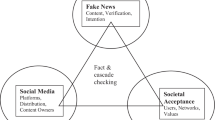
Abstract
Nowadays, it becomes increasingly difficult to find reliable multimedia content in the Web 2.0. Open decentralized networks (on the Web) are populated with lots of unauthenticated agents providing fake multimedia. Conventional automatic detection and authentication approaches lack scalability and the ability to capture media semantics by means of forgery. Using them in online scenarios is computationally expensive. Thus, our aim was to develop a trust-aware community approach to facilitate fake media detection. In this paper, we present our approach and highlight four important outcomes. First, a Media Quality Profile (MQP) is proposed for multimedia evaluation and semantic classification with one substantial part on estimating media authenticity based on trust-aware community ratings. Second, we employ the concept of serious gaming in our collaborative fake media detection approach overcoming the cold-start problem and providing sufficient data powering our Media Quality Profile. Third, we identify the notion of confidence, trust, distrust and their dynamics as necessary refinements of existing trust models. Finally, we improve the precision of trust-aware aggregated media authenticity ratings by introducing a trust inference algorithm for yet unknown sources uploading and rating media.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Rahman A, Hailes S (2000) Supporting trust in virtual communities. In: Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences, vol 6. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, pp 1–7. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=820262.820322
Ahn LV (2006) Games with a purpose. IEEE Comput Mag 39:92–94
Ahn LV, Dabbish L (2008) Designing games with a purpose. Commun ACM 51(8):58–67
Albert R, Jeong H, Barabási AL (1999) Diameter of the World-Wide Web. Nature 401(9):130–131
Arrow KJ (1974) The limits of organization (Fels lectures on public policy analysis). W. W. Norton & Company
Bashan A, Parshani R, Havlin S (2011) Percolation in networks composed of connectivity and dependency links. Phys Rev E 83(5):1–8. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.83.051127
Bober M, Brasnett P (2009) MPEG-7 visual signature tools. In: ICME’09: proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo. IEEE Press, Piscataway, NJ, USA, pp 1540–1543. ISBN 978-1-4244-4290-4
Brugion DA (1999) Photo fakery: the history and techniques of photographic deception and manipulation. Brasssyes Publishers, Dulles verginia
Callaway DS, Newman MEJ, Strogatz SH, Watts DJ (2000) Network robustness and fragility: percolation on random graphs. Phys Rev Lett 85(25):5468–5471. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.5468
Cheng R, Vassileva J (2005) User motivation and persuasion strategy for peer-to-peer communities. In: Hawaii international conference on system sciences, vol 7, p 193a. doi:10.1109/HICSS.2005.653
Clary EG, Snyder M, Ridge RD, Copeland J, Stukas AA, Haugen J, Miene P (1998) Understanding and assessing the motivations of volunteers: a functional approach. JPSP 74:1516–1530
Cofta P (2006) Distrust. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on electronic commerce, ICEC ’06. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 250–258. doi:10.1145/1151454.1151498
Cohen R, Erez K, ben Avraham D, Havlin S (2001) Breakdown of the internet under intentional attack. Phys Rev Lett 86(16):3682–3685. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.3682
Deutsch M (1958) Trust and suspicion. JCR 2:265–279
Douceur JR (2002) The Sybil attack. In: Revised papers from the first international workshop on peer-to-peer systems, IPTPS ’01. Springer, London, UK, pp 251–260
Erickson T (2003) Designing visualizations of social activity: six claims. In: CHI ’03 extended abstracts on human factors in computing systems. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 846–847
Farid H (2009) A survey of image forgery detection. IEEE Sig Proc Mag 2(26):16–25. www.cs.dartmouth.edu/farid/publications/spm09.html
Finin T, Kagal L, Olmedilla D (eds) (2006) Proceedings of the WWW’06 workshop on models of trust for the Web (MTW’06), Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, 22 May 2006. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 190. CEUR-WS.org
