Abstract
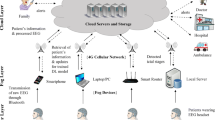
We propose a cognitive Internet of Things (IoT)–cloud-based smart healthcare framework, which communicates with smart devices, sensors, and other stakeholders in the healthcare environment; makes an intelligent decision based on a patient’s state; and provides timely, low-cost, and accessible healthcare services. As a case study, an EEG seizure detection method using deep learning is also proposed to access the feasibility of the cognitive IoT–cloud smart healthcare framework. In the proposed method, we use smart EEG sensors (apart from general healthcare smart sensors) to record and transmit EEG signals from epileptic patients. Thereafter, the cognitive framework makes a real-time decision on future activities and whether to send the data to the deep learning module. The proposed system uses the patient’s movements, gestures, and facial expressions to determine the patient’s state. Signal processing and seizure detection take place in the cloud, while signals are classified as seizure or non-seizure with a probability score. The results are transmitted to medical practitioners or other stakeholders who can monitor the patients and, in critical cases, make the appropriate decisions to help the patient. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves an accuracy and sensitivity of 99.2 and 93.5%, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin Y, Zeng Y, Chen X, Fan Y (2016) The internet of things in healthcare: an overview. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 1:3–13
Chen M, Zhang Y, Qiu M, Guizani N, Hao Y (2018) SPHA: smart personal health advisor based on deep analytics. IEEE Communications 56(3):164–169
Hu, L et al (2016) Internet of Things Cloud: Architecture and Implementation. IEEE Commun Mag 54(12-Supp):32–39
Chen, M et al (2018) Edge-CoCaCo: Toward Joint Optimization of Computation, Caching, and Communication on Edge Cloud. IEEE Wireless Commun 25(3):21–27
Muhammad G, Rahman SKMM, Alelaiwi A, Alamri A (2017) Smart health solution integrating IoT and cloud: a case study of voice pathology monitoring. IEEE Commun Mag 55(1):69–73
Chen M, Herrera F, Hwang K (2018) Cognitive computing: architecture, technologies and intelligent applications. IEEE Access 6:19774–19783
Hossain, MS (2016) Patient State Recognition System for Healthcare Using Speech and Facial Expressions. J Medical Systems 40(12):272:1–272:8
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2016) Audio-visual emotion recognition using multi-directional regression and Ridgelet transform. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces 10(4):325–333
Hossain MS et al (2015) Audio–visual emotion-aware cloud gaming framework. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 25(12):2105–2118
Zanella A (2014) Internet of things for smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J 1(1):22–32
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2016) Cloud-assisted industrial internet of things (IIoT)-enabled framework for health monitoring. Comput Netw 101:192–202
Chen M, Li W, Hao Y, Qian Y, Humar I (2018) Edge cognitive computing based smart healthcare system. Futur Gener Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.03.054
World Health Organization (2017) Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs999/en/
Litt B, Echauz J (2002) Prediction of epileptic seizures. Lancet Neurol 1:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(02)00003-0
Chen M, Yang J, Hao Y, Mao S, Hwang K (2017) A 5G cognitive system for healthcare. Big Data Cogn Comput 1(1):2
Qian Y, Chen M et al (2018) Secure enforcement in cognitive internet of vehicles. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 5(2):1242–1250
Hossain MS, Muhammad G, Al-Qurishi M (2018) Verifying the images authenticity in cognitive internet of things (CIoT)-oriented cyber physical system. MONET 23(2):239–250
Zhang M et al (2012) Cognitive internet of things: concepts and application example. Int J Comput Sci Issues 9(3):151–158
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2017) Emotion-aware connected healthcare big data towards 5G. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 5(4):2399-2406 (2018)
Hossain MS, Muhammad G, Alamri A (2017) Smart healthcare monitoring: a voice pathology detection paradigm for smart cities. Multimedia Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-017-0561-x
Samani H, Zhu R (2016) Robotic automated external defibrillator ambulance for emergency medical service in smart cities. IEEE Access 4:268–283
Muhammad G, Alsulaiman M, Amin SU, Ghoneim A, Alhamid MF (2017) A facial-expression monitoring system for improved healthcare in smart cities. IEEE Access 5(1):10871–10881
