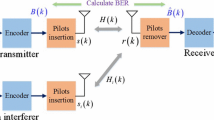
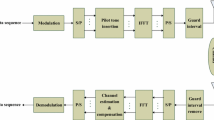
Abstract
How to estimate channel parameters more effectively, intelligently and accurately is the key problem to realize the requirements of intelligent and adaptive short-wave communication system. Based on the detailed analysis of chirp signal and fractional Fourier transform, an intelligent channel parameter estimation system is constructed. By building and training the regression model of multilayer fully connected neural network, the estimation error of Doppler shift is reduced. The simulation results show that the hierarchical channel estimation algorithm improves the precision of channel parameter estimation and the anti-noise performance of the system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergadà P, Deumal M, Vilella C, Regué J, Altadill D, Marsal S (2009) Remote sensing and Skywave digital communication from Antarctica[J]. Sensors 9(12):10136–10157
Huang H, Yang J, Huang H, Song Y, Gui G (2018) Deep learning for super-resolution channel estimation and DOA estimation based massive MIMO system[J]. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(9):8549–8560
Wang T, Zheng Z, Rehmani MH et al (2018) Privacy preservation in big data from the communication perspective—a survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 21(1):753–778
Alsina-Pagès R, Hervás M, Orga F, Pijoan J, Badia D, Altadill D (2016) Physical layer definition for a long-haul HF Antarctica to Spain radio link[J]. Remote Sens 8(5):380
Alsina-Pagès RM, Salvador M, Hervás M et al (2015) Spread spectrum high performance techniques for a long haul high frequency link[J]. IET Commun 9(8):1048–1053
Pijoan JL, Altadill D, Torta JM et al (2014) Remote geophysical observatory in Antarctica with HF data transmission: a review[J]. Remote Sens 6(8):7233–7259
Lin Y, Wang M, Zhou X, et al. (2020) Dynamic Spectrum interaction of UAV flight formation communication with priority: a deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking
Liu M, Song T, Hu J et al (2018) Deep learning-inspired message passing algorithm for efficient resource allocation in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(1):641–653
Yihan X, Cheng X, Taining Z et al (2019) An intrusion detection model based on feature reduction and convolutional neural networks [J]. IEEE Access 7:42210–42219
Wang H, Guo L, Dou Z, Lin Y (2018) A new method of cognitive signal recognition based on hybrid information entropy and DS evidence theory[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications 23(4):677–685
Zheng S, Qi P, Chen S, Yang X (2019) Fusion methods for CNN-based automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Access 7:66496–66504
Wang M, Li Z, Huang D, Guo X (2018) Performance analysis of information fusion method based on bell function[J]. International Journal of Performability Engineering 14(4):729–740
Lin Y, Wang C, Wang J, Dou Z (2016) A novel dynamic spectrum access framework based on reinforcement learning for cognitive radio sensor networks[J]. Sensors 16(10):1675
Xue Z, Wang J, Ding G, Wu Q, Lin Y, Tsiftsis TA (2018) Device-to-device communications underlying UAV-supported social networking[J]. IEEE Access 6:34488–34502
Bland EC, McDonald AJ, de Larquier S et al (2014) Determination of ionospheric parameters in real time using SuperDARN HF radars[J]. J Geophys Res Space Physics 119(7):5830–5846
Thomas EG, Shepherd SG (2018) Statistical patterns of Ionospheric convection derived from mid-latitude, high-latitude, and polar SuperDARN HF radar observations[J]. J Geophys Res Space Physics 123(4):3196–3216
De Larquier S (2013) The mid-latitude ionosphere under quiet geomagnetic conditions: propagation analysis of SuperDARN radar observations from large ionospheric perturbations[D]. Virginia Tech
Wagner LS, Goldstein JA, Rupar MA, Kennedy EJ (1995) Delay, Doppler, and amplitude characteristics of HF signals received over a 1300-km transauroral sky wave channel[J]. Radio Sci 30(3):659–676
Warrington EM, Stocker AJ (2003) Measurements of the Doppler and multipath spread of HF signals received over a path oriented along the mid-latitude trough[J]. Radio Sci 38(5):1080–1091
Warrington EM, Stocker AJ, Siddle DR (2006) Measurement and modeling of HF channel directional spread characteristics for northerly paths[J]. Radio Sci 41(02):1–13
Stocker AJ, Warrington EM (2011) The effect of solar activity on the Doppler and multipath spread of HF signals received over paths oriented along the midlatitude trough[J]. Radio Sci 46(01):1–11
Vilella C, Bergadà P, Deumal M, et al. (2006) Transceiver architecture and digital down converter design for a long distance, low power HF ionospheric link[C]. 10th IET International Conference on Ionospheric Radio Systems and Techniques (IRST 2006), 95–99
Vilella C, Miralles D, Pijoan JL (2008) An Antarctica-to-Spain HF ionospheric radio link: sounding results[J]. Radio Sci 43(04):1–17