Fox A (1974) Beyond contract: work, power and trust relations. Faber
Gambetta D (1988) Can we trust trust?, chap. Trust: making and breaking cooperative relations. Blackwell, pp 213–237
Gans G (2008) An agent-based modeling-and simulation-methodology for strategic inter-organizational networks. PhD thesis, RWTH Aachen University
Gans G, Jarke M, Kethers S, Lakemeyer G, Ellrich L, Funken C, Meister M (2001) Towards (Dis)Trust-based simulations of agent networks. In: Proceedings of the 4th workshop on deception, fraud, and trust in agent societies, Montreal, pp 49–60. http://www-i5.informatik.rwth-aachen.de/~gans/tropos/dokumente/Agent01.pdf
Golbeck J (2009) Computing with social trust (human-computer interaction series), 1st edn. Springer
Golbeck J, Parsia B, Hendler J (2003) Trust networks on the semantic web. In: Proceedings of seventh international workshop on cooperative intelligent agents (CIA-03), pp 238–249. http://www.mindswap.org/papers/Trust.pdf
Golbeck JA (2005) Computing and applying trust in web-based social networks. PhD thesis, University of Maryland, College Park
Golle P, Leyton-Brown K, Mironov I (2001) Incentives for sharing in peer-to-peer networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd ACM conference on electronic commerce, EC ’01. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 264–267
Grandison T, Sloman M (2000) A survey of trust in internet applications. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials 3(4):2–16. http://pubs.doc.ic.ac.uk/TrustSurvey/
Gretarsson B, O’Donovan J, Bostandjiev S, Hall C, Höllerer T (2010) SmallWorlds: visualizing social recommendations. Computer Graphics Forum 29(3):833–842
Herlocker JL, Konstan JA, Riedl J (2000) Explaining collaborative filtering recommendations. In: Proceedings of CSCW00: ACM conference on computer supported cooperative work, pp 241–250
Hinduja S, Patchin JW (2008) Cyberbullying: an exploratory analysis of factors related to offending and victimization. Deviant Behav 29(2):129–156
Iwata M, Hori T, Shiozaki A, Ogihara A (2010) Digital watermarking method for tamper detection and recovery of JPEG images. In: International symposium on information theory and its applications (ISITA), pp 309–314
ISO/IEC/15938-3/Amd.3 (2009) Image signature tools
Jøsang A, Ismail R, Boyd C (2007) A survey of trust and reputation systems for online service provision. Decis Support Syst 43:618–644. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2005.05.019
Kamvar SD, Schlosser MT, Garcia-Molina H (2003) The eigentrust algorithm for reputation management in P2P networks. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on world wide web, WWW ’03. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 640–651. doi:10.1145/775152.775242
Keith S, Martin ME (2005) Cyber-bullying: creating a culture of respect in a cyber world. RCY Journal 13(4):224–228
Kim AJ (2000) Community building on the web: secret strategies for successful online communities. Peachpit Press
Klamma R, Spaniol M, Renzel D (2007) Community-aware semantic multimedia tagging—from folksonomies to commsonomies. In: Tochtermann K, Maurer H, Kappe F, Scharl A (eds) Proceedings of I-Media ’07. International conference on new media technology and semantic systems, Graz, Austria, 5–7 Sept 2007. J.UCS (Journal of Universal Computer Science) Proceedings, pp 163–171
Kleinberg JM (1999) Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment. J ACM 46:604–632. doi:10.1145/324133.324140
Kuznetsov S (2006) Motivations of contributors to Wikipedia. ACM SIGCAS Comput Soc 36(2):1–7
Lee S, Shamma DA, Gooch B (2006) Detecting false captioning using common-sense reasoning. Digital Investigation 3(Supplement-1):65–70
Levien R (2003) Attack resistant trust metrics. PhD thesis, UC Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA
Levien R (2009) Attack-resistant trust metrics. In: Golbeck J (ed) Computing with social trust, human-computer interaction series. Springer, London Limited, pp 121–132
Lewis JD, Weigert AJ (1985) Trust as a social reality. Soci Force 63(4):967–985
Li XY, Gui XL (2009) A comprehensive and adaptive trust model for large-scale P2P networks. J Comput Sci Technol 24:868–882. doi:10.1007/s11390-009-9278-4
