Abstract
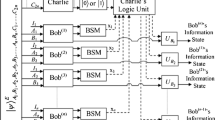
In this paper, we propose a communication protocol called Controlled Bidirectional Quantum Secret Direct Communication (CBQSDC) for mobile networks. In mobile networks, telecom companies assist the agent ensuring both sides could receive the other’s secret messages in the transmission by quantum theory simultaneously. This protocol is based on n-particle GHZ states (Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger-states) which are transformed to Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) pairs by entanglement swapping. GHZ states are used to carry both sides’ messages and entanglement swapping could reduce the number of transmission, so we could decrease the probability of eavesdropping. If any eavesdropper tries to steal dealer’s messages, the lawful participants will perceive it and abort their transmission.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang L-P, Wu T-C, Hsu C-L, Lu C-F (2010) Two level authenticated group key agreement protocol with privacy-preservation for resource-limited mobile devices. J Internet Technol 11(4):519–528
del Álamo JM, Fernández AM, Trapero R, Yelmo JC, Monjas MA (2011) A privacy-considerate framework for identity management in mobile services. Mob Netw Appl 15(4):446–459
Chou YH, Chen C-Y, Chao H-C, Park JH, Fan R-K (2011) Quantum entanglement and non-locality based secure computation for future communication. IET Inf Secur 5(1):69–79
Bennett CH, Brassard G (1984) Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, p 175
Ekert AK (1991) Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett 67:661–663
Bennett CH, Brassard G, Mermin ND (1992) Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett 68:557–559
Xue P, Li CF, Guo GC (2002) Conditional efficient multiuser quantum cryptography network. Phys Rev A 65:022317
Acin A, Gisin N, Scarani V (2004) Coherent-pulse implementations of quantum cryptography protocols resistant to photon-number-splitting attacks. Phys Rev A 69:012309
Vernam GS (1926) Cipher printing telegraph systems for secret wire and radio telegraphic communications. American Institute of Electrical Engineers, pp 295–301
Boström K, Felbinger T (2002) Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys Rev Lett 89:187902
Deng F, Long G, Liu X (2003) Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys Rev A 68:042317
Deng F, Long G (2004) Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys Rev A 69:052319
Lucamarini M, Mancini S (2005) Secure deterministic communication without entanglement. Phys Rev Lett 94:140501
Beige A, Englert BG, Kurtsiefer C, Weinfurter H (2002) Secure communication with a publicly known key. Acta Phys Pol, A 101:357–368
Chou YH, Chen CY, Fan RK, Chao HC, Lin FJ (2012) Enhanced multiparty quantum secret sharing of classical messages by using entanglement swapping. IET Inf Secur 6(2):84–92
Deng FG, Zhou HY, Long GL (2005) Bidirectional quantum secret sharing and secret splitting with polarized single photons. Phys Lett A 337:329–334
Chen CY, Chou YH, Chao HC (2012) Distributed quantum entanglement sharing model for high-performance real-time system. Soft Comput 16:427–435
Long GL, Liu XS (2002) Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys Rev A 65:032302
Shimizu K, Imoto N (1999) Communication channels secured from eavesdropping via transmission of photonic Bell states. Phys Rev A 60:157–166
Deng FG, Li CY, Zhou P, Zhou HY (2006) Quantum secure direct communication network with Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pairs. Phys Lett A 359:359–365
Li XH, Zhou P, Liang YJ, Li CY, Zhou HY, Deng FG (2006) Quantum secure direct communication network with two-step protocol. Chin Phys Lett 23:1080–1083
Wang C, Deng FG, Li YS, Liu XS, Long GL (2005) Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys Rev A 71:044305
Wang C, Deng FG, Long GL (2005) Multi-step quantum secure direct communication using multi-particle Green-Horne-Zeilinger state. Opt Commun 253:15–20
Zhou P, Li XH, Liang YJ, Deng FG, Zhou HY (2007) Multiparty quantum secret sharing with pure entangled states and decoy photons. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 381:164–169
Cai QY, Li BW (2004) Improving the capacity of the Boström-Felbinger protocol. Phys Rev A 69:054301
Cai QY, Li BW (2004) Deterministic secure communication without using entanglement. Chin Phys Lett 21:601–603
Wang J, Zhang Q, Tang CJ (2006) Quantum secure direct communication based on order rearrangement of single photons. Phys Lett A 358:256–258
Cai QY (2003) The “Ping-Pong” protocol can be attacked without eavesdropping. Phys Rev Lett 91:109801
Cai QY (2006) Eavesdropping on the two-way quantum communication protocols with invisible photons. Phys Lett A 351:23–25
Shi GF, Xi XQ, Tian XL, Yue RH (2009) Bidirectional quantum secure communication based on a shared private Bell state. Opt Commun 282:2460–2463
Gao G, Wang LP (2010) A protocol for bidirectional quantum secure communication based on Genuine four-particle entangled states. Commun Theor Phys 54:447–451
Shi GF (2010) Bidirectional quantum secure communication scheme based on Bell states and auxiliary particles. Opt Commun 283:5275–5278
Shi GF, Xi XQ, Hu ML, Yue RH (2010) Quantum secure dialogue by using single photons. Opt Commun 283:1984–1986
Gao G (2010) Two quantum dialogue protocols without information leakage. Opt Commun 283:2288–2293
Man ZX, Xia YJ (2006) Controlled bidirectional quantum direct communication by using a GHZ state. Chin Phys Lett 23:1680–1682
Dong L, Xiu XM, Gao YJ, Chi F (2008) A controlled quantum dialogue protocol in the network using entanglement swapping. Opt Commun 281:6135–6138
Kao SH, Tsai CW, Hwang TL (2011) Enhanced multiparty controlled QSDC using GHZ state. Commun Theor Phys 55:1007
Wang J, Zhang Q, Tang CJ (2006) Multiparty controlled quantum secure direct communication using Greenber-Horne-Zeilinger state. Opt Commun 266:732–737
Gao F, Lin S, Wen QY, Zhu FC (2008) A special eavesdropping on one-sender versus N-receiver QSDC protocol. Chin Phys Lett 25:1561–1563
Gao F, Qin SJ, Wen QY, Zhu FC (2010) Cryptanalysis of multiparty controlled quantum secure direct communication using Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state. Opt Commun 283:192–195
Acknowledgment
This research was funded by the National Science Council of the R.O.C. under grants NSC 100-2221-E-260-038 and NSC 101-2221-E-260-033.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, YH., Zeng, GJ., Lin, FJ. et al. Quantum Secure Communication Network Protocol with Entangled Photons for Mobile Communications. Mobile Netw Appl 19, 121–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-013-0454-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-013-0454-y