Ads AG, Bergadà P, Vilella C et al (2013) A comprehensive sounding of the ionospheric HF radio link from Antarctica to Spain[J]. Radio Sci 48(1):1–12
Shi C, Dou Z, Lin Y, Li W (2018) Dynamic threshold-setting for RF-powered cognitive radio networks in non-Gaussian noise[J]. Physical Communication 27:99–105
Hervás M, Alsina-Pagès R, Orga F, Altadill D, Pijoan J, Badia D (2015) Narrowband and wideband channel sounding of an Antarctica to Spain ionospheric radio link[J]. Remote Sens 7(9):11712–11730
Xianglin W, Yu B, Xie H, Song Z (2006) Pulse cumulating method for multi-targets’ joint azimuth-elevation frequency-delay estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics (China) 23(3):370–373
Li A, Wu Z, Lu H, Chen D, Sun G (2018) Collaborative self-regression method with nonlinear feature based on multi-task learning for image classification[J]. IEEE Access 6:43513–43525
Kirsanov EA (2008) An estimation of temporal parameters of signals sequence with pseudo-random frequency tuning at the output of digital panoramic radio receiving device[J]. Radioelectron Commun Syst 51(9):502–509
Sharma KK, Joshi SD (2007) Time delay estimation using fractional Fourier transform[J]. Signal Process 87(5):853–865
Yu J, Zhang L, Liu K, Liu D (2015) Separation and localization of multiple distributed wideband chirps using the fractional Fourier transform[J]. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2015(1):266
Staelin DH (1969) Fast folding algorithm for detection of periodic pulse trains[J]. Proc IEEE 57(4):724–725
Assous S, Hopper C, Lovell M, Gunn D, Jackson P, Rees J (2010) Short pulse multi-frequency phase-based time delay estimation[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 127(1):309–315
Lin Y, Zhu X, Zheng Z, Dou Z, Zhou R (2019) The individual identification method of wireless device based on dimensionality reduction and machine learning[J]. J Supercomput 75(6):3010–3027
Zhou JT, Du J, Zhu H et al (2019) Anomalynet: an anomaly detection network for video surveillance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 14(10):2537–2550
Riedinger R, Hong S, Norte RA, Slater JA, Shang J, Krause AG, Anant V, Aspelmeyer M, Gröblacher S (2016) Non-classical correlations between single photons and phonons from a mechanical oscillator[J]. Nature 530(7590):313–316
Zhang Z (2018) Optimization performance analysis of 1090ES ADS-B signal separation algorithm based on PCA and ICA[J]. International Journal of Performability Engineering 14(4):741–750
Adams DM (2013) Real-time auto tuning of a closed-loop second-order system with internal time-delay using pseudo-random binary sequences[J]. Dissertations & Theses - Gradworks 10:1552240
Liu S, Bai W, Liu G et al (2018) Parallel fractal compression method for big video data[J]. Complexity 2018:2016976
Liu S, Pan Z, Cheng X (2017) A novel fast fractal image compression method based on distance clustering in high dimensional sphere surface[J]. Fractals 25(04):1740004
Tai N, Pan YJ, Yuan NC (2015) Quasi-coherent noise jamming to LFM radar based on Pseudo-random sequence phase-modulation[J]. Radioengineering 24(4):1013–1024
Liu S, Liu G, Zhou H (2019) A robust parallel object tracking method for illumination variations[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications 24(1):5–17
Zhou T, Li H, Zhu J, Xu C (2014) Subsample time delay estimation of chirp signals using FrFT[J]. Signal Process 96:110–117
Khan NA, Taj IA, Jaffri MN (2010) Instantaneous frequency estimation using fractional Fourier transform and Wigner distribution[C]. 2010 International Conference on Signal Acquisition and Processing. IEEE, 319–321
Wang ZW, Wang XL, Xiang M, Liu JH, Zhang XA, Yang C (2012) Reservoir information extraction using a fractional fourier transform and a smooth pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution[J]. Appl Geophys 9(4):391–400
Tseng FM, Yu HC, Tzeng GH (2002) Combining neural network model with seasonal time series ARIMA model[J]. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 69(1):71–87
Xiao Z, Ye SJ, Zhong B, Sun CX (2009) BP neural network with rough set for short term load forecasting[J]. Expert Syst Appl 36(1):273–279
Gui G, Huang H, Song Y, Sari H (2018) Deep learning for an effective nonorthogonal multiple access scheme[J]. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 67(9):8440–8450
Jin W, Li Z J, Wei L S, et al. (2000) The improvements of BP neural network learning algorithm[C]. WCC 2000-ICSP 2000. 2000 5th international conference on signal processing proceedings. 16th world computer congress 2000. IEEE, 3: 1647–1649
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Liu, Y. & Li, W. Intelligent Channel Parameter Estimation System Based on Neural Network Regression Model. Mobile Netw Appl 25, 2291–2301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01612-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-020-01612-5