 (2010)
Pang, Z., Chen, Q., Tian, J., Zheng, L., Dubrova, E.: Ecosystem analysis in the design of open platform-based in-home healthcare terminals towards the internet-of-things. In: 2013 15th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), pp. 529–534 (2013)
Sahin, Y. G, and Celikkan, U., Medwise: an innovative public health information system infrastructure. J. Med. Syst. 36(3):1719–1729, 2012.
Saldaña, J. D, García, V. J. P, Cosio, L. M, González, R. M. L, Beltran Julián, A., Garibali, P. G. A, Nieto, H. J. I: Information and communication technology interventions to support elderly patients with noncommunicable diseases: a scoping review. In: Multidisciplinary national congress of education, science and technology (CONAMTEC) (2015)
Saliba, V., Legido-Quigley, H., Hallik, R., Aaviksoo, A., Car, J., McKee, M., Telemedicine across borders: a systematic review of factors that hinder or support implementation. Int. J. Med. Inform. 81(12):793–809, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2012.08.003.
Secretaria de Gobernacion: Dof diario oficial de la federacion. http://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4792400
Secretaria de Gobernacion: DOF Diario Oficial de la Federacion. http://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5147409
Secretaria de Salud: Norma oficial mexicana nom-024-ssa 3-2010. http://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/4151/salud/salud.htm (2015)
Secretaria de Salud: Norma oficial mexicana nom-040-ssa2-2004. http://www.salud.gob.mx/unidades/cdi/nom/040ssa204.html (2015)
Secretaria de Salud: Norma oficial mexicana nom-206-ssa 1-2002. http://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/4151/salud/salud.htm (2015)
Serbanati, L. D, and Vasilateanu, A.: Conceptual modeling of the healthcare ecosystem. In: Proceedings of 23rd international conference of the european federation for medical informatics, MIE 2011 (2011)
Seven, H. L: Health level seven. http://www.hl7.org/ (2015)
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: 2011/65/eu electric and electronic devices. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1438501146313&uri=CELEX:32011L0065 (2015)
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Council directive 93/42/eec. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:31993L0042 (2015)
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Directive 1999/5/ec harmonized. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1438500925792&uri=CELEX:31999L0005 (2015)
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Directive 2004/108/ec. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1438500759975&uri=CELEX:32004L0108 (2015)
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Directive 2006/95/ec. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1438500281173&uri=CELEX:32006L0095 (2015)
World Health Organization: Health in 2015: from mdgs to sdgs electronic. http://www.who.int/gho/publications/mdgs-sdgs/en/ (2015)
World Organization of Family Doctors: WONCA Global Family Doctor. http://www.globalfamilydoctor.com/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
This article is part of the bilateral research project C0011-2013-CONACYT-CDTI-209240 supported by National Council for Science and Technology, CONACYT (Mexico)- Center for Industrial Technological Development, CDTI (Spain). Through the ESTS-ECDP consortium (Autonomous University of Baja California - Siteldi Solutions and IKUSI España)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
León, M.C., Nieto-Hipólito, J.I., Garibaldi-Beltrán, J. et al. Designing a Model of a Digital Ecosystem for Healthcare and Wellness Using the Business Model Canvas. J Med Syst 40, 144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0488-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0488-3