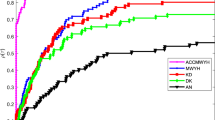
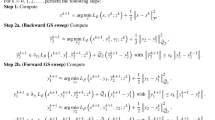Abstract
Deinterlacing, defined as the process of converting a stream of interlaced frames into a sequence of progressive frames, represents a key feature in video processing. The interlaced video format, introduced by the old analog television transmission systems as a trade-off between framerate and bandwidth capacity, has become obsolete nowadays, when all transmissions are digital. Moreover, almost all recent displays—whether LCD or plasma—require progressive video input, whereas much of the available video content is in interlaced format. In this paper an adaptive, edge-preserving motion-compensated approach for video deinterlacing is proposed. The algorithm preserves strong edges and interpolates the missing pixels along the contours depending on the motion-degree of the region to which they belong. Our proposal is optimized to lower heavy computation, which is the main drawback of motion-compensated deinterlacing algorithms. Therefore it provides complexity scalability as a trade-off tool between performance and computation time. Experiments demonstrate a significant gain in reconstruction quality as compared to other deinterlacing implementations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellers EB, Shuttent RJ, Kruetzmann M, Van der Heijden H, He H (2006) Directional and motion-compensated de-interlacing. In: Proceedings of the international conference on consumer electronics, pp 181–182
Biswas M, Kumar S, Nguyen TQ (2006) Performance analysis of motion-compensated de-interlacing systems. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(9):2596–2609
Brox P, Baturone I, Sanchez-Solano S (2009) Fuzzy motion-adaptive interpolation with picture repetition detection for deinterlacing. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 58(9):2952–2958
Canny J (1986) A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell PAMI-8(6):679–698
Chang J, Kim YD, Shin GS, Kang MG (2009) Adaptive arbitration of intra-field and motion compensation methods for de-interlacing. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(8):1214–1220
Chen YR, Tai SC (2009) True motion-compensated de-interlacing algorithm. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(10):1489–1498
Chen T, Wu H, Yu ZH (2000) Efficient de-interlacing algorithm using edge-based line average interpolation. Opt Eng 39(8):2101–2105
Chen M-J, Huang C-H, Hsu C-T (2004) Efficient de-interlacing technique by inter-field information. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 50(4):1202–1207
Choi Y-J, Lim KW, Ra JB (2009) Improvement on optical flow based video deinterlacing by adopting flow vector and intensity reliabilities. In: 2009 16th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 393–396
Dai S, Baker S, Kang SB (2009) An mrf-based deinterlacing algorithm with exemplar-based refinement. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(5):956–968
De Haan G, Bellers EB (1997) De-interlacing of video data. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 43:819–825
Doyle T, Looymans M (1989) Progressive scan conversion using edge information. In: Proc. of the 3rd international workshop on HDTV, pp 711–721
Dubois E, de Haan G, Kurita T (1994) Motion estimation and compensation technologies for standards conversion. Signal Process Image Commun 6(3):189–190
El-Qawasmeh E (2003) Scene change detection schemes for video indexing in uncompressed domain. Informatica 14:19–36
Engstorm EW (1935) A study of television image characteristics. Part II: Determination of frame frequency for television in terms of flicker characteristics. Proc IRE 23(4):295–310
Fan Y-C, Chung C-H (2009) De-interlacing algorithm using spatial-temporal correlation-assisted motion estimation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(7):932 –944
Fan YC, Lin HS, Chiang A, Tsao HW, Kuo CC (2008) Motion compensated deinterlacing with efficient artifact detection for digital television displays. J. Display Technol 4(2):218–228
Ghodstinat M, Bruhn A, Weickert J (2009) Deinterlacing with motion-compensated anisotropic diffusion. In: Cremers D, Rosenhahn B, Yuille A, Schmidt F (eds) Statistical and geometrical approaches to visual motion analysis, Lecture notes in computer science, vol 5064. Springer, Berlin, pp 91–106
Haan GD, Bellers EB (1998) Deinterlacing - An overview. In:Proceedings of the IEEE 86(9):1839–1857
Hong S-H, Park R-H, Yang S, Kim J-Y (2006) Edge-preserving spatial deinterlacing for still images using block-based region classification. Dept. of Electr. Eng., Sogang Univ., Seoul, South Korea