Lux M (2009) Caliph & Emir: MPEG-7 photo annotation and retrieval. In: ACM multimedia, pp 925–926
Lux M, Becker J, Krottmaier H (2003) Caliph & Emir: semantic annotation and retrieval in personal digital photo libraries. In: Proceedings of CAiSE ’03 forum at 15th conference on advanced information systems engineering, pp 85–89
Manjunath BS (2002) Introduction to MPEG-7, multimedia content description interface. Wiley
Manjunath BS, Ohm JR, Vasudevan VV, Yamada A (2001) Color and texture descriptors. IEEE Trans Circuits Systems Video Technol 11(6):703–715. doi:10.1109/76.927424
Manovich L (2001) The language of new media. The MIT Press
Marsh S, Briggs P (2009) Examining trust, forgiveness and regret as computational concepts. In: Golbeck J (ed) Computing with social trust, human-computer interaction series. Springer, London Limited, p 1
Massa P, Bhattacharjee B (2004) Using trust in recommender systems: an experimental analysis. In: Proceedings of iTrust2004 international conference, pp 221–235
Mcknight DH, Chervany NL (1996) The meanings of trust. Tech. rep., University of Minnesota, USA
Milgram S (1967) The small world problem. Psychol Today 1(1):61–67
Mishra AK (1996) Trust in organizations: frontiers of theory and research, chap. Organizational responses to crisis: the centrality of trust. Sage Publications, Inc, pp 261–287
Mui L (2002) Computational models of trust and reputation: agents, evolutionary games, and social networks. PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Mui L, Mojdeh Mohtashemi AH (2002) A computational model of trust and reputation. In: Proceedings of the 35th Hawaii international conference on system science (HICSS). IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, pp 2431–439. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=820745.821158
Nielsen J (2006) Participation inequality: encouraging more users to contribute. http://www.useit.com/alertbox/participation_inequality.html. Last access: June 2011
O’Donovan J, Smyth B, Gretarsson B, Bostandjiev S, Höllerer T (2008) PeerChooser: visual interactive recommendation. In: Proceedings of CHI08: twenty-sixth annual SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems. ACM, pp 1085–1088
Victor P, Cornelis C, Cock MD (2011) Trust networks for recommender systems. Atlantis Press
Rafelsberger W, Scharl A (2009) Games with a purpose for social networking platforms. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM conference on hypertext and hypermedia, HT ’09. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 193–198
Rashed KAN, Klamma R (2010) Towards detecting faked images. In: Carreras A, Delgado J, Maronas X, Rodriguez V (eds) Proceedings of the 11th international workshop on interoperable social multimedia applications (WISMA10), Barcelona, Spain, 19–20 May 2010. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 583
Renzel D, Klamma R, Spaniol M (2008) MobSOS–a testbed for mobile multimedia community services. In: Proceedings of the 2008 ninth international workshop on image analysis for multimedia interactive services. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, pp 139–142
Renzel D, Rashed KAN, Klamma R (2010) Collaborative fake media detection in a trust-aware real-time distribution network. In: Proceedings of the the 2nd workshop focusing on semantic multimedia database technologies SMDT2010, Saarbrucken, Germany. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 680
Resnick P, Kuwabara K, Zeckhauser R, Friedman E (2000) Reputation systems. Commun ACM 43:45–48
Rey C, Dugelay JL (2002) A survey of watermarking algorithms for image authentication. EURASIP J Appl Signal Process 2002(1):613–621
Richardson M, Agrawal R, Domingos P (2003) Trust management for the semantic web. In: Fensel D, Sycara K, Mylopoulos J (eds) The Semantic Web—ISWC 2003. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 2870. Springer Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 351–368
Saint-Andre P (2004) RFC 3920—Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP): core. Tech. rep., Jabber Software Foundation. http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3920.txt
Saint-Andre P (2004) RFC 3921 extensible messaging and presence protocol (XMPP): instant messaging and presence. Tech. rep., Jabber Software Foundation. http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3921.txt
