Abstract
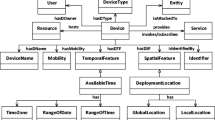
With the rapid development of new internet technologies, i.e. Internet of Things (IoT), the amount of IoT services has grown dramatically. To make people easier and faster to utilize the service resources, it becomes more and more important to gather the services on the IoT. Most of the current methods can only create automatic or semi-automatic service composition schemes, and lack support and consideration of real-time data and instant situation information, so they cannot achieve dynamic adaptive aggregation of services. In this paper, we focus on both the functional and non-functional constrains, and propose an IoT service aggregation method based on dynamic planning oriented QoE constraint. Firstly, the knowledge model of relationship among service category concepts are constructed. Secondly, the aggregation problem of service categories is mapped to a dynamic programming problem based on the relationship between service composition, and a new semantic similarity computing method is used as the main basis for service selection by using the ontology of IoT service category. Finally, for the selection of specific service resources, a trend-aware service selection algorithm for the QoE multi-constrained measurement is proposed. Experimental results show that the proposed method has better performance in terms of recall and precision.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 April 2019
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01250-6
References
Chavesdiguez D, Pelliterorivero A, Garcacoego D, et al. (2015) Providing IoT services in smart cities through dynamic augmented reality markers[J]. Sensors 15(7):16083–16104
Chen HM, Cui L, Xie KB (2013) A comparative study on architectures and implementation methodologies of internet of things. Chin J Comput 36(1):168–188
Qiao XQ, Sun YL, Zhang Y (2013) System for providing services of event-driven service-oriented internet of things and working method thereof CN 103458033 A
Bohn H, Bobek A, Golatowski F (2006) SIRENA - Service Infrastructure for Real-time Embedded Networked Devices: A service oriented framework for different domains[C]. In: International Conference on mobile communications and learning technologies, conference on networking, conference on systems. IEEE Computer Society, pp 43–43
Ostermaier B, RöMer K, Mattern F, et al. (2010) A real-time search engine for the Web of Things[C]. Internet of Things (IOT) IEEE 2010:1–8
Romer K, Ostermaier B, Mattern F, et al. (2010) Real-time search for real-world entities: a survey[J]. Proc IEEE 98(11):1887–1902
Mayer S, Guinard D (2011) An extensible discovery service for smart things[J]. Int Workshop Web Things Ser Wot, 1–6
Li LY, Liu N, Li GY (2016) A dynamic service composition method based on QoS in the semantic internet of things. Appl Res Comput 33(3):802–805
Zhang T, Zhang X, Liu ZD (2013) A service portfolio approach driven by the internet of things needs. Appl Res Comput 30(6):1756–1759
Zhou M, Yan MA (2013) QoS-aware computational method for IoT composite service[J]. J China Univ Posts Telecommun 20 :35–39
Li CL, Liao D, Xiong L, Huang YJ (2015) A service selection algorithm based on QoE quantization evaluation. Acta Electronica Sinica 43(11):2145–2150
Jia B, Liu S, Yang Y (2014) Fractal cross-layer service with integration and interaction in internet of things. Int J Distrib Sensor Netw 2014(1):1–11
Li CM, Gong XB (2016) Study on the optimal service radius of rain water pump station based on dynamic programming. J Shenzhen Univ Sci Eng 33(4):388–393
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 41761086, 61461037, 61761035 and 61661041, the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China under Grant No.2016YFB0502102, the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China under Grant 2017JQ09, and the “Grassland Elite” Project of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region under Grant CYYC5016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, B., Hao, L., Zhang, C. et al. An IoT Service Aggregation Method Based on Dynamic Planning for QoE Restraints. Mobile Netw Appl 24, 25–33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1135-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-018-1135-7