Huang Q, Gao W, Zhao D, Sun H (2006) An efficient and robust adaptive deinterlacing technique. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 52(3):888–895
Huang Q, Zhao D, Ma S, Gao W, Sun H (2010) Deinterlacing using hierarchical motion analysis. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 20(5):673–686
Jeon G, Anisetti M, Kim D, Bellandi V, Damiani E, Jeong J (2009) Fuzzy rough sets hybrid scheme for motion and scene complexity adaptive deinterlacing. Image Vis Comput 27(4):425–436
Jeon G, You J, Jeong J (2009) Weighted fuzzy reasoning scheme for interlaced to progressive conversion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(6):842 –855
Ji G, Zhong Q (2010) A fast motion compensated deinterlacing method with true sub-pixel accurate motion vectors. In: 2010 IEEE 10th international conference on signal processing (ICSP), pp 771–774
Kim W, Jin S, Jeong J (2007) Novel intra deinterlacing algorithm using content adaptive interpolation. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 53(3):1036–1043
Kwon O, Sohn K, Lee C (2003) Deinterlacing using directional interpolation and motion compensation. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 49(1):198–203
Lee K, Lee C (2010) High quality deinterlacing using content adaptive vertical temporal filtering. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 56(4):2469 –2474
Lee GG, Wang M-J, Li H-T, Lin H-Y (2008) A motion-adaptive deinterlacer via hybrid motion detection and edge-pattern recognition. EURASIP J Image Video Process 2008:10
Lee K, Lee J, Lee C (2009) Deinterlacing with motion adaptive vertical temporal filtering. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 55(2):636 –643
Li M, Nguyen T (2007) A de-interlacing algorithm using markov random field model. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(11):2633–2648
Lin S-F, Chang Y-L, Chen L-G (2003) Motion adaptive interpolation with horizontal motion detection for deinterlacing. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 49(4):1256–1265
Lin C-C, Sheu M-H, Chiang H-K, Wei C-J, Liaw C (2007) A high-performance architecture of motion adaptive de-interlacing with reliable interfield information. IEICE Trans Fundam Electron Commun Comput Sci 90(11):2575–2583
Mohammadi HM, Langlois P, Savaria Y (2007) A five-field motion compensated deinterlacing method based on vertical motion. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 53(3):1117–1124
Park MK, Kang MG, Nam K, Oh SG (2003) New edge dependent deinterlacing algorithm based on horizontal edge pattern. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 49(4):1508–1512
Pigeon S, Vandendorpe L, Cuvelier L, Maison B (1995) Specification of a generic format converter. CEC RACE/HAMLET deliverable no R2110/WP2/DS/S/006/b1
Spen Y, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Li J (2006) Motion adaptive deinterlacing of video data with texture detection. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 52(4):1403–1408
Sze K-W, Lam K-M, Qiu G (2003) Scene cut detection using the colored pattern appearance model. Model, ICIP 2:1017–1020
Tu S-F, Au OC, Wu Y, Luo E, Yeung C-H (2009) A robust spatial-temporal line-warping based deinterlacing method. In:Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME’09), pp 77–80
Usama S, Montaser M, Ahmed O (2005) A complexity and quality evaluation of block based motion estimation algorithms. Czech J Adv Eng Acta Polytech 45(1):29–41
Wang D, Vincent A, Blanchfield P (2005) Hybrid de-interlacing algorithm based on motion vector reliability. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 15(8):1019–1025
Yang S, Kim D, Jeong J (2009) Fine edge-preserving deinterlacing algorithm for progressive displays. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 55(3):1654–1662
Yu L, Li J, Zhang Y, Shen Y (2006) Motion adaptive deinterlacing with accurate motion detection and anti-aliasing interpolation filter. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 52(2):712–717
Zhanguzin D, Trocan M, Mikovicova B (2010) An edge-preserving motion-compensated approach for video deinterlacing. In: IEEE/IET/BCS 3rd international workshop on future multimedia networking
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trocan, M., Mikovicova, B. & Zhanguzin, D. An adaptive motion-compensated approach for video deinterlacing. Multimed Tools Appl 61, 819–837 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0845-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0845-7