Abstract
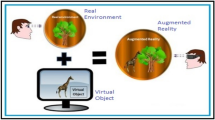
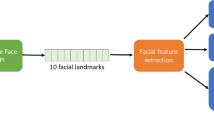
IoTtalk is a platform for IoT device interaction, which has been used to develop many IoT applications such as home automation. This paper uses Flower Sermon artwork as an example to show how interactive visual design can be conveniently implemented in IoTtalk. The Flower Sermon artwork conducts cyber physical interaction, which animates a dandelion in a mirror when a person smiles at that mirror. The dandelion grows larger as the person smiles bigger. The flower also vibrates following the heartbeat rate of the person. In our approach, the camera detecting the face expression and the heartbeat rate is considered as an input IoT device, and the mirror display for dandelion animation is considered as an output IoT device. In IoTtalk, the features of the dandelion animation are considered as the actuators that can be independently controlled. IoTtalk nicely connects these IoT devices, where various features can be created for interactive visual design with little or without any programming effort. We also measure the time complexity for data delivery among the input and the output IoT devices. Our study indicates that the time delays are less than 0.07 s on the average even if the IoTtalk server is located in a cloud.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crawford C (2003) The art of interactive design. William Pollock, San Francisco
Kolko J (2011) Thoughts on interaction design. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco
Saffer D (2010) Designing for interaction. Berkeley, California
Mendelowitz E, Seeley D, Glicksman D (2016) Whorl: an immersive dive into a world of flowers, color, and play. In: ACM CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp 3871–3874
Xiao X, Puentes P, Ackermann E, Ishii H (2016) Andantino: teaching children piano with projected animated characters. In: ACM Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Interaction Design and Children, pp 37–45
AllSeen Alliance (2016) https://allseenalliance.org/. Accessed 13 July 2017
oneM2M (2016) Standards for M2M and the Internet of Things. http://www.onem2m.org/. Accessed 13 July 2017
OpenMTC (2016) The open machine type communications platform. http://www.open-mtc.org/. Accessed 13 July 2017
Lin YB, Lin YW, Chih CY, Li TY, Tai CC, Wang YC, Lin FJ, Kuo HC, Huang CC, Hsu SC (2015) Easy connect: a management system for IoT devices and its applications for interactive design and art. IEEE Internet Things J 2(6):551–561
Lin YB, Lin YW, Huang CM, Chih CY, Lin P (2017) IoTtalk: a management platform for reconfigurable sensor devices. IEEE Internet Things J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2017.2682100
Lin YW, Lin YB, Hsiao CY, Wang YY (2017) IoTtalk-RC: sensors as universal remote control for aftermarket home appliances. IEEE Internet Things J 4(4):1104–1112
Lin YW, Lin YB, Yang MT, Lin JH (2017) ArduTalk: an arduino network application development platform based on IoTtalk. IEEE Syst J 99:1–9
Intel (2016) Intel RealSense SDK Developer Reference. https://software.intel.com/intel-realsense-sdk/. Accessed 13 July 2017
Huang SC (2009) MSOrgm (motivational sensitive organism). Leonardo 42(4):374–375
Open CV Open Source Computer Vision (2017) http://opencv.org. Accessed 13 July 2017
Processing (2016) https://processing.org. Accessed 13 July 2017
Intel (2016) Intel RealSense Example Code, https://software.intel.com/sites/default/files/managed/d1/2d/Tutorial_VisualStudioProjectSolution.zip. Accessed 13 July 2017
Acer (2017) Acer aBeing One, http://home.cloud.acer.com/abeing-one/. Accessed 13 July 2017
Acknowledgements
The first version of Dandelion1 is implemented by Qing Liu. This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology under Grant 106-2221-E-009 -006 and Grant 106-2221- E-009 -049 -MY2, in part by the Ministry of Education through the SPROUT Project-Center for Open Intelligent Connectivity, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan, in part by Academia Sinica under Grant AS-105-TP-A07, and in part by the Ministry of Economic Affairs under Grant 106-EC-17-A-24-0619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsiao, CY., Huang, CC., Lin, YB. et al. Flower Sermon: An Interactive Visual Design Using IoTtalk. Mobile Netw Appl 24, 724–735 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1086-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1086-z