Schein A, Popescul A, Ungar L, Pennock D (2002) Methods and metrics for cold-start recommendations. In: Proceedings of the 25th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval (SIGIR 2002), pp 253–260
Schlebusch P (2009) XMPP based monitoring and analysis of mobile communities. Master’s thesis, RWTH Aachen University
Shneiderman B (2004) Designing for fun: how can we design user interfaces to be more fun? Interactions 11(5):48–50. doi:10.1145/1015530.1015552
Shneiderman B, Plaisant C (2004) Designing the user interface: strategies for effective human-computer interaction, 4th edn. Bosten, Addison Wesley
Skopik F, Schall D, Dustdar S (2009) Start trusting strangers? Bootstrapping and prediction of trust. In: Proceedings of 10th international conference WISE, Poznan, Poland, 5–7 Oct 2009. Springer, pp 275–289
Spaniol M, Klamma R, Janßen H, Renzel D (2006) LAS: a lightweight application server for MPEG-7 services in community engines. In: Tochtermann K, Maurer H (eds) Proceedings of I-KNOW ’06, 6th international conference on knowledge management, Graz, Austria. J. UCS (Journal of Universal Computer Science) Proceedings. Springer, pp 592–599
Stølen K, Winsborough WH, Martinelli F, Massacci F (eds) (2006) Trust management. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference, iTrust 2006, Pisa, Italy, 16–19 May 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3986. Springer Berlin Heidelberg
Susi T, Johannesson M, Backlund P (2007) Serious games—an overview. Tech. rep., School of Humanities and Informatics University of Skvde, Sweden
Technical Standardization Committee on AV & IT Storage Systems and Equipmen (2002) Exchangeable image file format for digital still cameras: Exif Version 2.2. Tech. rep., Standard of Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association
Turner R (2007) Your online community beta program: Metcalfe’s law and the cold start. http://www.websocialarchitecture.com/community/2007/09/. Last access: June 2011
Wang RY, Reddy MP, Kon HB (1995) Toward quality data: an attribute-based approach. Decision Support Syst 13:349–372. http://web.mit.edu/tdqm/www/tdqmpub/Toward%20Quality%20Data.pdf
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 393(6684):440–442
Webster A, Vassileva J (2006) Visualizing personal relations in online communities. In: Lecture notes in computer science adaptive hypermedia and adaptive webbased systems, pp 223–233. doi:10.1007/11768012_24
Wu B, Davison BD (2005) Identifying link farm spam pages. In: Special interest tracks and posters of the 14th international conference on world wide web. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 820–829
Yang Y, Sun YL, Kay S, Yang Q (2009) Defending online reputation systems against collaborative unfair raters through signal modeling and trust. In: Proceedings of the 2009 ACM symposium on applied computing, SAC ’09. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 1308–1315
Yaniv I, Kleinberger E (2000) Advice taking in decision making: egocentric discounting and reputation formation. OBHDP Journal 83(2):260– 281
Zaihrayeu I, da Silva PP, McGuinness DL (2005) IWTrust: improving user trust in answers from the web. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on trust management (iTrust2005), pp 384–392
Zajonc RB (1965) Social facilitation. Science 149:269–274
Ziegler CN, Golbeck J (2007) Investigating interactions of trust and interest similarity. Deci Supp Syst 43:460–475. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2006.11.003
Ziegler CN, Lausen G (2005) Propagation models for trust and distrust in social networks. Inf Syst Front 7:337–358. doi:10.1007/s10796-005-4807-3
Zyda M (2005) From visual simulation to virtual reality to games. IEEE Comput Mag 38:25–32
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from B-IT Research School and the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no 231396 (ROLE project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashed, K.A.N., Renzel, D., Klamma, R. et al. Community and trust-aware fake media detection. Multimed Tools Appl 70, 1069–1098 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1103-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1103-3