Chen M, Song J, Lai C, Hu B (2016) Smart clothing: connecting human with clouds and big data for sustainable health monitoring. Mob Netw Appl 21(5):825–845
Vlacheas P et al (2013) Enabling smart cities through a cognitive management framework for the internet of things. IEEE Commun Mag 51(6):102–111
Piniewski B et al (2010) Empowering healthcare patients with smart technology. Computer 43(7):27–34
Ghoneim A, Muhammad G, Amin SU, Gupta B (2018) Medical image forgery detection for smart healthcare. IEEE Commun Mag 56(4):33–37
Muhammad G (2015) Automatic speech recognition using interlaced derivative pattern for cloud based healthcare system. Cluster Computing (Springer) 18(2):795–802
Hills M (2014). Seizure detection using FFT, Temporal and Spectral Correlation Coefficients, Eigenvalues and Random Forest. Technical Report. Github
Park Y, Luo L, Parhi KK, Netoff T (2011) Seizure prediction with spectral power of EEG using cost-sensitive support vector machines. Epilepsia 52:1761–1770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03138.x
Parvez MZ, Paul M (2015) Epileptic seizure detection by exploiting temporal correlation of electroencephalogram signals. IET Signal Processing 9(6):467–475. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2013.0288
Thodoroff P, Pineau J, Lim A (2016). Learning robust features using deep learning for automatic seizure detection, Proceedings of the 1st Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference. PMLR 56:178–190
Panayiotopoulos, CP (2010) A Clinical Guide To Epileptic Syndromes And Their Treatment. Springer-Verlag, London, pp 654
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Pereira F, Burges CJC, Bottou L, Weinberger KQ (ed) Advances in neural information processing systems 25, pages 1097–1105. Curran Associates, Inc.. URL http://papers.nips.cc/paper/ 4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf
Pramod S, Page A, Mohsenin T, Oates T (2014) Detecting epileptic seizures from EEG data using neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv 1412:6502
Turner JT, Page A, Mohsenin T, Oates T (2014) Deep belief networks used on high resolution multichannel electroencephalography data for seizure detection. In 2014 AAAI Spring Symposium Series
Li D, Wang G, Song T, Jin Q (2016) Improving convolutional neural network using accelerated proximal gradient method for an epilepsy diagnosis. In Control (CONTROL), 2016 UKACC 11th International Conference on. IEEE, 1–6
Shoeb A (2009) Application of Machine Learning to Epileptic Seizure Onset Detection and Treatment. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Canolty RT, Edwards E, Dalal SS, Soltani M, Nagarajan SS, Kirsch HE, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Knight RT (2006) High gamma power is phase-locked to theta oscillations in human neocortex. Science 313:1626–1628
Schirrmeister RT, Springenberg JT, Fiederer LDJ, Glasstetter M, Eggensperger K, Tangermann M, Hutter F, Burgard W, Ball T (2017) Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum Brain Mapp 38:5391–5420. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23730
Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H (2007) Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 19:153
Wilson S, Scheuer M, Emerson R, Gabor A (2004) Seizure detection: evaluation of the Reveal algorithm. Clin Neurophysiol 10:2280–2291
Fergus P, Hussain A, Hignett D, Al-Jumeily D, Abdel-Aziz K, Hamdan H (2016) A machine learning system for automated whole-brain seizure detection. Applied Computing and Informatics 12(1):70–89, ISSN 2210-8327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aci.2015.01.001
Supartak A, Li L, Guo Y (2014) Feature extraction with stacked autoencoders for epileptic seizure detection, 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, pp. 4184–4187. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2014.6944546
Xun G, Jia X, Zhang A (2015) Context-learning based electroencephalogram analysis for epileptic seizure detection, 2015 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Washington, DC, 2015, pp. 325–330. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2015.7359702
Chen D, Wan S, Xiang J, Bao FS (2017) A high-performance seizure detection algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and EEG. PLoS One 12(3):e0173138. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173138
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia through the Research Group Project No: RG-1436-016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhussein, M., Muhammad, G., Hossain, M.S. et al. Cognitive IoT-Cloud Integration for Smart Healthcare: Case Study for Epileptic Seizure Detection and Monitoring. Mobile Netw Appl 23, 1624–1635 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1113-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1113-0