Abstract
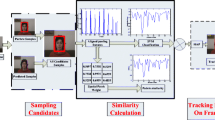
Smart transportation plays an important role in building smart cities. We can obtain mass data from multi-source and use it to manage transportation in an intelligent way. Images and videos can be easily obtained from various sensors in modern road system. They offer abundant information about the transportation. Therefore, visual analysis is a key point in smart transportation management. In this paper we propose a robust visual object tracking algorithm using adaptive local appearance model, which can be applied to transportation system. As the main challenge of tracking is to adapt to the target’s appearance change, we build the model with a local patch dictionary which is composed of a static part and an online updated part. The updating scheme is important to determine the quality of tracking results. We propose a coefficient quality based on sparse representation as the sign of updating and introduce incremental learning to compute the new information to update the dictionary. This strategy adapts the templates to appearance change and helps reduce the drifting problem. Experimental results on several challenging benchmark image sequences demonstrate the proposed tracking algorithm achieves favorable performance when the target undergoes large occlusion, illumination change and scale variation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam A, Rivlin E, Shimshoni I (2006) Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. In: 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 1. IEEE, pp 798–805
Avidan S (2007) Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(2):261–271
Babenko B, Yang MH, Belongie S (2009) Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE, pp 983– 990
Chen Z, Huang W, Lv Z (2015) Towards a face recognition method based on uncorrelated discriminant sparse preserving projection. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 1–15
Danelljan M, Khan FS, Felsberg M, van de Weijer J (2014) Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1090–1097
Erhan D, Szegedy C, Toshev A, Anguelov D (2014) Scalable object detection using deep neural networks. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2155–2162
Fu C, Zhang P, Jiang J et al (2015) A bayesian approach for sleep and wake classification based on dynamic time warping method. Multimedia Tools and Applications
Gu W, Lv Z, Hao M (2015) Change detection method for remote sensing images based on an improved markov random field. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 1–16
Hong S, Han B (2014) Visual tracking by sampling tree-structured graphical models. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2014. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–16
Jia X, Lu H, Yang MH (2012) Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1822– 1829
Jiang D, Xu Z, Li WEA (2015) An energy-ecient multicast algorithm with maximum network throughput in multi-hop wireless networks. Journal of communications and networks
Jiang D, Xu Z, Lv Z (2015) A multicast delivery approach with minimum energy consumption for wireless multi-hop networks. Telecommunication systems
Jiang D, Ying X, Han Y, Lv Z (2015) Collaborative multi-hop routing in cognitive wireless networks. Wireless personal communications, pp 1–23
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J (2012) Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(7):1409–1422
Kwon J, Lee KM (2010) Visual tracking decomposition. In: 2010 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1269–1276
Li X, Lv Z, Zheng Z et al (2015) Assessment of lively street network based on geographic information system and space syntax. Multimedia Tools and Applications
Lin Y, Yang J, Lv Z, Wei W, Song H (2015) A self-assessment stereo capture model applicable to the internet of things. Sensors 15(8):20,925–20,944
Liu B, Huang J, Yang L, Kulikowsk C (2011) Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and k-selection. In: 2011 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1313–1320
Lv Z, Halawani A, Fen S, Li H et al (2015) Touch-less interactive augmented reality game on vision based wearable device. arXiv:1504.06359
Lv Z, Halawani A, Feng S, Li H, Réhman SU (2014) Multimodal hand and foot gesture interaction for handheld devices. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl(TOMM) 11(1s):10
Lv Z, Tek A, Da Silva F, Empereur-Mot C, Chavent M, Baaden M (2013) Game on, science-how video game technology may help biologists tackle visualization challenges. PloS one 8(3):57, 990
Mei X, Ling H (2009) Robust visual tracking using ℓ1 minimization. In: 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision. IEEE, pp 1436–1443
Mei X, Ling H, Wu Y, Blasch E, Bai L (2011) Minimum error bounded efficient ℓ1 tracker with occlusion detection. In: 2011 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1257–1264
Prokaj J, Medioni G (2014) Persistent tracking for wide area aerial surveillance. In: 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1186–1193
Ross DA, Lim J, Lin RS, Yang MH (2008) Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 77(1–3):125–141
Su T, Wang W, Lv Z, Wu W, Li X (2016) Rapid delaunay triangulation for randomly distributed point cloud data using adaptive hilbert curve. Comput Graph 54:65–74
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31 (2):210–227
Wu Y, Ling H, Yu J, Li F, Mei X, Cheng E (2011) Blurred target tracking by blur-driven tracker. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 1100–1107
Yang J, Ding Z, Guo F, Wang H (2014) Multiview image rectification algorithm for parallel camera arrays. J Electron Imaging 23(3):033,001–033,001
Yang J, He S, Lin Y, Lv Z (2015) Multimedia cloud transmission and storage system based on internet of things. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pp 1–16
Yang J, Wright J, Huang TS, Ma Y (2010) Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(11):2861–2873
Yao R, Shi Q, Shen C, Zhang Y, van den Hengel A (2013) Part-based visual tracking with online latent structural learning. In: 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2363–2370
Zhang K, Zhang L, Yang MH (2012) Real-time compressive tracking. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2012. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 864–877
Zhang T, Ghanem B, Liu S, Ahuja N (2012) Robust visual tracking via multi-task sparse learning. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 2042– 2049
Zhong W, Lu H, Yang MH (2012) Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1838–1845
Acknowledgments
This research is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61471260 and No.61271324) and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Xu, R., Cui, J. et al. Robust visual tracking using adaptive local appearance model for smart transportation. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 17487–17500 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3285-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3285-6